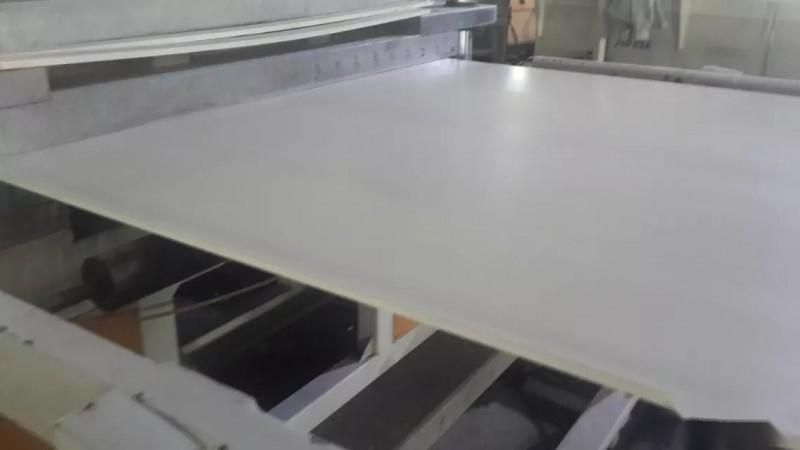
What is a plastic formwork?
Plastic formwork is an energy-saving and environmentally friendly product. It is a new type of replacement product following wood formwork, combined steel formwork, bamboo-wood laminated formwork, and full steellarge formwork. In fact, it is a new type of construction formwork designed to replace traditional wood formwork.
Plastic formwork and wood formwork: Similarities and Differences
The material of plastic formwork is PVC. The first point is that PVC is waterproof and flame-retardant, and it does not have the issue of deformation and decay that wood formwork experiences when exposed to water. The only difference in usage compared to wood formwork is that there is no need to apply a release agent. The surface of plastic formwork is smooth and clean, and the walls do not require secondary plastering, thus saving two processes compared to wood formwork. Nailing, sawing, planing, and drilling are the same as with wood formwork, and the specifications are also identical. Furthermore, plastic formwork can be custom-produced according to customer requirements, allowing for any cutting. An important point is that plastic formwork is fully recyclable, even the scraps can be reused.
Why is the usage rate of plastic formwork still low after several years of development?
First, the government has only recently begun to emphasize green building. The promotion of plastic formwork has been weak in terms of policy, and there has been no mandatory policy for the use of green building materials. However, at the two sessions in 2016, Premier Li Keqiang pointed out in the government report that the country is actively promoting new urbanization construction. Many regions are facing demolition and reconstruction, with a huge demand for building materials. Traditional building materials have significant issues such as high usage, high energy consumption, and serious pollution, which can no longer meet market needs. Therefore, it is necessary to actively promote green buildings and materials and vigorously develop energy-saving and environmentally friendly industries, which is a significant favorable policy for plastic formwork.
Second, the quality is uneven and many products are poorly made. Although national standards were issued in 2013, the technology is still far from mature. To produce high-quality plastic formwork, the cost remains high, and if the raw materials are compromised, it can lead to issues such as thermal expansion and contraction of the plastic formwork, making it brittle in winter and soft in summer, although the appearance may not show significant differences. There are many cheaply priced plastic formworks in the market, and some of these prices seem absurdly low, lower than our production costs. Don’t tell me they have better formulas that greatly reduce costs; currently, the formula for plastic formwork remains a difficult issue, with no more than 2% difference in cost among companies. If the price is too low, it only indicates one problem: cost-cutting, and quality issues will inevitably arise. Given current technology, low prices absolutely mean low quality—there are no other possibilities.
Third, the acceptance of carpenters and builders is low. Whenever a new product is introduced, there are always some who wait and see how others use it. The first to try is always a minority. If not, the builders who use it are still few. Moreover, carpenters earn their living based on work progress. They are used to using wood formwork, and suddenly switching to other products will make them uncomfortable. Initially, they will certainly resist, and we have experienced severe cases on construction sites where a team of workers went on strike against the use of plastic formwork. At that time, the project team was also quite strong and directly replaced the carpenters, which eventually resolved the issue.
Our product positioning: Only make standard multi-storey high-end buildings.
Usage situation of Zhengzhou Lanbowan construction site


Why do so many companies choose to use Linyi plastic formwork?
First, we have hundreds of domestic and foreign cooperative clients, exporting to multiple countries and regions.
Second, our production scale and supply capacity are three times that of our peers.
Third, we can deliver to the client's construction site in three days.
Fourth, we can customize production according to customer requirements.
Fifth, we save more than 10% in costs compared to our peers.
Linyi plastic formwork's quality advantages
1. We have been engaged in the plastic chemical industry for thirty years, holding multiple patents, and have developed the third generation of improved plastic formwork which has been on the market for two years.
2. Each batch of plastic formwork undergoes a series of tests, including elastic modulus, Vicat temperature, impact strength, and nail-holding power, before being shipped out of the factory.
3. Strength: We have independently developed a plastic formwork formula that maintains the product's strength and toughness, reducing the breakage rate during violent disassembly by workers. On average, our product can be used 3 to 5 more times than competing products.
4. Temperature resistance: Using high-temperature-resistant plastic additives for modification, our plastic formwork exceeds national temperature resistance standards by 10 degrees.
5. The extrusion temperature is high, resulting in a smoother surface and greater hardness of the plastic formwork.
How plastic formwork can save 50% in costs
A previous case was the Zhengzhou China State Construction Seventh Engineering Bureau Guanhua International project, where the initial contract budget was over 3 million, based on the budget for wood formwork. After the floor was topped, the actual expenditure was only over 1 million, resulting in a savings of more than 50%.
To save costs, the primary point is that the product must meet standards. If the product does not meet standards, as long as it does not exceed the budget, one can only hope for the best; otherwise, stick to using wood formwork.
Secondly, construction management is crucial. Since plastic formwork is a new product, some carpenters may not be familiar with it. Additionally, compared to wood formwork, plastic formwork may be slightly heavier, which can lead to resistance from workers. When workers are not keen to use it, they might express negative sentiments about the product. We have encountered these issues before, and these sentiments sound very familiar; similar situations arose during the promotion of wood formwork. The introduction of a new product will inevitably have a transitional period, but this is an inevitable trend. If the construction site insists on using it, there will be no problem.
Another significant issue is waste, which is also related to construction management. Sometimes, some plastic formwork can still be used, but workers, upon seeing new boards, prefer not to use the old ones, leading to significant waste. The management approach of China State Construction Seventh Engineering Bureau is commendable; they allow two buildings to use plastic formwork simultaneously and then compare waste levels. If there is a significant difference, it indicates that one of the teams is not performing well, which provides a direct way to address the situation with labor management. With this comparison, workers will be more cautious during use, concerned about waste. As a result, the cost savings achieved through the completion of both buildings can exceed 50%.
Many people often ask me how many times plastic formwork can be recycled. This is a difficult question for me to answer because the number of cycles is directly related to the construction team. If used normally with wear and tear, 30 uses should be no problem, and there are even cases of 50 uses depending on how it is handled. If it is carelessly thrown or dropped, I cannot guarantee anything. Therefore, the premise of achieving 30 uses is that it must be due to normal wear and tear, not reckless waste.
Therefore, to save more than 50% of the budget, the first step is product quality, and the second is effective management.