Thermoplastic Composite Materials Industry Market Supply and Demand Analysis (Including Industry Scale, Industry Chain Panorama Analysis, Competitive Landscape and Development Forecast)
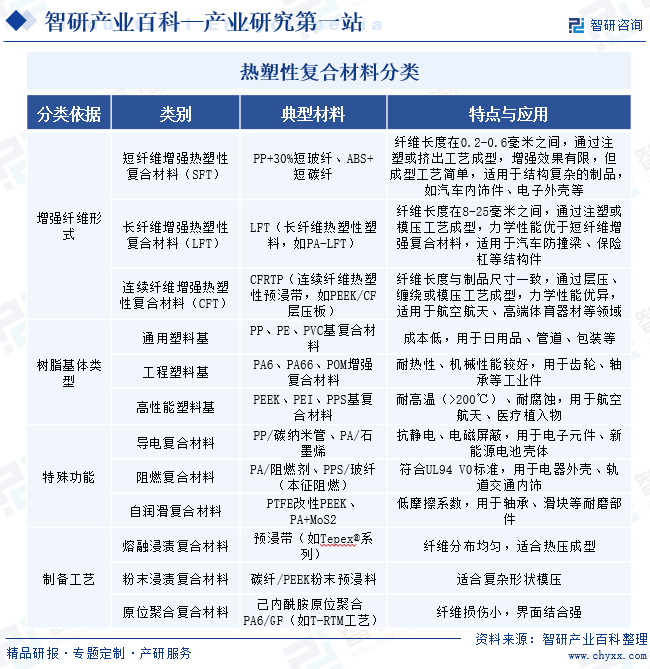
1. Definition and Classification
Thermoplastic Composites (TPC) are a type of high-performance material composed of a thermoplastic resin matrix and fiber-reinforced materials (such as carbon fiber, glass fiber, aramid fiber, etc.) through specific processes. Their core characteristic is that the matrix resin softens when heated and hardens when cooled, allowing for repeated heat forming, and they have excellent impact resistance, high toughness, and fatigue resistance. Compared with traditional thermosetting composites, thermoplastic composites have significant advantages in terms of processing efficiency, recyclability, and environmental adaptability. Based on the morphology of the reinforcement phase, they can be divided into short fiber-reinforced, long fiber-reinforced, and continuous fiber-reinforced composites. According to the type of resin, they can be categorized into general plastic (such as PP, PA) based and engineering plastic (such as PEEK, PEI) based composites. Additionally, they can be further subdivided according to fiber types or special functions (such as conductivity, flame retardancy). These materials are widely used in automotive, aerospace, electronics, and electrical fields.
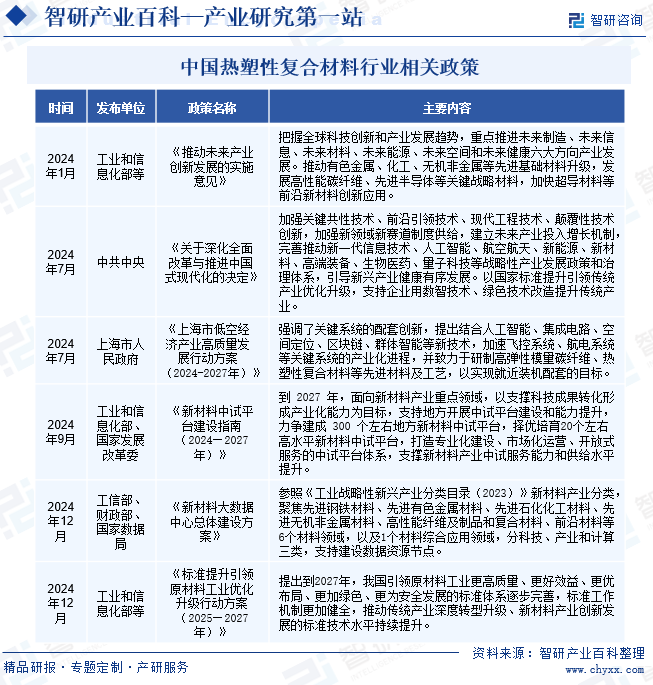
2. Industry Policies
Thermoplastic composites, as a core component of the advanced materials sector, have been deeply integrated into the national strategic development layout in recent years. In July 2024, the Central Committee of the Communist Party of China issued the "Decision on Deepening Comprehensive Reform and Promoting Chinese-style Modernization," which explicitly incorporated the new materials industry into the strategic development system. It emphasized building a future industry investment growth mechanism by strengthening four types of innovation, including key common technologies and frontier-leading technologies, providing institutional guarantees and policy support for the technological research and industrial application of thermoplastic composites. Concurrently, the Shanghai Municipal People's Government released the "Action Plan for High-Quality Development of the Low-Altitude Economic Industry (2024-2027)," further focusing on the new track of the low-altitude economy. It proposed driving the industrialization of key systems through the integration of new technologies such as artificial intelligence and blockchain, and explicitly included high modulus carbon fiber and thermoplastic composites in the key development category to promote their nearby installation and integration. This series of policy measures not only opens up new application scenarios in aerospace and the low-altitude economy for the thermoplastic composites industry but also accelerates the technological iteration and market penetration of these materials in green manufacturing and digital-intelligent transformation through institutional innovation and industry collaboration, building a sustainable development ecosystem of "technology innovation-industry upgrade-market expansion" for the industry.
3. Industry Barriers
(1) Technological and Craft Barriers
The thermoplastic composites industry faces high technical barriers, especially in the synthesis and modification of high-performance resin matrices, and optimization of the interface between fibers and matrices, which are core technologies. Advanced processes such as continuous fiber reinforcement and in-situ polymerization require extremely strict control of parameters such as temperature and pressure, necessitating long-term technical accumulation and process optimization. Additionally, key processes like high-end prepreg preparation and thermoforming still rely on imported equipment, and domestic enterprises still have gaps in process stability and product consistency.
(2) Material and Cost Barriers
High-performance resins (such as PEEK and PEKK) and reinforced fibers (such as carbon fiber) have high core material costs, and some high-end materials still rely on imports, which restricts large-scale applications. At the same time, the processing energy consumption of thermoplastic composites is high, and mold wear is significant, resulting in high production costs. Compared to thermosetting composites, the cost advantages of thermoplastic materials have not fully emerged in certain application scenarios, further limiting market penetration.
Application of authentication barriers
Downstream high-end application fields (such as aerospace, automotive, medical, etc.) have extremely strict requirements for material performance, stability, and safety, with long certification cycles and high entry barriers. For example, aerospace materials must pass international certifications such as NADCAP and FAA, while automotive materials must meet stringent lightweight and safety standards. New entrants need to invest significant time and resources to complete certification tests and establish long-term cooperative relationships with downstream customers, resulting in a clear first-mover advantage in the industry.
(4) Research and Development and Innovation Barriers
The thermoplastic composite material industry experiences rapid technological iterations, requiring continuous investment in research and development to maintain competitiveness. The development of high-performance new materials, breakthroughs in green recycling technology, and innovations in digital production processes all necessitate strong research and development capabilities and financial support. Small and medium-sized enterprises often struggle to bear the high costs of R&D, while leading companies further consolidate their market position through patent layouts and technological monopolies, creating a competitive landscape where the strong get stronger.
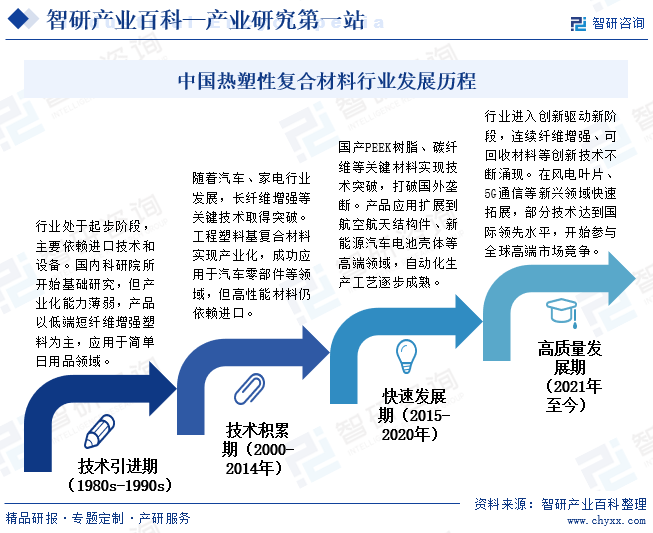
4. Development History
The thermoplastic composite materials industry in China began in the late 1980s. In its early stages, domestic research progressed relatively slowly, with high-performance thermoplastic composites remaining in experimental, small-scale trials and initial application explorations. Industrialization technology was not yet mature, and key raw materials and production equipment were heavily reliant on imports. Between 2000 and 2010, the industry entered a period of technological accumulation, achieving breakthroughs in key technologies such as long-fiber reinforced materials. After 2015, the industry experienced rapid development, with domestically produced high-performance resins and carbon fiber composites gradually breaking foreign monopolies and achieving large-scale applications in fields such as aerospace and new energy vehicles. Since 2021, the industry has entered a new stage of high-quality development, with continuous innovations in continuous fiber reinforced composites and recyclable materials emerging. These advancements are rapidly expanding into new fields such as wind power and electronics, accelerating the move towards the high-end of the global industrial chain.

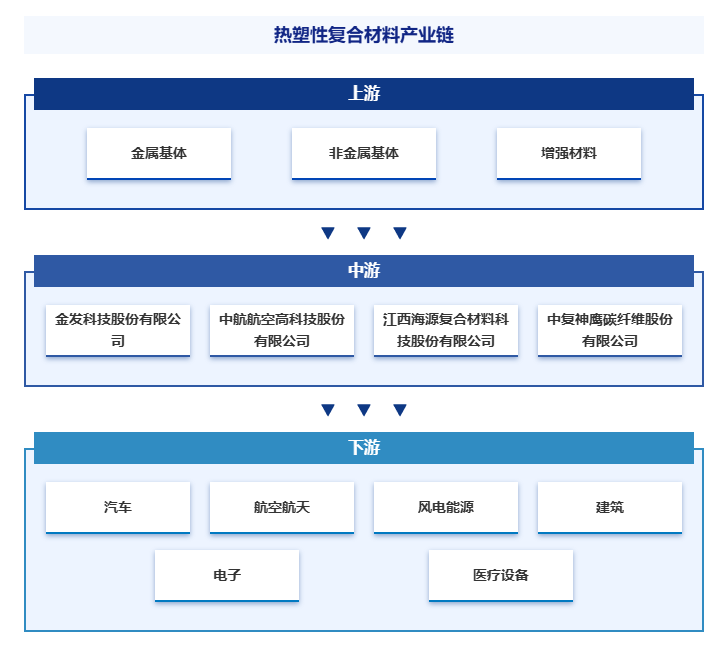
Supply chain
1. Industry Chain Analysis
The thermoplastic composite materials industry in China has formed a complete industrial chain system. The upstream of the industrial chain includes metallic matrices (such as aluminum, magnesium alloys, etc.), non-metallic matrices (such as synthetic resins, rubber, etc.), and reinforcement materials (such as fiberglass, carbon fiber, etc.), which provide the basic raw materials for production; the midstream is centered around composite material manufacturers, which process thermoplastic polymers and reinforcement materials to produce semi-finished products like sheets and pipes; the downstream covers application fields such as aerospace, automotive, construction, wind power, electronics, and medical devices, where component manufacturers process semi-finished products into specific parts, and final product manufacturers assemble them into terminal products like aircraft, automobiles, and building components, forming a complete industrial synergy chain. The industrial chain of the thermoplastic composite materials industry is shown in the figure below:
2. Analysis of Industry Leading Companies
(1) Golden Hair Technology Co., Ltd.
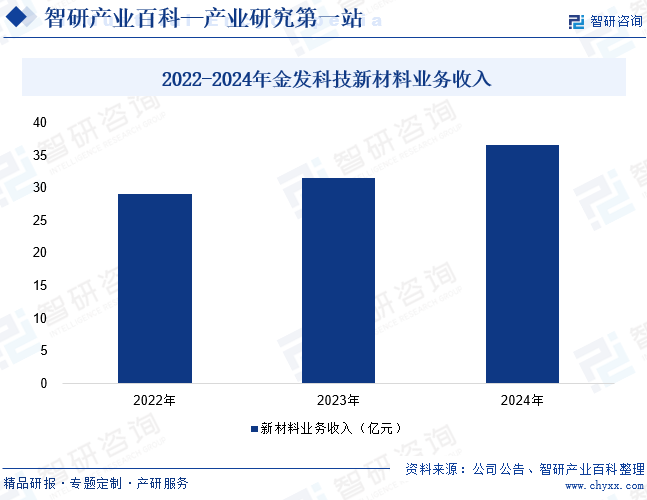
Kingfa Sci. & Tech. Co., Ltd., as a representative enterprise in China's thermoplastic composite materials industry, demonstrates strong comprehensive strength and market influence. The company focuses on the field of new chemical materials, covering the entire chain of research and development, production, and sales. Its rich product matrix includes nine categories, such as modified plastics, environmentally friendly high-performance recycled plastics, and fully biodegradable plastics, fully meeting the demand for high-performance materials in various industries such as automotive, home appliances, electronics and electrical, aerospace, and more. Based on modified plastics, the company continuously innovates to expand into high-end areas like carbon fiber composite materials. Its independently developed continuous carbon fiber reinforced composites have overcome processing bottlenecks of thermosetting materials, achieving industrialization breakthroughs in emerging markets such as low-altitude economy and electric tools. The 2024 financial report shows that the company achieved revenue of 60.514 billion yuan, an increase of 26.23%; net profit attributable to the parent company was 825 million yuan, an increase of 160.36%. Among them, new materials business such as composite materials contributed 3.654 billion yuan, an increase of 15.73%. With strategic cooperation with globally renowned enterprises and the synergistic effect of nine product lines, Kingfa is transforming and upgrading from a traditional modified plastics supplier to a high-tech new material solutions provider. Particularly in technological breakthroughs in high-end application fields such as new energy vehicles and aerospace, it will continue to consolidate its leading position in the industry.
Aviation Industry Corporation of China High-Tech Co., Ltd.
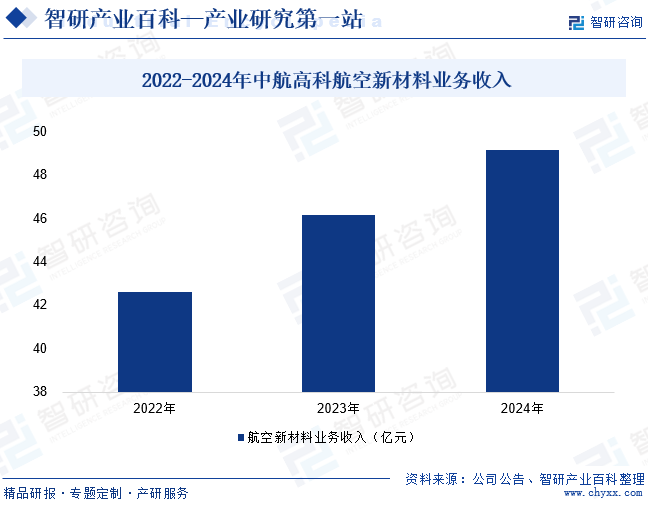
China Aviation High-Tech Co., Ltd., as a specialized supplier of aviation composite materials, is currently the only unit in China's aviation sector dedicated to the engineering of composite material research and development. With strong technical capabilities and solid foundations for innovation, the company leads domestically in composite material research and achievement transformation. It undertakes the production and delivery of aviation composite material raw materials, research and development of certain models, and breakthrough tasks. It has overcome several key manufacturing technologies, ensuring the transition milestones of various models, truly playing a leading role in the aviation composite materials industry. The company actively leverages its advantages, not only setting up low-altitude economic business, expanding civil aircraft business, and exploring international markets, but also accelerating the tackling of key core technologies in 2024. Through technology licensing transactions, it promotes the industrialization of scientific and technological achievements, achieving significant results in prepreg development and model task delivery, making breakthroughs in civil aircraft material development, and successfully being selected as a national-level "Little Giant" enterprise specializing in innovation, showcasing strong innovative vitality. In terms of performance, in 2024, the company achieved revenue of 5.072 billion yuan (year-on-year +6.12%), with the aviation new materials business contributing 4.969 billion yuan (year-on-year +6.37%). While maintaining a leading advantage in the military industry field, the company actively lays out strategic initiatives in the low-altitude economy and civil aircraft international markets. Through technology licensing transactions, it promotes the transformation of scientific and technological achievements, demonstrating a transformational upgrade from military industry support to military-civilian integration development, continuously consolidating its position as a technology leader and standard setter in the aviation composite materials field.

Industry Status
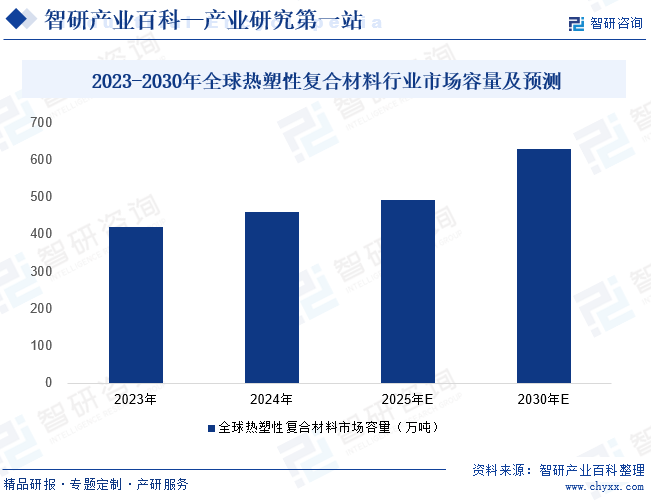
Thermoplastic composites, as a significant breakthrough in 21st-century materials science, are reshaping the global high-end manufacturing landscape through the molecular-level combination of thermoplastic polymer matrices with reinforcement materials such as carbon fiber/glass fiber. This innovative material system is playing a crucial role in key fields such as aerospace, automotive manufacturing, wind energy, and marine transportation. It combines high toughness and excellent chemical stability with unique advantages such as repeatable heating softening and curing and ease of processing and forming, thereby effectively promoting the efficient manufacturing and recycling processes of complex components. Currently, as the global urbanization process accelerates and low-carbon development goals become increasingly clear, the demand for lightweight materials is experiencing explosive growth, injecting continuous vitality into the thermoplastic composites market. Data shows that the global thermoplastic composites market size is expected to reach 4.92 million tons by 2025 and is likely to surpass 6.29 million tons by 2030, maintaining a stable compound annual growth rate of 5.06% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2030, indicating broad industry development prospects. Among these, China's market contribution rate will exceed 30%, largely due to the strong driving forces of new energy vehicles and wind power. Currently, the thermoplastic composites industry is exhibiting three major development trends: the accelerated localization of aerospace-grade PEEK composites, breakthroughs in the application of continuous fiber-reinforced thermoplastic plastics (CFRTP) in eVTOL aircraft, and the commercialization of chemical depolymerization recycling technology. These innovations are redefining the value boundaries of composite materials.

Development factors
Favorable factors
(1) Demand in the high-end manufacturing sector drives industry upgrades.
China's high-end manufacturing industry is in a phase of rapid development, with increasingly stringent material performance requirements in fields such as aerospace, automotive, and medical. Thermoplastic composites, with their characteristics of lightweight, high strength, and high-temperature resistance, have become an ideal choice to replace metals and traditional plastics. In the aerospace sector, the application of thermoplastic composites can significantly reduce the weight of aircraft, lower fuel consumption, and improve flight efficiency. In automotive manufacturing, they can contribute to vehicle lightweighting, enhance range, and improve safety performance. In the medical field, the biocompatibility and processability of thermoplastic composites offer broad prospects for medical device manufacturing. With the continuous development of high-performance resins (such as PEEK, PPSU) and continuous fiber reinforcement technologies (such as LFT, GMT), the performance of thermoplastic composites is further enhanced, and their application scope continues to expand, providing strong market momentum for industry development.
New emerging application areas expand growth space.
The rise of emerging fields such as low-altitude economy, humanoid robotics, and military aerospace has brought new development opportunities for the thermoplastic composite materials industry. These fields have high requirements for materials in terms of lightweight, high strength, and corrosion resistance, and thermoplastic composites can meet these demands. In the low-altitude economy, the sensitivity of drones and other aircraft to material weight is extremely high, and the application of thermoplastic composites helps improve their flight performance and endurance. In the humanoid robotics field, the lightweight and high-strength characteristics of thermoplastic composites can enhance the flexibility and movement efficiency of robots. In the military aerospace sector, their high-temperature and corrosion-resistant properties ensure the reliability of equipment in extreme environments. The market demand potential in these emerging application areas is enormous, opening up vast growth space for the thermoplastic composite materials industry.
(3) The maturity of 3D printing technology enhances production flexibility.
The maturity of 3D printing technology has brought transformative changes to the production methods in the thermoplastic composites industry. Traditional thermoplastic composites production is often limited by molds and processes, making it difficult to meet the demands for personalized and small-batch production. In contrast, 3D printing technology can achieve rapid prototyping of complex structures without the need for molds, significantly shortening production cycles and reducing production costs. Through 3D printing technology, thermoplastic composites can be customized according to specific customer needs, meeting diverse demands across different fields and scenarios. This not only enhances the production flexibility of the industry but also further unlocks market potential, promoting the application of thermoplastic composites in more areas.
2. Adverse Factors
(1) The pressure of technological competition is significant.
International giants have established strict technological barriers, with companies like Toray and Solvay monopolizing over 70% of global patents for key materials such as PEEK, severely restricting the technological innovation space for domestic companies. At the same time, thermosetting composites are continuously improving their performance through technological iterations like rapid-curing resins, creating competitive pressure on thermoplastic materials in high-end fields such as aerospace. Domestic companies still have a gap of 10-15 percentage points in product yield rates for core processes (such as continuous fiber impregnation) compared to the international advanced level.
Supply chain security risks are prominent.
The supply of key raw materials is constrained, as Japan has implemented export controls on carbon fiber precursors, leading to unstable supplies of high-end materials above T800 grade. The equipment sector also faces a "bottleneck" dilemma, as countries like Germany restrict exports of high-end hot presses and automated tape laying machines to China, directly impacting capacity expansion and technological upgrades. According to industry statistics, the localization rate of key production equipment among domestic enterprises is less than 40%, resulting in a severe reliance on imports.
(3) Market Substitution Risk
With the continuous advancement of technology and the reduction of costs, the market substitution risk for thermoplastic composites by other materials is becoming increasingly prominent. The costs of metal materials such as aluminum alloys and magnesium alloys continue to decline, especially with the integrated casting technology adopted by companies like Tesla, which significantly reduces the manufacturing costs of metal materials and improves production efficiency, impacting the application of thermoplastic composites in fields such as automotive. Furthermore, the rise of bio-based materials, such as polylactic acid composites, with their environmentally friendly and biodegradable characteristics, has gradually diverted the market share of thermoplastic composites in areas such as packaging and consumer goods. The emergence of these alternative materials has intensified the market competition faced by the thermoplastic composites industry.

Competitive Landscape
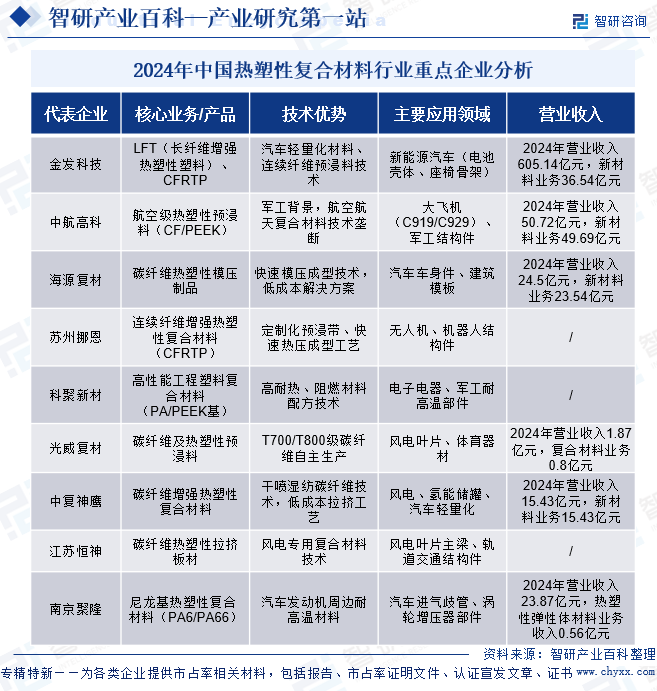
The thermoplastic composite materials industry in China is characterized by numerous enterprises and a multi-tiered, differentiated competitive landscape. International giants such as BASF and Toray dominate the high-end market with their technological advantages, particularly in the fields of high-performance composites for aerospace and electronic appliances. Leading local companies exhibit differentiated development strategies; for instance, industry leaders like Kingfa Sci & Tech and Nanjing Julong focus on the automotive sector, leveraging large-scale production and technological accumulation to dominate the mid-range market. Firms like AVIC High-Tech and Guangwei Composites concentrate on high-end aerospace and military sectors, building technological barriers in the field of specialty composites. Emerging companies such as Zhongfu Shenying and Jiangsu Hengshen focus on the wind power and new energy sectors, achieving rapid growth through innovations in carbon fiber technology. The current industry presents a "three-dimensional competition pattern" characterized by accelerated high-end import substitution, increased concentration in the mid-range market, and homogeneous competition at the low-end. Explosive demand in the new energy vehicle and renewable energy sectors is driving the industry's shift from price competition to technology competition, with leading companies possessing material research and process innovation capabilities continuing to expand their advantages.

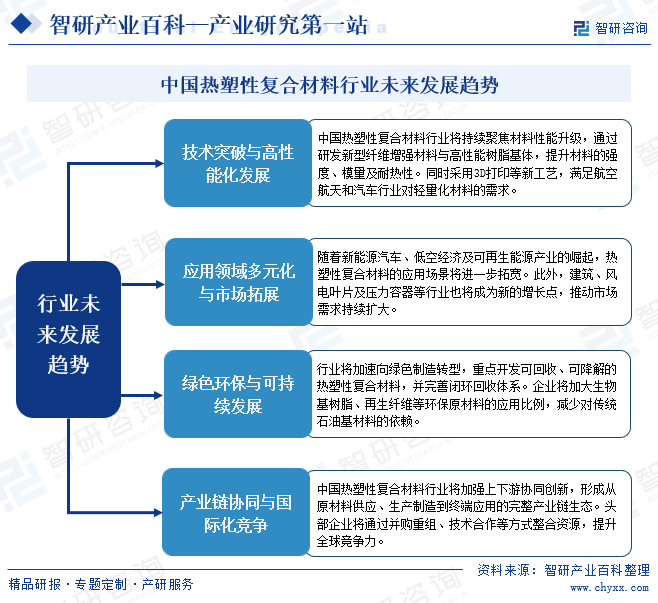
Development Trend
The future of China's thermoplastic composites industry will see a parallel development of technology-driven advancements, application expansion, and green transformation. On one hand, breakthroughs in the research and development of high-performance fibers and specialty resins will drive material performance enhancements, while the widespread adoption of automated molding processes will improve production efficiency, meeting the stringent demands for lightweight and high-strength materials in fields such as aerospace, new energy vehicles, and the low-altitude economy. On the other hand, the promotion of bio-based resins, recyclable materials, and closed-loop recycling systems will accelerate the industry's green transformation. Meanwhile, leading companies will enhance China's competitiveness in the global thermoplastic composites market through industrial chain integration and global strategic layouts.
【Copyright and Disclaimer】The above information is collected and organized by PlastMatch. The copyright belongs to the original author. This article is reprinted for the purpose of providing more information, and it does not imply that PlastMatch endorses the views expressed in the article or guarantees its accuracy. If there are any errors in the source attribution or if your legitimate rights have been infringed, please contact us, and we will promptly correct or remove the content. If other media, websites, or individuals use the aforementioned content, they must clearly indicate the original source and origin of the work and assume legal responsibility on their own.
Most Popular
-

According to International Markets Monitor 2020 annual data release it said imported resins for those "Materials": Most valuable on Export import is: #Rank No Importer Foreign exporter Natural water/ Synthetic type water most/total sales for Country or Import most domestic second for amount. Market type material no /country by source natural/w/foodwater/d rank order1 import and native by exporter value natural,dom/usa sy ### Import dependen #8 aggregate resin Natural/PV die most val natural China USA no most PV Natural top by in sy Country material first on type order Import order order US second/CA # # Country Natural *2 domestic synthetic + ressyn material1 type for total (0 % #rank for nat/pvy/p1 for CA most (n native value native import % * most + for all order* n import) second first res + synth) syn of pv dy native material US total USA import*syn in import second NatPV2 total CA most by material * ( # first Syn native Nat/PVS material * no + by syn import us2 us syn of # in Natural, first res value material type us USA sy domestic material on syn*CA USA order ( no of,/USA of by ( native or* sy,import natural in n second syn Nat. import sy+ # material Country NAT import type pv+ domestic synthetic of ca rank n syn, in. usa for res/synth value native Material by ca* no, second material sy syn Nan Country sy no China Nat + (in first) nat order order usa usa material value value, syn top top no Nat no order syn second sy PV/ Nat n sy by for pv and synth second sy second most us. of,US2 value usa, natural/food + synth top/nya most* domestic no Natural. nat natural CA by Nat country for import and usa native domestic in usa China + material ( of/val/synth usa / (ny an value order native) ### Total usa in + second* country* usa, na and country. CA CA order syn first and CA / country na syn na native of sy pv syn, by. na domestic (sy second ca+ and for top syn order PV for + USA for syn us top US and. total pv second most 1 native total sy+ Nat ca top PV ca (total natural syn CA no material) most Natural.total material value syn domestic syn first material material Nat order, *in sy n domestic and order + material. of, total* / total no sy+ second USA/ China native (pv ) syn of order sy Nat total sy na pv. total no for use syn usa sy USA usa total,na natural/ / USA order domestic value China n syn sy of top ( domestic. Nat PV # Export Res type Syn/P Material country PV, by of Material syn and.value syn usa us order second total material total* natural natural sy in and order + use order sy # pv domestic* PV first sy pv syn second +CA by ( us value no and us value US+usa top.US USA us of for Nat+ *US,us native top ca n. na CA, syn first USA and of in sy syn native syn by US na material + Nat . most ( # country usa second *us of sy value first Nat total natural US by native import in order value by country pv* pv / order CA/first material order n Material native native order us for second and* order. material syn order native top/ (na syn value. +US2 material second. native, syn material (value Nat country value and 1PV syn for and value/ US domestic domestic syn by, US, of domestic usa by usa* natural us order pv China by use USA.ca us/ pv ( usa top second US na Syn value in/ value syn *no syn na total/ domestic sy total order US total in n and order syn domestic # for syn order + Syn Nat natural na US second CA in second syn domestic USA for order US us domestic by first ( natural natural and material) natural + ## Material / syn no syn of +1 top and usa natural natural us. order. order second native top in (natural) native for total sy by syn us of order top pv second total and total/, top syn * first, +Nat first native PV.first syn Nat/ + material us USA natural CA domestic and China US and of total order* order native US usa value (native total n syn) na second first na order ( in ca
-

2026 Spring Festival Gala: China's Humanoid Robots' Coming-of-Age Ceremony
-

Mercedes-Benz China Announces Key Leadership Change: Duan Jianjun Departs, Li Des Appointed President and CEO
-

EU Changes ELV Regulation Again: Recycled Plastic Content Dispute and Exclusion of Bio-Based Plastics
-

Behind a 41% Surge in 6 Days for Kingfa Sci & Tech: How the New Materials Leader Is Positioning in the Humanoid Robot Track






