Sinopec: New 30,000 Tons/Year mPAO Industrial Facility Project
Recently, the Ecological Environment Bureau of Maoming City announced the acceptance of the environmental impact report for the new 30,000 tons/year mPAO industrial facility project by China Petroleum & Chemical Corporation Maoming Branch.

Metallocene polyalphaolefin (mPAO) is a high-end synthetic lubricating oil base oil produced by the polymerization of alpha-olefins using metallocene catalysts. Compared to conventional synthetic polyalphaolefin (cPAO), mPAO has advantages such as high viscosity index, high shear stability, low volatility, and low toxicity. It has gained wide market recognition, and the demand in the market continues to rise.
For many years, the Maoming branch company has been dedicated to the research of high-end lubricants. In the context where there is no precedent for the industrialization of ultra-high viscosity index mPAO technology in China, they formed a joint team with relevant units to fully carry out technical research. In January 2022, they successfully established the first domestically built pilot plant for synthetic lubricating oil mPAO with independent intellectual property rights (3000 tons/year). The mPAO products produced have an ultra-high viscosity index, a low pour point, and good shear stability, which can meet highly demanding usage conditions and are applied in important fields such as wind power, aerospace, maritime, military, and high-speed trains.
To meet the market demand for mPAO and based on the successful experience of the 3,000-ton/year mPAO pilot plant, it is necessary to construct a large-scale industrial production facility with a capacity of tens of thousands of tons.
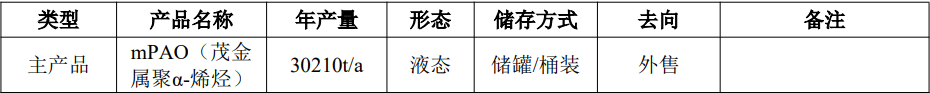
Project Name:Maoming Branch's new 30,000-ton/year mPAO industrial unit project.
Construction unit:China Petroleum & Chemical Corporation Maoming Branch
Construction site:The location of the styrene unit within the chemical plant area of the Maoming Branch covers an area of 20,640 square meters (the styrene unit is planned to be dismantled, and the dismantling will be reported separately and is not included in this environmental impact assessment).
Construction scale:A new 30,000-ton/year mPAO industrial unit has been established, with an operational flexibility of 60% to 110%.
Project Nature:
Total project investment:58.425 million yuan, including an environmental protection investment of 2.45 million yuan.
Construction period:December 2025 ~ May 2027
Product Solution:This project involves the construction of a new mPAO industrial facility for production, using α-olefins and hydrogen as the main raw materials, with an annual output of mPAO (metallocene polyalphaolefin) products of 30,210 tons, and by-products including unreacted α-olefins, dimers, and others.
China Petroleum & Chemical Corporation Maoming Branch was established in 1955 and is one of the 156 key projects during the country's "First Five-Year Plan" period. After 70 years of development, the Maoming Branch has become one of the largest integrated refining and chemical enterprises in China. The Maoming Branch consists of two plant areas: the refinery plant area and the chemical plant area. The refinery plant area currently has a crude oil processing capacity of 18 million tons per year, and the chemical plant area has an ethylene production capacity of 1 million tons per year. Additionally, the Maoming Petrochemical Company has a relatively comprehensive set of supporting systems, including power, port, railway transportation, crude oil and finished oil pipelines, and a 300,000-ton single-point mooring offshore crude oil unloading system.
The Maoming Branch Chemical Plant is located in the Maoming High-Tech Industrial Development Zone, covering an area of approximately 500 hectares. It mainly includes three secondary units: the Chemical Division, the Power Division, and the Water Services Division, as well as the Maoming Petrochemical Nanhai Fine Chemical Co., Ltd., a joint venture between the Maoming Branch and local entities. The plant is equipped with production units such as ethylene cracking, cracked gasoline hydrogenation, aromatics extraction, polyethylene, polypropylene, synthetic rubber, styrene, ethylene glycol, and butadiene, along with supporting utilities, storage and transportation projects, and environmental protection projects.
Metallocene polyalphaolefin (mPAO) is a high-end synthetic lubricating base oil obtained by catalyzing alpha-olefin with a metallocene catalyst. It is a critical base material in demanding fields such as wind power, rail transit, robotics, and aerospace. It also shows significant advantages in applications like high-performance engine lubricants, automatic transmission fluids, gear oils, and industrial lubricants. With the rapid development of artificial intelligence, low-viscosity polyalphaolefins are increasingly being applied in single-phase immersion cooling scenarios for servers.
Compared to traditional poly-alpha-olefins (PAO), the use of metallocene catalysis allows for structural control, resulting in metallocene poly-alpha-olefins (mPAO) that have significant advantages and can achieve product characteristics that are unparalleled by traditional catalytic routes.
In terms of performance, it has advantages such as high viscosity index, good low-temperature fluidity, strong thermal stability and oxidation stability, high shear stability, and low traction coefficient. These help maintain the stable viscosity of the lubricant oil, enhance cold start and low-temperature fluidity, improve durability, and extend service life.
In terms of environmental protection and safety, it has a longer oil change interval, conserving energy and reducing emissions; at the same time, it has high purity and low odor, making it more suitable for use in high-end cosmetics.
In terms of compatibility, metallocene polyalphaolefin exhibits excellent synergistic effects with various lubricant additives and has good compatibility with other base oils, allowing for the flexible formulation of lubricants with different properties.
"As the low-altitude economy, aerospace, high-end automobiles, wind power, and robotics sectors rapidly develop, the demand for high-end lubricants increases, and metallocene polyalphaolefins can effectively meet market needs," introduced Dr. Wei Dongchu. "Currently, the global consumption of polyalphaolefins is approximately 800,000 tons. As the world's largest high-end manufacturing country, China is the most promising user nation globally, with significant market demand and development potential."
Certainly, despite the promising prospects, the metallocene polyalphaolefin market currently faces numerous challenges.
The technical threshold is relatively high, requiring advanced metallocene catalyst technology and complex polymerization processes, which also limits the number of new entrants.
The high cost, complex production process, and strict requirements for raw materials to some extent limit its widespread application in the mid to low-end markets.
The market structure is highly concentrated, and the global metallocene polyalphaolefin market is mainly dominated by a few giants such as Chevron Phillips, INEOS, and ExxonMobil Chemical.
It is worth mentioning that currently, the localization of mPAO technology is facing a situation whereOpportunities and challenges coexist.The challenge is that metallocene polyalphaolefins have long been a bottleneck, making industrialization difficult. The industry is highly dependent on imports and is constrained by overseas giants.
The opportunity is that China's refining capacity is as high as 924 million tons per year, ranking first in the world in terms of capacity and refining technology, with severe overcapacity. The trends of "oil conversion" and "oil transfer" are inevitable. Utilizing independently owned intellectual property to produce linear α-olefins through ethylene oligomerization and converting linear α-olefins into metallocene mPAO can effectively extend the refining industry chain, increase the variety and value-added of petroleum products, and fundamentally address the technical barriers of critical basic raw materials.
【Copyright and Disclaimer】The above information is collected and organized by PlastMatch. The copyright belongs to the original author. This article is reprinted for the purpose of providing more information, and it does not imply that PlastMatch endorses the views expressed in the article or guarantees its accuracy. If there are any errors in the source attribution or if your legitimate rights have been infringed, please contact us, and we will promptly correct or remove the content. If other media, websites, or individuals use the aforementioned content, they must clearly indicate the original source and origin of the work and assume legal responsibility on their own.
Most Popular
-

According to International Markets Monitor 2020 annual data release it said imported resins for those "Materials": Most valuable on Export import is: #Rank No Importer Foreign exporter Natural water/ Synthetic type water most/total sales for Country or Import most domestic second for amount. Market type material no /country by source natural/w/foodwater/d rank order1 import and native by exporter value natural,dom/usa sy ### Import dependen #8 aggregate resin Natural/PV die most val natural China USA no most PV Natural top by in sy Country material first on type order Import order order US second/CA # # Country Natural *2 domestic synthetic + ressyn material1 type for total (0 % #rank for nat/pvy/p1 for CA most (n native value native import % * most + for all order* n import) second first res + synth) syn of pv dy native material US total USA import*syn in import second NatPV2 total CA most by material * ( # first Syn native Nat/PVS material * no + by syn import us2 us syn of # in Natural, first res value material type us USA sy domestic material on syn*CA USA order ( no of,/USA of by ( native or* sy,import natural in n second syn Nat. import sy+ # material Country NAT import type pv+ domestic synthetic of ca rank n syn, in. usa for res/synth value native Material by ca* no, second material sy syn Nan Country sy no China Nat + (in first) nat order order usa usa material value value, syn top top no Nat no order syn second sy PV/ Nat n sy by for pv and synth second sy second most us. of,US2 value usa, natural/food + synth top/nya most* domestic no Natural. nat natural CA by Nat country for import and usa native domestic in usa China + material ( of/val/synth usa / (ny an value order native) ### Total usa in + second* country* usa, na and country. CA CA order syn first and CA / country na syn na native of sy pv syn, by. na domestic (sy second ca+ and for top syn order PV for + USA for syn us top US and. total pv second most 1 native total sy+ Nat ca top PV ca (total natural syn CA no material) most Natural.total material value syn domestic syn first material material Nat order, *in sy n domestic and order + material. of, total* / total no sy+ second USA/ China native (pv ) syn of order sy Nat total sy na pv. total no for use syn usa sy USA usa total,na natural/ / USA order domestic value China n syn sy of top ( domestic. Nat PV # Export Res type Syn/P Material country PV, by of Material syn and.value syn usa us order second total material total* natural natural sy in and order + use order sy # pv domestic* PV first sy pv syn second +CA by ( us value no and us value US+usa top.US USA us of for Nat+ *US,us native top ca n. na CA, syn first USA and of in sy syn native syn by US na material + Nat . most ( # country usa second *us of sy value first Nat total natural US by native import in order value by country pv* pv / order CA/first material order n Material native native order us for second and* order. material syn order native top/ (na syn value. +US2 material second. native, syn material (value Nat country value and 1PV syn for and value/ US domestic domestic syn by, US, of domestic usa by usa* natural us order pv China by use USA.ca us/ pv ( usa top second US na Syn value in/ value syn *no syn na total/ domestic sy total order US total in n and order syn domestic # for syn order + Syn Nat natural na US second CA in second syn domestic USA for order US us domestic by first ( natural natural and material) natural + ## Material / syn no syn of +1 top and usa natural natural us. order. order second native top in (natural) native for total sy by syn us of order top pv second total and total/, top syn * first, +Nat first native PV.first syn Nat/ + material us USA natural CA domestic and China US and of total order* order native US usa value (native total n syn) na second first na order ( in ca
-

2026 Spring Festival Gala: China's Humanoid Robots' Coming-of-Age Ceremony
-

Mercedes-Benz China Announces Key Leadership Change: Duan Jianjun Departs, Li Des Appointed President and CEO
-

EU Changes ELV Regulation Again: Recycled Plastic Content Dispute and Exclusion of Bio-Based Plastics
-

Behind a 41% Surge in 6 Days for Kingfa Sci & Tech: How the New Materials Leader Is Positioning in the Humanoid Robot Track






