Revolutionary New Dressing: 1-Minute Rapid Hemostasis Using Bacterial Cellulose as the Base Material
On July 22, 2025, the team led by Zhong Chao from the Shenzhen Institute of Advanced Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, in collaboration with the team led by Liu Yan from Ruijin Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, jointly developed a new type of hemostatic dressing called T-BC based on bacterial cellulose. This innovative material offers a novel solution for the treatment of burns and complex wounds. The research findings were published in the international academic journal Advanced Materials.

Controlling bleeding during clinical burn debridement has always been a challenge. Traditional electrocautery hemostasis poses a risk of thermal damage to surrounding tissues and has low operational efficiency. Commonly used hemostatic agents often lead to re-bleeding during dressing changes, have poor adhesion, and lack sufficient mechanical strength.
The research team employed synthetic biology techniques to precisely bind recombinant human thrombin with a specific cellulose-binding domain (CBD), anchoring it onto a bacterial cellulose (BC) matrix to construct an integrated dressing, T-BC, which possesses both hemostatic and wound-healing functions.
Performance Advantages of T-BC
Rapid Hemostasis: In a rat liver incision model, T-BC dressing can achieve rapid hemostasis within 1 minute, with significantly better hemostatic efficiency compared to traditional materials.
Promoting Healing: In a rat model simulating deep second-degree burn wounds, the wound closure rate in the experimental group treated with T-BC dressing was approximately 40% higher than that of the control group after just 5 days of treatment. Studies have shown that the T-BC dressing significantly accelerates the healing process by promoting neovascularization, regulating the inflammatory response, and reconstructing skin tissue structure through a synergistic triple mechanism. At the molecular level, it achieves multi-faceted regulation of the wound repair process.
High biosafety: The research team conducted comprehensive biosafety evaluations, including cytotoxicity assays, hemolysis tests, and tissue compatibility assessments. The experimental results all confirmed that the T-BC dressing possesses excellent biosafety.
Environmental advantages: This study employs biomolecular self-assembly technology, achieving efficient thrombin immobilization simply through mild protein solution immersion. It eliminates the reliance on organic solvents and harsh reaction conditions associated with traditional chemical crosslinking, thereby offering significant environmental benefits.
The technology is currently in the patent application stage and plans to collaborate with enterprises to accelerate the clinical translation process. This new material can be used not only for burn treatment but also has potential applications in emergency trauma, surgical hemostasis, and chronic wound fields.
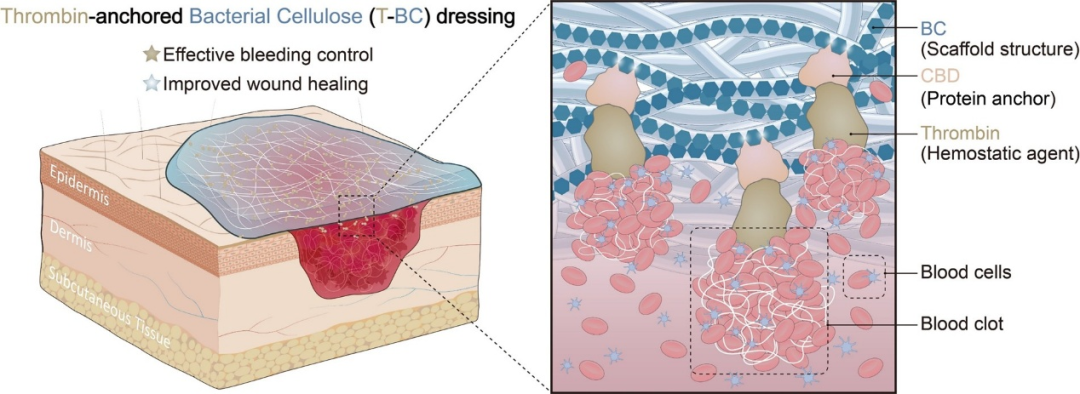
The mechanism of action of T-BC dressing in wound treatment.

T-BC auxiliary material samples. (Image provided by the research team)
【Copyright and Disclaimer】The above information is collected and organized by PlastMatch. The copyright belongs to the original author. This article is reprinted for the purpose of providing more information, and it does not imply that PlastMatch endorses the views expressed in the article or guarantees its accuracy. If there are any errors in the source attribution or if your legitimate rights have been infringed, please contact us, and we will promptly correct or remove the content. If other media, websites, or individuals use the aforementioned content, they must clearly indicate the original source and origin of the work and assume legal responsibility on their own.
Most Popular
-

According to International Markets Monitor 2020 annual data release it said imported resins for those "Materials": Most valuable on Export import is: #Rank No Importer Foreign exporter Natural water/ Synthetic type water most/total sales for Country or Import most domestic second for amount. Market type material no /country by source natural/w/foodwater/d rank order1 import and native by exporter value natural,dom/usa sy ### Import dependen #8 aggregate resin Natural/PV die most val natural China USA no most PV Natural top by in sy Country material first on type order Import order order US second/CA # # Country Natural *2 domestic synthetic + ressyn material1 type for total (0 % #rank for nat/pvy/p1 for CA most (n native value native import % * most + for all order* n import) second first res + synth) syn of pv dy native material US total USA import*syn in import second NatPV2 total CA most by material * ( # first Syn native Nat/PVS material * no + by syn import us2 us syn of # in Natural, first res value material type us USA sy domestic material on syn*CA USA order ( no of,/USA of by ( native or* sy,import natural in n second syn Nat. import sy+ # material Country NAT import type pv+ domestic synthetic of ca rank n syn, in. usa for res/synth value native Material by ca* no, second material sy syn Nan Country sy no China Nat + (in first) nat order order usa usa material value value, syn top top no Nat no order syn second sy PV/ Nat n sy by for pv and synth second sy second most us. of,US2 value usa, natural/food + synth top/nya most* domestic no Natural. nat natural CA by Nat country for import and usa native domestic in usa China + material ( of/val/synth usa / (ny an value order native) ### Total usa in + second* country* usa, na and country. CA CA order syn first and CA / country na syn na native of sy pv syn, by. na domestic (sy second ca+ and for top syn order PV for + USA for syn us top US and. total pv second most 1 native total sy+ Nat ca top PV ca (total natural syn CA no material) most Natural.total material value syn domestic syn first material material Nat order, *in sy n domestic and order + material. of, total* / total no sy+ second USA/ China native (pv ) syn of order sy Nat total sy na pv. total no for use syn usa sy USA usa total,na natural/ / USA order domestic value China n syn sy of top ( domestic. Nat PV # Export Res type Syn/P Material country PV, by of Material syn and.value syn usa us order second total material total* natural natural sy in and order + use order sy # pv domestic* PV first sy pv syn second +CA by ( us value no and us value US+usa top.US USA us of for Nat+ *US,us native top ca n. na CA, syn first USA and of in sy syn native syn by US na material + Nat . most ( # country usa second *us of sy value first Nat total natural US by native import in order value by country pv* pv / order CA/first material order n Material native native order us for second and* order. material syn order native top/ (na syn value. +US2 material second. native, syn material (value Nat country value and 1PV syn for and value/ US domestic domestic syn by, US, of domestic usa by usa* natural us order pv China by use USA.ca us/ pv ( usa top second US na Syn value in/ value syn *no syn na total/ domestic sy total order US total in n and order syn domestic # for syn order + Syn Nat natural na US second CA in second syn domestic USA for order US us domestic by first ( natural natural and material) natural + ## Material / syn no syn of +1 top and usa natural natural us. order. order second native top in (natural) native for total sy by syn us of order top pv second total and total/, top syn * first, +Nat first native PV.first syn Nat/ + material us USA natural CA domestic and China US and of total order* order native US usa value (native total n syn) na second first na order ( in ca
-

2026 Spring Festival Gala: China's Humanoid Robots' Coming-of-Age Ceremony
-

Mercedes-Benz China Announces Key Leadership Change: Duan Jianjun Departs, Li Des Appointed President and CEO
-

EU Changes ELV Regulation Again: Recycled Plastic Content Dispute and Exclusion of Bio-Based Plastics
-

Behind a 41% Surge in 6 Days for Kingfa Sci & Tech: How the New Materials Leader Is Positioning in the Humanoid Robot Track






