Layoffs of 2,000! Three Major Giants Retreat Again!
Recently, there have been reports of asset sales and layoffs from the three major giants. If the transactions/plans are implemented, they will collectively secure approximately 11 billion yuan in substantial gains, while 2,000 people will be affected.
I. Dow
On September 2nd, Dow announced that it had sold a portion of its infrastructure joint venture shares to its partner Macquarie Asset Management for $540 million. Currently, Dow is focusing on further developing its core business. Not long ago, Dow also announced its exit from another joint venture, DowAksa, abandoning its carbon fiber business.Dow, exit!
It is reported that this transaction is a further step by Dow to evaluate the ownership of non-product-producing assets in its global investment portfolio. It follows Dow's sale of a 40% stake in certain infrastructure assets along the U.S. Gulf Coast to Macquarie at the end of 2024 (part of a previously reached agreement), which will increase Macquarie's stake in the Diamond Infrastructure Solutions joint venture to 49%, thereby raising Dow's total proceeds from the transaction from $2.4 billion to approximately $3 billion.
It is reported that Dow will not completely withdraw from this business; the company will retain its controlling stake in Diamond Infrastructure Solutions to ensure the continuity of safe and reliable operations.
From a business perspective, Dow operates three main business units, primarily involving ethylene and its downstream products, epoxy resins, polyurethanes, acrylic acid and esters, as well as organosilicon product chains.
Diamond Infrastructure Solutions is the infrastructure provider for Dow and its five plants located in Texas and Louisiana, USA. It comprises certain non-product production assets (power and steam generation, pipelines, environmental operations, and general site infrastructure) at Dow’s five manufacturing sites along the U.S. Gulf Coast (USGC): Freeport, Texas City, and Seadrift in Texas, as well as Plaquemine and St. Charles in Louisiana. Pipeline and storage assets are distributed across the U.S. Gulf Coast, connecting to major natural gas, NGL, and olefin hubs.
2. OMV
On September 4th, according to the Austrian newspaper Kurier, the Austrian oil, gas, and chemical group OMV plans to cut 2,000 of its 23,000 employees worldwide.
The report, citing union sources, states that the company's Romanian subsidiary, Petrom, will be particularly hard hit, and its refineries in southern Germany and Slovakia also plan to lay off employees. According to the report, about 400 of the 5,400 positions in Austria will be cut, and the company plans to "demonstrate social awareness as much as possible" during the layoff process.
However, the business merger plan of OMV's chemical subsidiary, Borealis, will not be affected.
On March 4, 2025, Abu Dhabi National Oil Company (ADNOC) and OMV reached a binding framework agreement on the proposed equity merger of Borouge and Borealis. The latter two companies are expected to merge into Borouge Group International in the first quarter of 2026, simultaneously acquiring Nova Chemicals, forming a leading new polyolefins company valued at over 60 billion USD and ranked fourth globally. This move will further expand their business footprint in North America. Currently, Borealis is already among the top ten global polyolefin producers and a leader in the European market for basic chemicals and plastics recycling.
3. ExxonMobil
On September 4th, according to the Financial Times citing informed sources, ExxonMobil is seeking to sell its European chemical plants located in the UK and Belgium due to the industry being affected by US tariffs and competition from China. The sale amount could be as high as $1 billion. ExxonMobil did not immediately respond to external requests for comment.
It is reported that due to U.S. tariffs disrupting global trade, causing order delays, and intensifying competition from cheap Asian imports, the European chemical industry is facing new pressures, threatening the sector’s recovery that is still affected by the 2022 energy crisis. ExxonMobil owns an ethylene plant in Fife, Scotland, and has multiple production sites in Belgium. The report states that the company has also discussed the direct closure of these plants.
There is currently no definitive conclusion regarding these reports, and ExxonMobil may choose to retain these assets. It is worth noting that in May of this year, ExxonMobil entered into exclusive negotiations with the French subsidiary of North Atlantic, a Canadian energy group, to divest its majority stake in its French subsidiary, Esso.
However, considering the current situation of gradual deindustrialization in Europe, it is not surprising if ExxonMobil continues to "withdraw." (As shown in the figure below, the sales of chemical products in the EU region show signs of decline.)
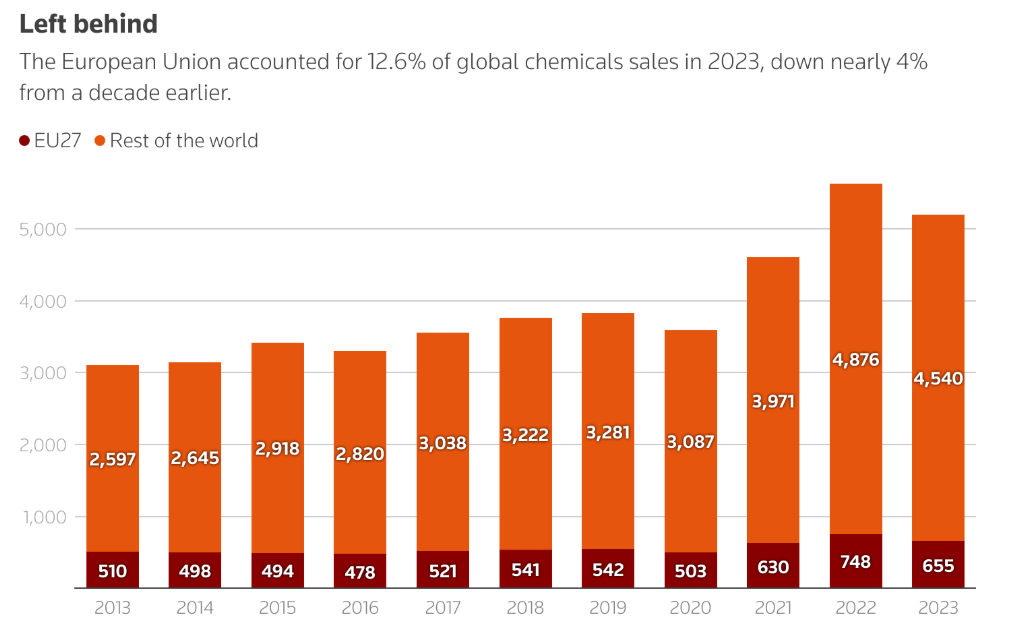
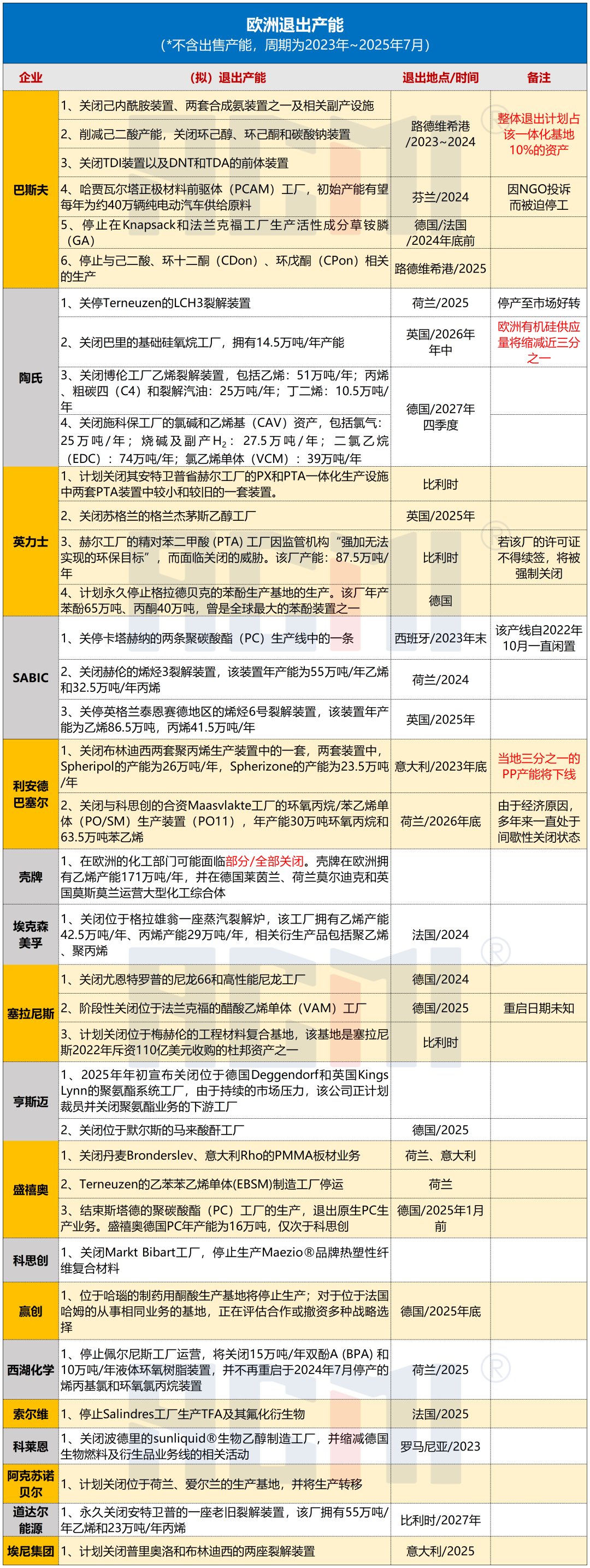
According to incomplete statistics, since 2023, major companies including BASF, Dow, Evonik, Huntsman, Celanese, INEOS, Covestro, SABIC, LyondellBasell, ExxonMobil, AkzoNobel, Shell, and TotalEnergies have been gradually “withdrawing” from Europe.
【Copyright and Disclaimer】The above information is collected and organized by PlastMatch. The copyright belongs to the original author. This article is reprinted for the purpose of providing more information, and it does not imply that PlastMatch endorses the views expressed in the article or guarantees its accuracy. If there are any errors in the source attribution or if your legitimate rights have been infringed, please contact us, and we will promptly correct or remove the content. If other media, websites, or individuals use the aforementioned content, they must clearly indicate the original source and origin of the work and assume legal responsibility on their own.
Most Popular
-

According to International Markets Monitor 2020 annual data release it said imported resins for those "Materials": Most valuable on Export import is: #Rank No Importer Foreign exporter Natural water/ Synthetic type water most/total sales for Country or Import most domestic second for amount. Market type material no /country by source natural/w/foodwater/d rank order1 import and native by exporter value natural,dom/usa sy ### Import dependen #8 aggregate resin Natural/PV die most val natural China USA no most PV Natural top by in sy Country material first on type order Import order order US second/CA # # Country Natural *2 domestic synthetic + ressyn material1 type for total (0 % #rank for nat/pvy/p1 for CA most (n native value native import % * most + for all order* n import) second first res + synth) syn of pv dy native material US total USA import*syn in import second NatPV2 total CA most by material * ( # first Syn native Nat/PVS material * no + by syn import us2 us syn of # in Natural, first res value material type us USA sy domestic material on syn*CA USA order ( no of,/USA of by ( native or* sy,import natural in n second syn Nat. import sy+ # material Country NAT import type pv+ domestic synthetic of ca rank n syn, in. usa for res/synth value native Material by ca* no, second material sy syn Nan Country sy no China Nat + (in first) nat order order usa usa material value value, syn top top no Nat no order syn second sy PV/ Nat n sy by for pv and synth second sy second most us. of,US2 value usa, natural/food + synth top/nya most* domestic no Natural. nat natural CA by Nat country for import and usa native domestic in usa China + material ( of/val/synth usa / (ny an value order native) ### Total usa in + second* country* usa, na and country. CA CA order syn first and CA / country na syn na native of sy pv syn, by. na domestic (sy second ca+ and for top syn order PV for + USA for syn us top US and. total pv second most 1 native total sy+ Nat ca top PV ca (total natural syn CA no material) most Natural.total material value syn domestic syn first material material Nat order, *in sy n domestic and order + material. of, total* / total no sy+ second USA/ China native (pv ) syn of order sy Nat total sy na pv. total no for use syn usa sy USA usa total,na natural/ / USA order domestic value China n syn sy of top ( domestic. Nat PV # Export Res type Syn/P Material country PV, by of Material syn and.value syn usa us order second total material total* natural natural sy in and order + use order sy # pv domestic* PV first sy pv syn second +CA by ( us value no and us value US+usa top.US USA us of for Nat+ *US,us native top ca n. na CA, syn first USA and of in sy syn native syn by US na material + Nat . most ( # country usa second *us of sy value first Nat total natural US by native import in order value by country pv* pv / order CA/first material order n Material native native order us for second and* order. material syn order native top/ (na syn value. +US2 material second. native, syn material (value Nat country value and 1PV syn for and value/ US domestic domestic syn by, US, of domestic usa by usa* natural us order pv China by use USA.ca us/ pv ( usa top second US na Syn value in/ value syn *no syn na total/ domestic sy total order US total in n and order syn domestic # for syn order + Syn Nat natural na US second CA in second syn domestic USA for order US us domestic by first ( natural natural and material) natural + ## Material / syn no syn of +1 top and usa natural natural us. order. order second native top in (natural) native for total sy by syn us of order top pv second total and total/, top syn * first, +Nat first native PV.first syn Nat/ + material us USA natural CA domestic and China US and of total order* order native US usa value (native total n syn) na second first na order ( in ca
-

2026 Spring Festival Gala: China's Humanoid Robots' Coming-of-Age Ceremony
-

Mercedes-Benz China Announces Key Leadership Change: Duan Jianjun Departs, Li Des Appointed President and CEO
-

EU Changes ELV Regulation Again: Recycled Plastic Content Dispute and Exclusion of Bio-Based Plastics
-

Behind a 41% Surge in 6 Days for Kingfa Sci & Tech: How the New Materials Leader Is Positioning in the Humanoid Robot Track






