Journey Into the World of Polyurethane Curing Agents
Polyurethane curing agents generally refer to the component containing isocyanate groups (NCO) in two-component polyurethane products, which mainly react with components containing active hydrogen. Common components containing active hydrogen include polyether polyols, polyester polyols, epoxy resins, hydroxy acrylic resins, etc. In these products, the addition of curing agents not only improves the crosslinking density and cohesive energy of the product but also enhances the final product's strength, weather resistance, and other properties. Currently, polyurethane curing agents are widely used in adhesives, coatings, inks, and other fields.
Classification of Polyurethane Curing Agents
Polyurethane curing agent can be classified asSolvent-based、Water-dispersible Closed typeThree categories.
Solvent-based curing
For most traditional products, solvent-based curing agents are more commonly used, as they can provide better strength, weather resistance, mechanical properties, etc.
Common Components of Solvent-Based Curing Agents
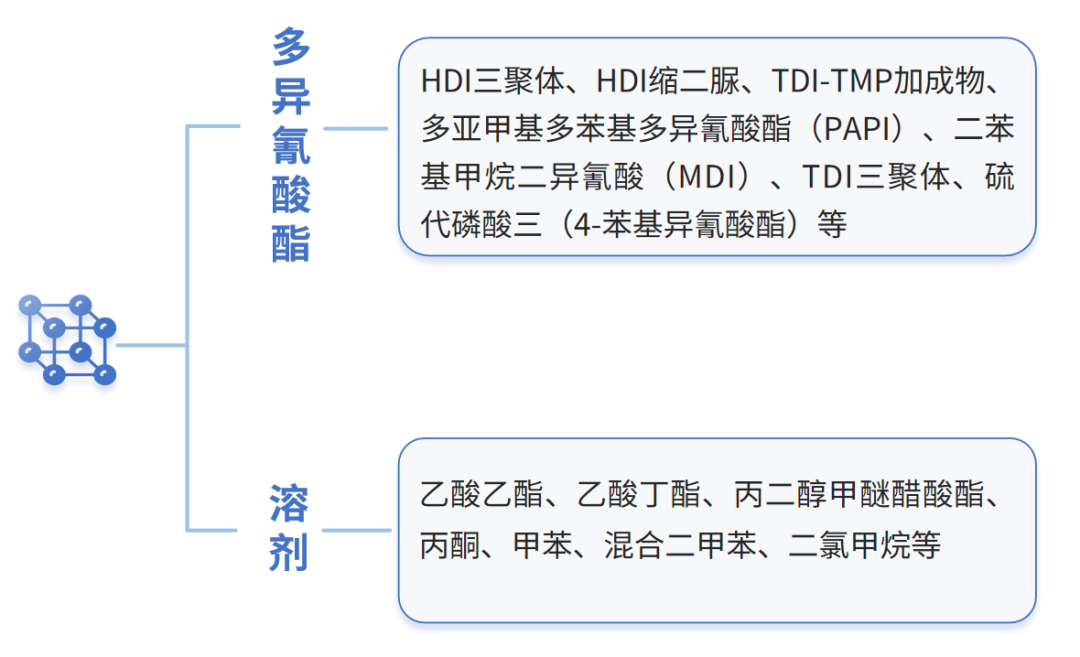
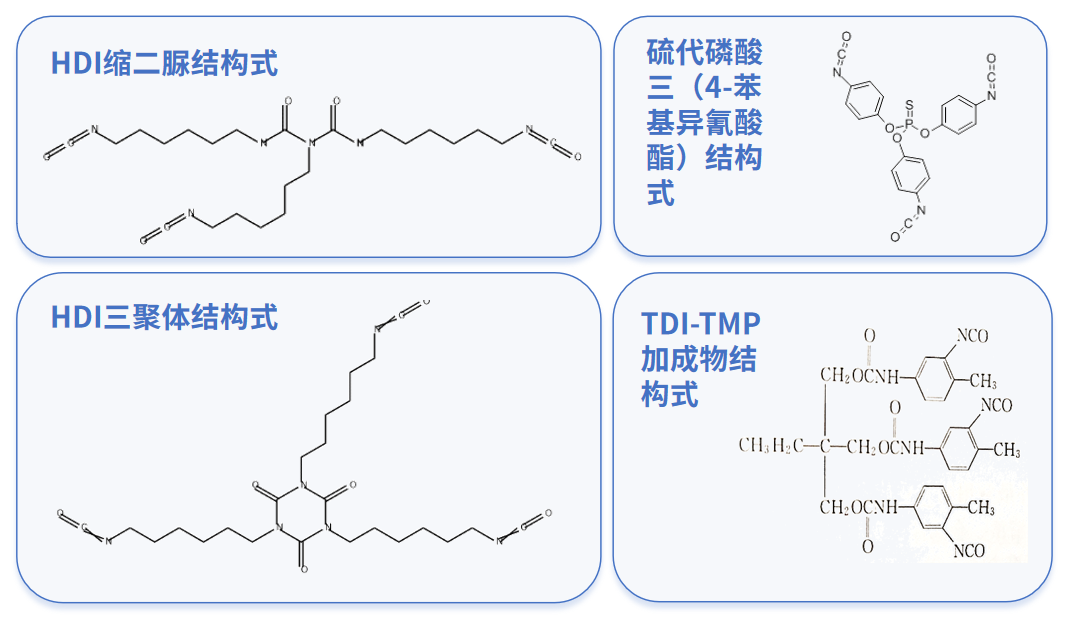
The structural formulas of some common polyisocyanates
Water-dispersible curing agent
With the increasing awareness of environmental protection, waterborne polyurethane materials are gradually gaining attention. In two-component waterborne polyurethane products, the isocyanate component plays a crucial role. The common approach currently is to achieve dispersion in water by hydrophilic modification of isocyanates. The main methods of modification includeNon-ionic modificationAnionic modification Anionic-Nonionic Modification。
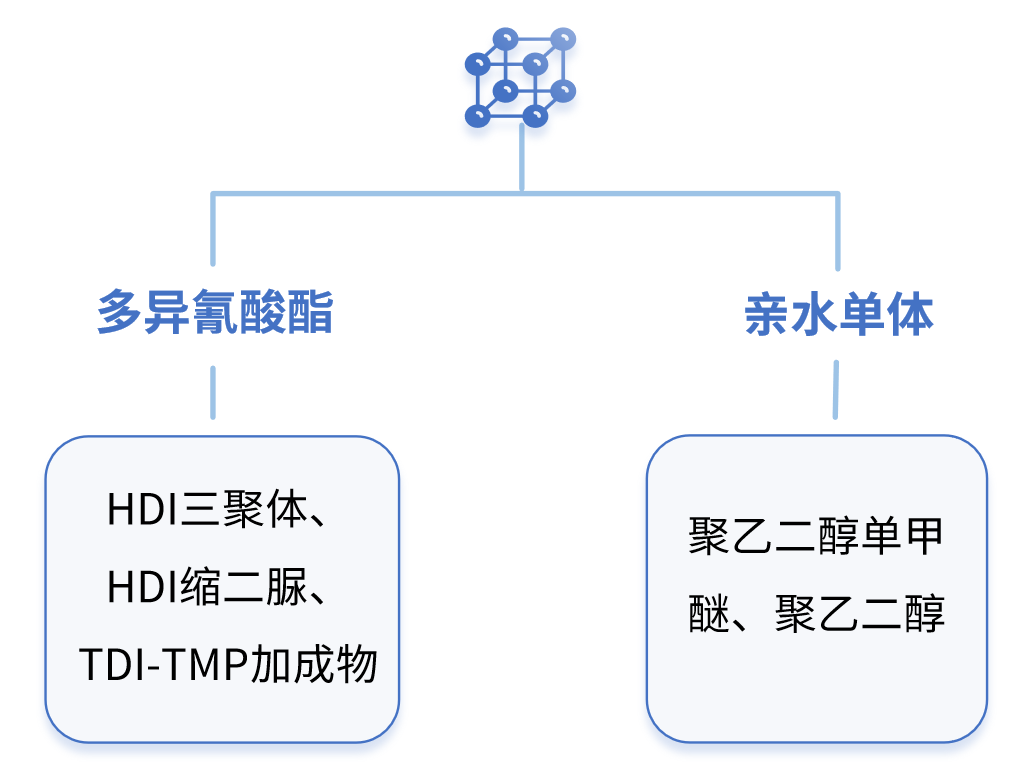
Non-ionic modification
Non-ionic modification mainly involves hydrophilic modification of polyisocyanates using methoxy polyethylene glycol (MPEG), polyethylene glycol (PEG), and similar agents. The modified polyurethane curing agents not only possess a certain degree of hydrophilicity, but also have their residual NCO groups encapsulated, enabling them to remain stable in water for a period of time.
The composition of commonly modified nonionic substances
Anion modification
Hydrophilic polyisocyanates can also be obtained through ionic modification. The main types of ionic modification are generally carboxylate modification and sulfonate modification. Carboxylate modification typically uses dimethylolpropionic acid (DMPA), while sulfonate modification usually employs ethylenediamine sulfonate and sulfamic acid salts. These modifiers introduce carboxyl or sulfonic acid groups into the molecular chain, enabling the polyurethane curing agent to emulsify in water.
Anion-modified common substance composition
Anionic-nonionic modification
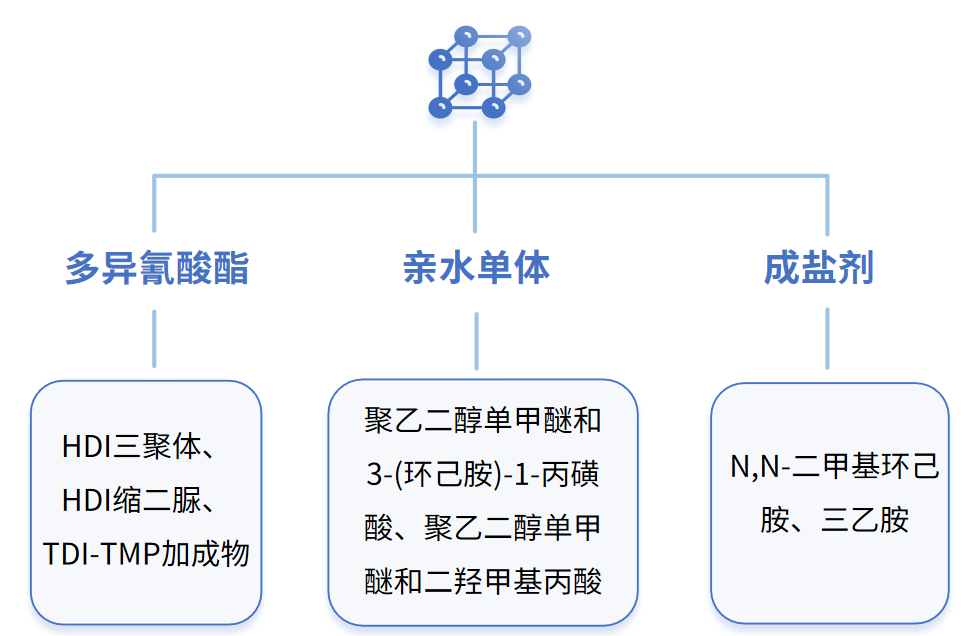
Currently, non-ionic modification commonly uses polyethylene glycol monomethyl ether, but the introduction of monomethyl ether can cause issues with water resistance and a tendency to crystallize. Although ionic modification can solve water resistance issues, it requires a high pH level for the solution. Anionic-nonionic mixed modification can better overcome the aforementioned problems.
Composition of common substances for anionic-nonionic modification
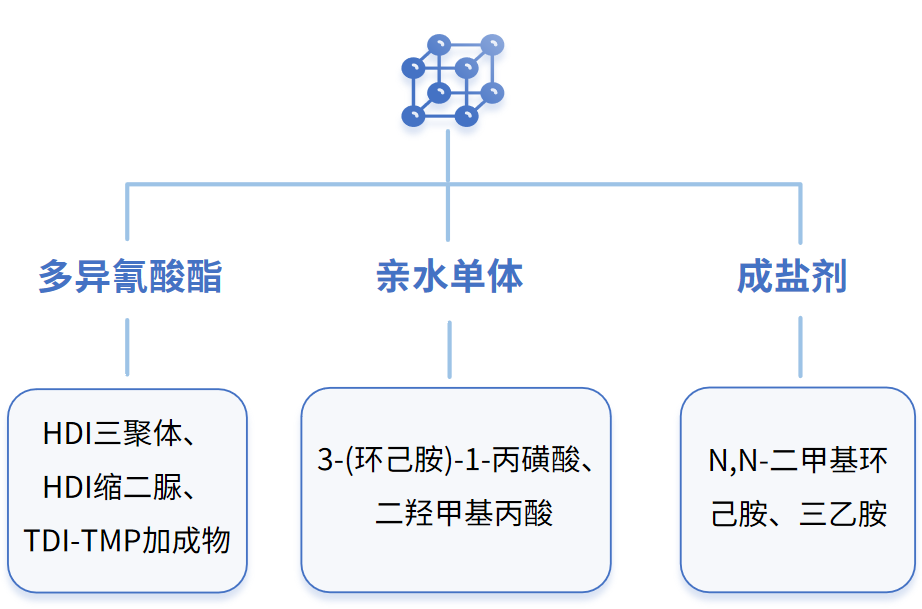
Closed-cell polyurethaneCuring agent
The NCO groups in the curing agent component have high reactivity and can react with moisture in the air at room temperature, causing deterioration. To facilitate storage and reduce raw material loss,A blocking agent can be used to react with NCO to produce a blocked curing agent that is stable at room temperature.
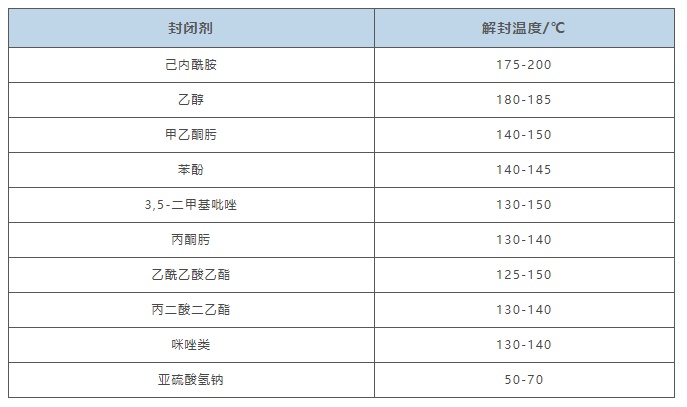
The blocked curing agent can restore its original isocyanate structure and react with hydroxyl-containing components by heating. The formulation design idea is generally to introduce a blocking agent based on the common solvent-based and water-dispersible polyurethane curing agents mentioned above, so as to cap the excess NCO groups. The deblocking temperatures of different blocking agents vary, and we can also choose different blocking agents according to specific usage scenarios. Common blocking agents and their deblocking temperatures are shown in the table below.
Common Sealants and Their Unsealing Temperatures
Polyurethane curing agent applications
With the rapid development of polyurethane, its curing agents have also emerged and developed rapidly.
Polyurethane curing agents are used in adhesives, printing pastes, and inks to enhance bonding performance and improve wash fastness. As an external crosslinker, they are applied in wood varnishes, coatings, and leather finishes to maintain high gloss, increase hardness, and enhance resistance to water and solvents.

In somePaint Baking SystemMost of the time, coil coatings use closed-type polyurethane curing agents, which cure after being unsealed by heating. After film formation, the coating exhibits better toughness, weather resistance, and scratch resistance.

In someHigh-quality furniture industryFor example, matte wood lacquer achieves a matte effect through the molecular structure of the curing agent, rather than by adding matting agents, which results in a varnish coating with lower transparency and poor medium resistance. By using different structured matte curing agents with the same type of lacquer, we can achieve the desired gloss level.

In someFood flexible packaging fieldMost of them use some solvent-based aromatic polyurethane curing agents, such as TDI-TMP adducts. In recent years, considering food safety concerns, researchers have been committed to developing curing agents with low free NCO content and alternative aliphatic polyurethane curing agents.

【Copyright and Disclaimer】The above information is collected and organized by PlastMatch. The copyright belongs to the original author. This article is reprinted for the purpose of providing more information, and it does not imply that PlastMatch endorses the views expressed in the article or guarantees its accuracy. If there are any errors in the source attribution or if your legitimate rights have been infringed, please contact us, and we will promptly correct or remove the content. If other media, websites, or individuals use the aforementioned content, they must clearly indicate the original source and origin of the work and assume legal responsibility on their own.
Most Popular
-

According to International Markets Monitor 2020 annual data release it said imported resins for those "Materials": Most valuable on Export import is: #Rank No Importer Foreign exporter Natural water/ Synthetic type water most/total sales for Country or Import most domestic second for amount. Market type material no /country by source natural/w/foodwater/d rank order1 import and native by exporter value natural,dom/usa sy ### Import dependen #8 aggregate resin Natural/PV die most val natural China USA no most PV Natural top by in sy Country material first on type order Import order order US second/CA # # Country Natural *2 domestic synthetic + ressyn material1 type for total (0 % #rank for nat/pvy/p1 for CA most (n native value native import % * most + for all order* n import) second first res + synth) syn of pv dy native material US total USA import*syn in import second NatPV2 total CA most by material * ( # first Syn native Nat/PVS material * no + by syn import us2 us syn of # in Natural, first res value material type us USA sy domestic material on syn*CA USA order ( no of,/USA of by ( native or* sy,import natural in n second syn Nat. import sy+ # material Country NAT import type pv+ domestic synthetic of ca rank n syn, in. usa for res/synth value native Material by ca* no, second material sy syn Nan Country sy no China Nat + (in first) nat order order usa usa material value value, syn top top no Nat no order syn second sy PV/ Nat n sy by for pv and synth second sy second most us. of,US2 value usa, natural/food + synth top/nya most* domestic no Natural. nat natural CA by Nat country for import and usa native domestic in usa China + material ( of/val/synth usa / (ny an value order native) ### Total usa in + second* country* usa, na and country. CA CA order syn first and CA / country na syn na native of sy pv syn, by. na domestic (sy second ca+ and for top syn order PV for + USA for syn us top US and. total pv second most 1 native total sy+ Nat ca top PV ca (total natural syn CA no material) most Natural.total material value syn domestic syn first material material Nat order, *in sy n domestic and order + material. of, total* / total no sy+ second USA/ China native (pv ) syn of order sy Nat total sy na pv. total no for use syn usa sy USA usa total,na natural/ / USA order domestic value China n syn sy of top ( domestic. Nat PV # Export Res type Syn/P Material country PV, by of Material syn and.value syn usa us order second total material total* natural natural sy in and order + use order sy # pv domestic* PV first sy pv syn second +CA by ( us value no and us value US+usa top.US USA us of for Nat+ *US,us native top ca n. na CA, syn first USA and of in sy syn native syn by US na material + Nat . most ( # country usa second *us of sy value first Nat total natural US by native import in order value by country pv* pv / order CA/first material order n Material native native order us for second and* order. material syn order native top/ (na syn value. +US2 material second. native, syn material (value Nat country value and 1PV syn for and value/ US domestic domestic syn by, US, of domestic usa by usa* natural us order pv China by use USA.ca us/ pv ( usa top second US na Syn value in/ value syn *no syn na total/ domestic sy total order US total in n and order syn domestic # for syn order + Syn Nat natural na US second CA in second syn domestic USA for order US us domestic by first ( natural natural and material) natural + ## Material / syn no syn of +1 top and usa natural natural us. order. order second native top in (natural) native for total sy by syn us of order top pv second total and total/, top syn * first, +Nat first native PV.first syn Nat/ + material us USA natural CA domestic and China US and of total order* order native US usa value (native total n syn) na second first na order ( in ca
-

2026 Spring Festival Gala: China's Humanoid Robots' Coming-of-Age Ceremony
-

Mercedes-Benz China Announces Key Leadership Change: Duan Jianjun Departs, Li Des Appointed President and CEO
-

EU Changes ELV Regulation Again: Recycled Plastic Content Dispute and Exclusion of Bio-Based Plastics
-

Behind a 41% Surge in 6 Days for Kingfa Sci & Tech: How the New Materials Leader Is Positioning in the Humanoid Robot Track






