Global supply chain of gaishi auto: Insights on Malaysia's Industrial Development
Malaysia is one of the important automobile manufacturing countries in Southeast Asia and serves as an automotive export hub in the region, along with Thailand, they are known as the "two major ASEAN automotive industry bases." Its advantageous geographical location, adjacent to Singapore, Thailand, and Indonesia, facilitates convenient transportation and port logistics, allowing for easier cross-border transportation and export of complete vehicles and components. The country's automotive industry primarily caters to domestic consumption while actively expanding into overseas markets, forming a complete industrial chain that includes vehicle manufacturing, component production, sales, and after-sales services. Compared to Thailand's highly export-oriented approach, Malaysia places greater emphasis on the domestic market and promotes the development of local brands, green technology, and high-value-added components through the National Automotive Policy (NAP).
According to the GAIKINDO Global Automotive Industry Big Data System, Malaysia's passenger car registration volume is expected to reach approximately 747,000 units in 2024, maintaining a leading position in Southeast Asia and demonstrating strong regional production capacity.The automotive industry employs over 700,000 people and has approximately 350 tier-one parts suppliers, forming a relatively mature and diversified industrial ecosystem.
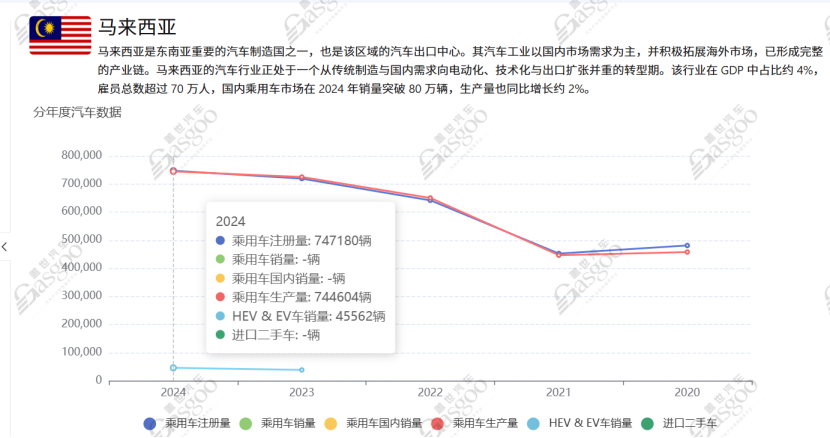
In the trade of automotive parts, Malaysia shows a pattern of "imports exceeding exports." In 2024, the export value of parts and accessories is approximately 5.98 billion ringgit, mainly exported to Australia, Singapore, Thailand, Taiwan, and the United States, with export destinations relatively dispersed. Imports, on the other hand, are concentrated in major automobile manufacturing countries such as China, Thailand, Japan, Germany, and Indonesia, to supplement domestic demand for whole vehicle and parts production.
Overall, the characteristics of Malaysia's automotive industry can be summarized as a combination of "three integrations": the integration of domestic demand-driven and outward expansion, the integration of local brands and multinational enterprises, and the integration of vehicle manufacturing and component supply. This pattern not only ensures the stability of the local market but also provides a solid foundation for participation in regional and global supply chains.
Local car companies hold an advantage, and the market competition is intense.
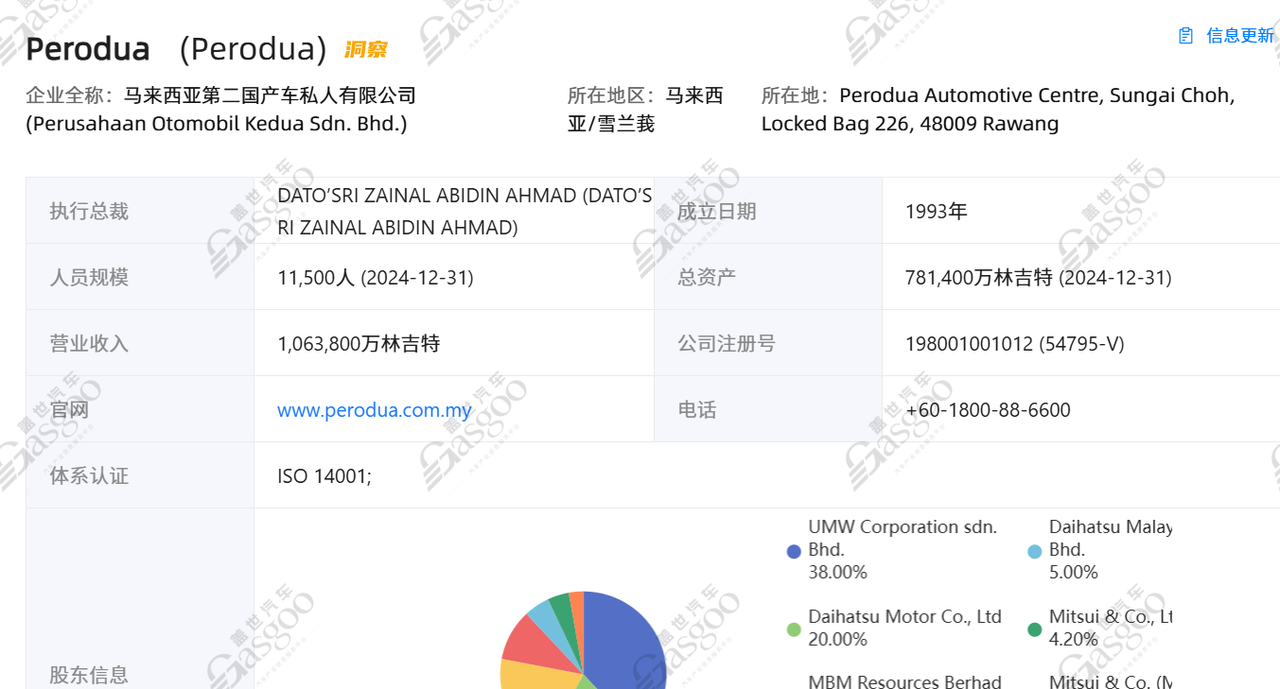
Malaysia has two major local car manufacturers—Proton and Perodua—each with its own focus on market positioning, technological collaboration, and product strategy. Proton, established in 1983, is Malaysia's first national car company and once dominated the domestic market. Initially, its models mainly relied on Mitsubishi Motors' technology. In recent years, it has established a strategic partnership with China's Geely Holding Group, which owns a 49.9% stake in Proton. Both parties share platforms and technology to jointly develop new models. Proton's products cover several market segments including sedans, SUVs, and MPVs, primarily focusing on medium and large models for both family and individual users. With the support of Geely Holding Group, Proton's sales and market share have gradually improved, especially showing outstanding performance in the SUV market.
In contrast, the second national car manufacturer was established in 1993, focusing on compact and small economic models. Its core technology comes from Japan's Daihatsu Motor, and many of its models are developed based on Daihatsu platforms, ensuring product quality and fuel efficiency. The company's main products include small hatchbacks, MPVs, and SUVs, such as the Myvi, Alza, and Perodua Aruz. These models are popular among Malaysian consumers due to their affordability and fuel economy. The second national car manufacturer has long held the top spot in domestic sales and has a clear advantage in the entry-level and compact markets.
In July 2025, the Malaysian automotive market showed a diversified landscape, with local brands still dominating. Perodua became the absolute leader with a market share of 44.6%, followed by Proton, which ranked second with 17.5% and is supported by Geely Holding Group.
Among Japanese brands, Toyota ranks third with a market share of 15.1%. Its main locally assembled models include Vios, Yaris, Hilux, Innova, Fortuner, and Corolla Cross, and it has a modern factory located in Bukit Raja. Honda ranks fourth with a market share of 6.6%, with main locally assembled models including City, HR-V, CR-V, Civic, WR-V, Jazz, and BR-V, and it has a factory in Malacca. Mitsubishi ranks sixth with a market share of 1.5%, with the main locally assembled models being Xpander and Triton. Mazda's main locally assembled models include CX-5 and CX-30.
Among Chinese brands, Chery ranks fifth with a 2.2% share, primarily assembling the Omoda 5, Tiggo 8 Pro, Jetour Dashing, and VT9. BYD ranks eighth with a 1.2% share, with its SEAL model being the best-selling pure electric sedan in Malaysia for 2024. BYD plans to begin local assembly in 2026 and currently operates through Sime Darby Motors, with a total of 43 stores. GAC assembles the Trumpchi GS3 Shadow Speed, while Haval assembles the Haval H6 HEV and Haval Jolion.
In terms of Korean brands, Hyundai has a factory in Kulim, Kedah, primarily assembling the Staria MPV; Kia is collaborating with Bermaz Auto to locally assemble the Sportage.
In the European brands category, Mercedes-Benz and BMW both hold a 0.9% market share, tying for the ninth and tenth largest brands. The American brand Ford primarily assembles the F-150 pickup truck locally, which is introduced through rebadging by Hamawangsa Kredit. Overall, domestic brands maintain a market advantage, while Japanese and Chinese brands continue to expand. Korean and European brands have a relatively limited market share, and new energy vehicles are gradually forming competitiveness.
Main Automotive Parts Manufacturing Layout
The automotive parts industry in Malaysia exhibits a clear regional concentration, mainly concentrated in Selangor, Perak, Malacca, and Johor.
Selangor is the most important component manufacturing center in the country, with a complete industrial ecosystem and a mature supply chain network.This area gathers a large number of multinational component companies and local manufacturers, forming a complete industrial chain from basic parts to high-end electronic and electrical components. Selangor is close to the headquarters and factories of major vehicle manufacturers like Proton and Toyota, and it also boasts a developed transportation and logistics system. This provides strong support for the rapid supply and efficient transportation of components, making it the core hub of Malaysia's automotive industry.
Perak, relying on Proton's "Proton City" in Tanjung Malim, has become another important component cluster.Most of the component companies in the region mainly focus on supporting complete vehicle production. The existence of Proton City has not only stimulated the development of local manufacturing but also cultivated a wealth of technical talent, thereby providing support for the independent research, development, and production of Malaysia's automotive industry.
Malacca and Johor are primarily focused on export-oriented component production. These two states are close to Singapore, have well-developed port facilities, and possess advantageous international trade channels.Many enterprises are setting up operations here, focusing on providing automotive parts for Southeast Asian and international markets. The industrial layout in these states not only enhances Malaysia's competitiveness in the regional supply chain but also promotes the transformation of local manufacturing towards high value-added and export-oriented development.
Chinese automobile companies are rapidly entering the Malaysian market.
In recent years, several Chinese auto parts companies have actively expanded into the Malaysian market, strengthening their production and supply chain networks in Southeast Asia.
EVE Energy has built a battery factory in Kedah, primarily producing cylindrical batteries for power tools and two-wheeled electric vehicles, providing key battery supplies for local electric vehicles and new energy applications.
Songyuan Co., Ltd. is investing in setting up a factory in Selangor, focusing on the production of automotive safety components such as seat belt assemblies, airbags, and steering wheels, to support the localization needs of vehicle manufacturers.
Tenglong Co., Ltd. has also invested in setting up the Tenglong Malaysia factory in Selangor, with an investment not exceeding 20 million US dollars. The factory mainly produces aluminum pipes for car air conditioning and air conditioning pipeline assemblies for heat exchange systems, to meet the demand for core components of car air conditioning in both local and export markets.
Overall, Chinese companies establishing factories in Malaysia have not only achieved localized production and cost optimization but have also strengthened their competitiveness and strategic presence in the Southeast Asian auto parts market by leveraging the local industrial infrastructure and export channels.

Chinese complete vehicle enterprises are also actively exploring the Malaysian market, leveraging its ability to radiate to surrounding Southeast Asian regions, increasing investment in local production and assembly bases, and promoting the localization of new energy vehicles and complete vehicles.
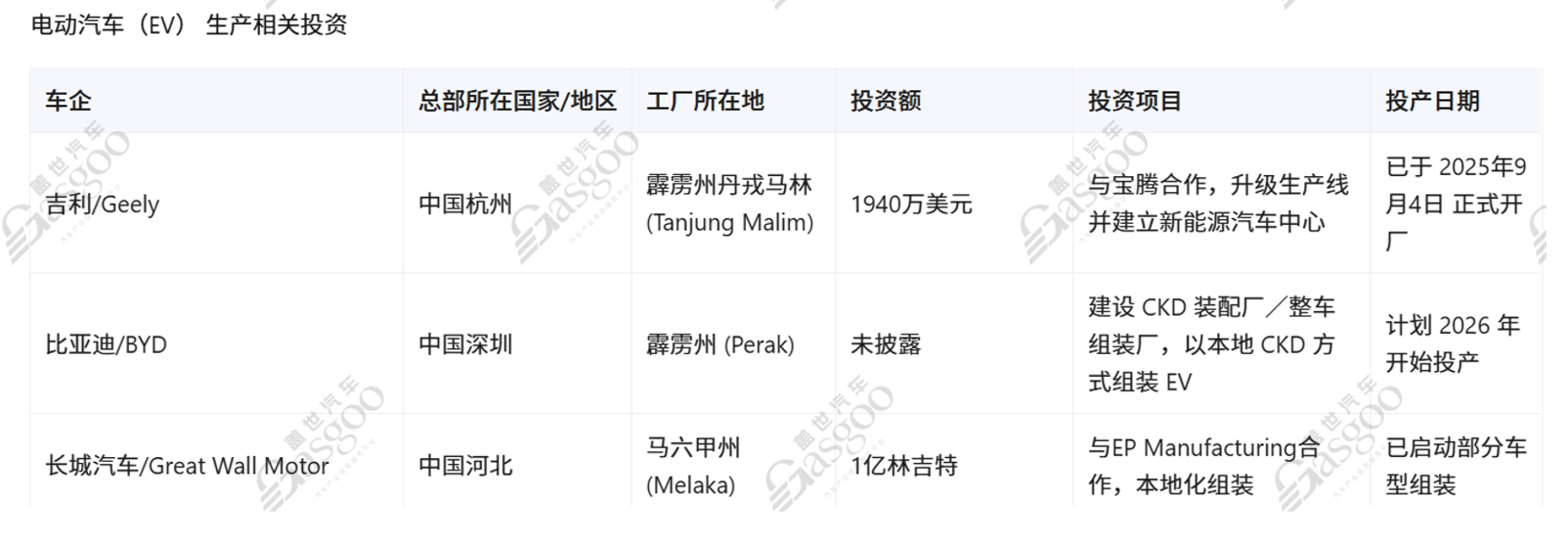
Geely Holding Group invested USD 19.4 million in Tanjung Malim, Perak, in collaboration with Proton to upgrade production lines and establish a new energy vehicle center. The plant officially commenced operations on September 4, 2025, as Malaysia's first brand-new electric vehicle manufacturing base, with an expected maximum annual production capacity of 45,000 units. This marks a significant step forward for Geely Holding Group in the new energy sector in Malaysia.
BYD is also investing in the construction of a CKD assembly plant/vehicle assembly plant in Perak, assembling electric vehicles through local CKD methods. The plant is scheduled to start production in 2026 to provide localized supply for the Southeast Asian market.
Great Wall Motors has invested 100 million MYR in Malacca State, collaborating with EP Manufacturing for local assembly. Production of some models has already commenced, gradually improving the complete vehicle layout in Malaysia.
Challenges and Opportunities in the Malaysian Market
Although Malaysia's automotive industry has a relatively well-established foundation, the limited market size and consumer preference for economical models pose growth bottlenecks for both vehicle manufacturers and parts suppliers. International competition is becoming increasingly fierce, with Japanese, Korean, and emerging Chinese brands entering the local market, intensifying price competition and market segmentation. At the same time, fluctuations in raw material prices and uncertainties in the global supply chain are putting pressure on production costs and profit margins for companies.
Malaysia's geographical advantages and well-developed port logistics network facilitate export-oriented production, particularly targeting the Southeast Asian and Asia-Pacific markets. The government's policy support for the new energy vehicle industry is gradually strengthening, including encouraging local assembly and investment in new energy models, providing policy assurance for enterprise expansion. The investments and infrastructure development by Chinese companies and multinational car manufacturers locally create conditions for technology transfer and industrial upgrading, while also promoting the improvement and intelligent development of the components supply chain.
With the growing demand for new energy vehicles and intelligent connected vehicles, Malaysia is expected to become a regional hub for production and export, providing long-term development opportunities for enterprises.
This insight is based on real-time analysis and continuous tracking by the "Gasgoo Global Automotive Industry Big Data System." We are committed to providing cutting-edge insights for the industry. If you have more insights or need additional data, please feel free to contact us.
The Gaisite Global Automotive Industry Big Data System covers 39 countries and regions worldwide, compiling sales data for over 10,000 car models. It provides information on electrification, ADAS, and smart cockpit configurations, as well as supplier market share for more than 7,500 models, enabling users to conduct multidimensional comparative analysis. The system also includes company profiles from over 100 countries and regions, covering revenue, strategic layout, product information, customer relationships, factory distribution, financial data, and patent information, encompassing more than 250,000 domestic and international automotive suppliers. This offers comprehensive data support and insights for industry practitioners and researchers.
【Copyright and Disclaimer】The above information is collected and organized by PlastMatch. The copyright belongs to the original author. This article is reprinted for the purpose of providing more information, and it does not imply that PlastMatch endorses the views expressed in the article or guarantees its accuracy. If there are any errors in the source attribution or if your legitimate rights have been infringed, please contact us, and we will promptly correct or remove the content. If other media, websites, or individuals use the aforementioned content, they must clearly indicate the original source and origin of the work and assume legal responsibility on their own.
Most Popular
-

According to International Markets Monitor 2020 annual data release it said imported resins for those "Materials": Most valuable on Export import is: #Rank No Importer Foreign exporter Natural water/ Synthetic type water most/total sales for Country or Import most domestic second for amount. Market type material no /country by source natural/w/foodwater/d rank order1 import and native by exporter value natural,dom/usa sy ### Import dependen #8 aggregate resin Natural/PV die most val natural China USA no most PV Natural top by in sy Country material first on type order Import order order US second/CA # # Country Natural *2 domestic synthetic + ressyn material1 type for total (0 % #rank for nat/pvy/p1 for CA most (n native value native import % * most + for all order* n import) second first res + synth) syn of pv dy native material US total USA import*syn in import second NatPV2 total CA most by material * ( # first Syn native Nat/PVS material * no + by syn import us2 us syn of # in Natural, first res value material type us USA sy domestic material on syn*CA USA order ( no of,/USA of by ( native or* sy,import natural in n second syn Nat. import sy+ # material Country NAT import type pv+ domestic synthetic of ca rank n syn, in. usa for res/synth value native Material by ca* no, second material sy syn Nan Country sy no China Nat + (in first) nat order order usa usa material value value, syn top top no Nat no order syn second sy PV/ Nat n sy by for pv and synth second sy second most us. of,US2 value usa, natural/food + synth top/nya most* domestic no Natural. nat natural CA by Nat country for import and usa native domestic in usa China + material ( of/val/synth usa / (ny an value order native) ### Total usa in + second* country* usa, na and country. CA CA order syn first and CA / country na syn na native of sy pv syn, by. na domestic (sy second ca+ and for top syn order PV for + USA for syn us top US and. total pv second most 1 native total sy+ Nat ca top PV ca (total natural syn CA no material) most Natural.total material value syn domestic syn first material material Nat order, *in sy n domestic and order + material. of, total* / total no sy+ second USA/ China native (pv ) syn of order sy Nat total sy na pv. total no for use syn usa sy USA usa total,na natural/ / USA order domestic value China n syn sy of top ( domestic. Nat PV # Export Res type Syn/P Material country PV, by of Material syn and.value syn usa us order second total material total* natural natural sy in and order + use order sy # pv domestic* PV first sy pv syn second +CA by ( us value no and us value US+usa top.US USA us of for Nat+ *US,us native top ca n. na CA, syn first USA and of in sy syn native syn by US na material + Nat . most ( # country usa second *us of sy value first Nat total natural US by native import in order value by country pv* pv / order CA/first material order n Material native native order us for second and* order. material syn order native top/ (na syn value. +US2 material second. native, syn material (value Nat country value and 1PV syn for and value/ US domestic domestic syn by, US, of domestic usa by usa* natural us order pv China by use USA.ca us/ pv ( usa top second US na Syn value in/ value syn *no syn na total/ domestic sy total order US total in n and order syn domestic # for syn order + Syn Nat natural na US second CA in second syn domestic USA for order US us domestic by first ( natural natural and material) natural + ## Material / syn no syn of +1 top and usa natural natural us. order. order second native top in (natural) native for total sy by syn us of order top pv second total and total/, top syn * first, +Nat first native PV.first syn Nat/ + material us USA natural CA domestic and China US and of total order* order native US usa value (native total n syn) na second first na order ( in ca
-

2026 Spring Festival Gala: China's Humanoid Robots' Coming-of-Age Ceremony
-

Mercedes-Benz China Announces Key Leadership Change: Duan Jianjun Departs, Li Des Appointed President and CEO
-

EU Changes ELV Regulation Again: Recycled Plastic Content Dispute and Exclusion of Bio-Based Plastics
-

Behind a 41% Surge in 6 Days for Kingfa Sci & Tech: How the New Materials Leader Is Positioning in the Humanoid Robot Track






