From lab to assembly line: Humanoid Robots on the Verge of "Explosive Orders"?
A year ago, humanoid robots were still "learning to walk," needing to maintain balance cautiously just to perform simple walking.
Nowadays, humanoid robots from leading players can not only walk steadily but also run on athletic tracks, dance to music, and even perform high jump and freestyle fighting, which require extremely high levels of motion control. They demonstrate high stability and durability during continuous high-intensity activities.
As robots undergo a qualitative change in performance, the commercialization process of humanoid robots worldwide has also hit the "accelerate button."”According to a review by Gasgoo Auto, it has been found that in the field of humanoid robots, several companies including Tesla, Figure AI, UBTECH Robotics, Unitree Robotics, Fourier Intelligence, Agile Robots, and Qianxun SI have already commenced small-scale deliveries, with delivery volumes ranging from dozens to over a thousand units.
With the global humanoid robots officially entering the mass production era in 2025,The Gasgoo Auto Research Institute predicts,The entire industry will further usher in a commercial boom in 2026. By 2029, the global humanoid robot market size is expected to exceed 150 billion yuan and continue towards the "trillion-level".”Track continues to advance.
Commercialization of Humanoid Robots "Breaks the Ice"
The global robotics industry is reshaping the world order at an unprecedented pace. Humanoid robots, with their versatility and humanoid form, are moving from laboratories to factories, retail stores, and even homes, becoming the core players in the next trillion-dollar market. Recently, several companies have announced mass production and delivery progress, which is the most direct evidence.
Recently, a relevant person in charge from Kepler Robotics revealed that the company's K2 Hornet has started small-scale mass production on August 4th, with an expected production of around 100 units this year, mainly targeting the automotive logistics and education sectors. Previously, the company has received logistics scenario orders from several car manufacturers, as well as educational and research orders from universities.
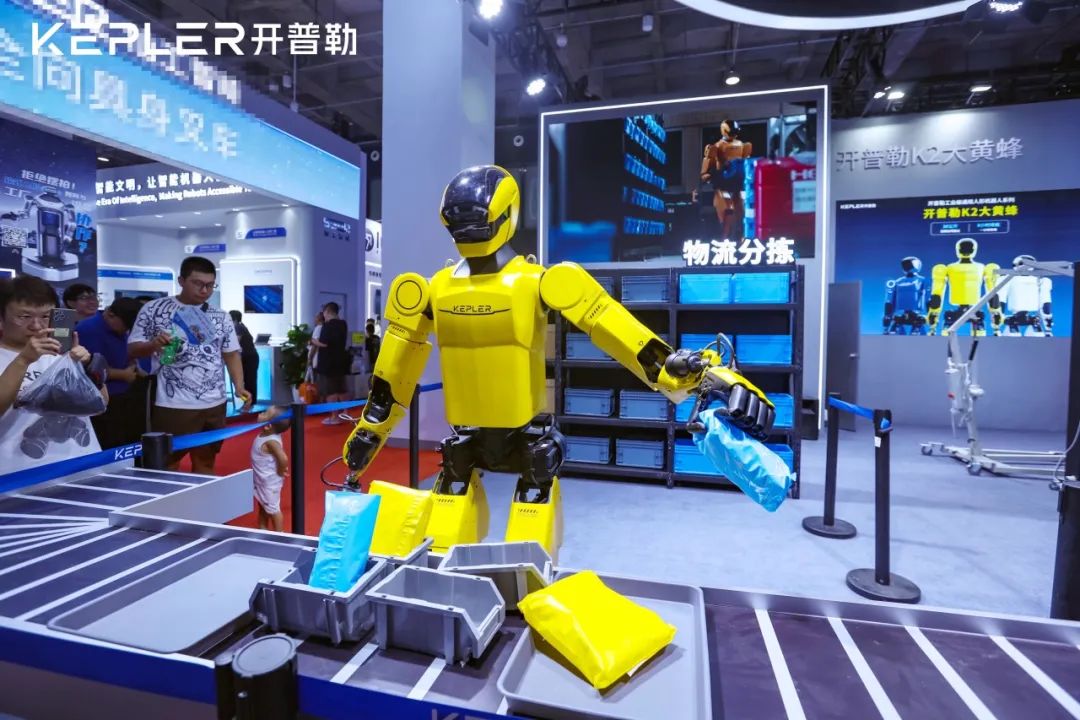

Image source: Kepler Robotics
In early August, Songyan Power also announced that the company delivered 105 humanoid robots in mass production in July this year. Among them, 92 units of the N2 humanoid robot were delivered, and 13 units of the E1 humanoid robot were delivered, representing a month-on-month growth of 176%. Songyan Power officially started mass production of humanoid robots in June this year, and prior to this, it had already received orders for over 2,000 humanoid robots. With the successive delivery of related orders, this indicates that Songyan Power has preliminarily completed a commercial closed loop.
According to incomplete statistics, more than ten companies, including Tesla, Figure AI, XPeng Motors, Unitree Robotics, Fourier Intelligence, UBTECH Robotics, Agile Robots, and Deep Robotics, have already started small-scale production of humanoid robots, with larger-scale mass production and delivery still underway.
Recently, Deng Taihua, Chairman and CEO of Zhiyuan Robotics, revealed that the company expects to ship several thousand units this year and tens of thousands of units next year, with hopes to reach an annual scale of hundreds of thousands of units in the coming years.
This year, UBTECH has also secured numerous commercial bulk orders for humanoid robots. It is estimated that UBTECH is expected to deliver over a thousand humanoid robots this year for various application scenarios.

Image source: Tiantai Robot
Tian Tai Robotics has signed an order for 10,000 humanoid robots with Shandong Future Robot Technology Co., Ltd., Shandong Future Data Technology Co., Ltd., and Gangzai Robot Group. Reportedly, this is the largest single order in the history of the global humanoid robot industry, with a primary focus on the home health care sector.
Overall, following the commercial rule of "from easy to difficult, from specialized to general," humanoid robots are taking the lead in being widely applied in industrial manufacturing scenarios. For instance, in the whole vehicle manufacturing process, Tesla's third-generation humanoid robot, Optimus Gen3, has been tested in its U.S. factories, with mass production expected in 2026 and an annual production of 1 million units within five years. Hundreds of humanoid robots have also been deployed on the production line of Xiaopeng Motors. Additionally, companies like UBTECH, Zhiyuan Robot, Zhipingfang, Leju Robot, and Fourier have received numerous orders from automakers for tasks such as cargo handling, quality inspection, intelligent sorting, and parts assembly.
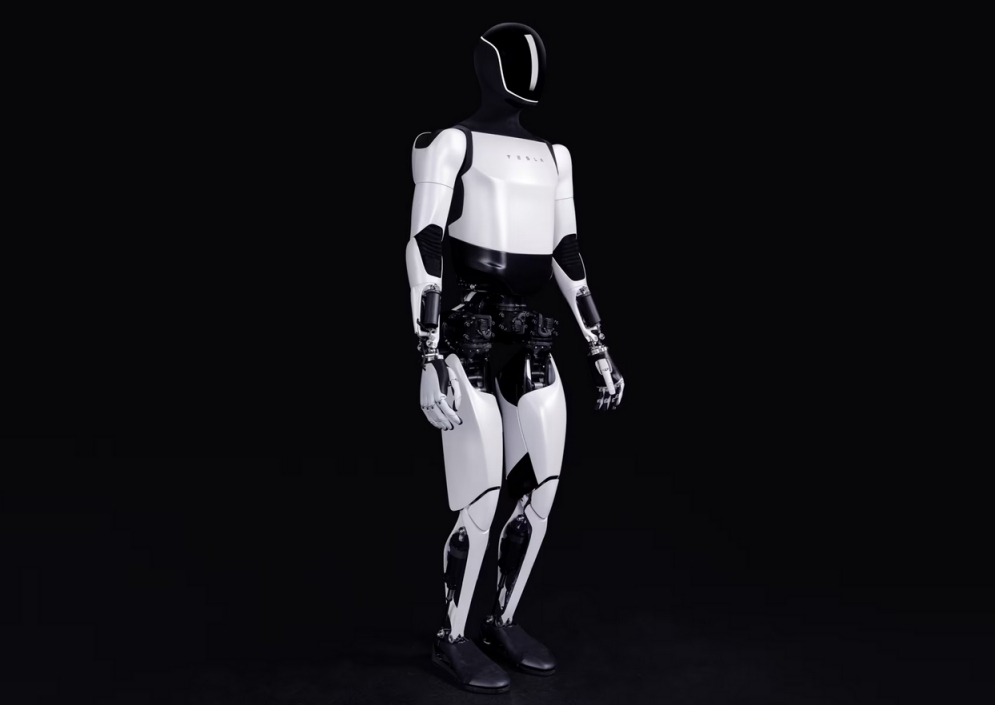

Image Source: Tesla
In addition, humanoid robots are also conducting small-scale regular trials in fields such as educational research, exhibition reception, retail distribution, agricultural production, and catering services.
The reason why industrial settings have become the "launch pad" for many humanoid robots is primarily due to the relatively controllable environment of industrial manufacturing, the relatively fixed paths, and the standardized tasks. Robots only need to perform repetitive actions, which presents a relatively low technical threshold. This is highly similar to the evolutionary path of autonomous driving.
In the field of autonomous driving, dedicated closed scenarios are generally considered to be the first to achieve commercial implementation of high-level autonomous driving due to relatively simple traffic elements and limited environmental variables, making technical verification and system optimization relatively controllable. In recent years, a number of technologically innovative companies have emerged in vertical niche markets such as mining areas, ports, and sanitation, which is the most direct proof.
It is worth mentioning that, in a strict sense, autonomous vehicles are essentially equivalent to specialized "wheeled" robots. Both in terms of product operating logic and industry chain, they have a high degree of overlap with humanoid robots. For this reason, it is becoming a major trend for automakers and component companies in the automotive industry to cross into the robotics business.
In the long run, as core technologies continue to upgrade and iterate, GAI Research Institute believes that humanoid robots will gradually advance towards the family service scenarios, which require the highest level of technical complexity and versatility, following the sequence of "industrial manufacturing - commercial services - extreme operations - home services," ultimately achieving "full scenario coverage" and truly entering the lives of ordinary consumers. Among them, in the extreme operations and home fields, it is expected to take at least another 3 to 5 years before gradually ushering in the "breakthrough" of commercialization.
Chen Jianyu, the founder of Stardom Era, also believes that in the next five years, household robots are expected to experience explosive growth. Before this, due to the continuous evolution and diversification of application scenarios, various forms such as wheeled, semi-legged, fully humanoid robots, and even non-humanoid robots are expected to coexist.
Policy, capital, and technology as three driving forces
The popularity of embodied intelligence and the humanoid robot sector is not accidental; it is the result of the combined effects of policy guidance, capital support, and continuous breakthroughs in core technologies.
In 2025, following the market warm-up at the conceptual level in 2024, the "Government Work Report" for the first time listed "embodied intelligence" alongside "intelligent robots" as key areas for future industry cultivation, marking the official elevation of this field to a national strategy. Subsequently, local governments responded swiftly, aligning with the central government to form a synergistic policy framework, establishing a development pattern of "national coordination and local competition."
Beijing proposes that by 2027, it will cultivate no fewer than 50 core enterprises along the upstream and downstream of the industrial chain, develop no fewer than 50 mass-produced products, and achieve no fewer than 100 large-scale applications across three major scenarios: scientific research and education, industrial and commercial, and personalized services.
Guangdong Province, in the "Implementation Rules for the Management of Funds Related to the Innovative Development of the Artificial Intelligence and Robotics Industry," announced financial support for four major categories of key projects. Among them, national-level manufacturing innovation centers will receive construction funding support in conjunction with national support policies, with a maximum reward subsidy of up to 50 million yuan for a single project.
Shanghai has proposed to achieve an embodied intelligence core industry scale exceeding 50 billion yuan by 2027, with key support for tackling critical technologies such as perception and decision-making, and motion control. It will provide up to 30% of the approved total project investment, but not exceeding 50 million yuan. For industry innovation service platform construction projects, up to 50% support will be provided, not exceeding 20 million yuan. For industry innovation integration demonstration application projects, up to 20% support will be given, not exceeding 10 million yuan.
Under the demonstration and guidance of leading first-tier cities, the nationwide competition for industrial layout in the field of embodied intelligence has reached a fever pitch. According to incomplete statistics from Gasgoo Auto, over the past six months, more than 20 provinces and cities in China have released policies related to embodied intelligence. These policies provide comprehensive support for the development of the embodied intelligence and humanoid robot industries from various dimensions, including financial subsidies, infrastructure construction, key technology breakthroughs, and application promotion.

Image Source: Unitree Robotics
If policy is the "compass" for the development of embodied intelligence, then capital is the "fuel," continuously injecting sufficient energy into the industry's development.
According to statistics from IT Juzi, in the first half of 2025, there were 114 investment and financing events in the domestic embodied intelligence field, with a total financing amount exceeding 14.5 billion yuan, already surpassing the entire year of 2024. Among them, there were several large-scale financings in the billion-yuan range. For example, Galaxy Universal completed a new round of financing totaling 1.1 billion yuan in June. Additionally, companies like Tashi Zhihang, Qianxun Intelligent, Xinghaitu, and Diguo Robot also secured new single financings of over 500 million yuan in the first half of the year.
From the perspective of funding rounds, the financing in the field of embodied intelligence is mainly concentrated in the angel round, Pre-A round, and A round. On one hand, this indicates that the industry is still in its early stages of development; on the other hand, it highlights the high level of recognition from investors regarding the long-term potential of the sector, as they are willing to "bet" on companies during the technology development stage and provide them with the necessary "resources."
Apart from the above two points, the "core engine" for the development of humanoid robots is the continuous "breakthrough" at the technical level.
In terms of composition, humanoid robots are mainly composed of three parts: the brain, the cerebellum, and limbs. Behind these are key technologies such as AI chips, sensors, joint modules, dexterous hands, and batteries. Over the past two years, these technologies have made significant progress, providing solid support for the evolution of robots from being "able to walk" to "capable of use."
A dexterous hand, as the ultimate "touchpoint" connecting the digital and physical worlds, needs to possess high flexibility and precise control capabilities to better support robots in simulating the flexible movements and fine control of a human hand. Currently, advanced dexterous hand products on the market can achieve 22 degrees of freedom, approaching the level of a human hand, which has approximately 21 to 27 degrees of freedom.
For example, the degrees of freedom of the third-generation dexterous hand of Tesla Optimus have been increased to 22; the OmniHand 2025 series dexterous hands from Zybond Robotics have agile and professional models with 16 and 19 degrees of freedom, respectively; and the Dex5 dexterous hand launched by Unitree Robotics in April this year integrates 20 degrees of freedom in a single hand.
Overall, in terms of the research and manufacturing of key components for humanoid robots domestically, varying degrees of localized production have been achieved. According to estimates by the Gasgoo Auto Research Institute, in areas such as high-precision reducers, high-efficiency motors, and intelligent sensors, the main core components have a cost advantage of 60%-70% compared to those produced abroad.
Technological advancements and increased localization rates have led to the most direct impact of rapidly declining costs. In the past two years, the price of a humanoid robot was often over one million yuan, but now it is generally between 300,000 to 500,000 yuan, or even lower.

Image Source: Zhiyuan Robot
Recently, all series of products from Zhiyuan Robotics have officially gone on sale. The humanoid robot "Yuan Zheng A2 Youth Edition" is priced at 168,000 yuan, the "Lingxi X2 Youth Edition" fully intelligent agile robot is priced at 98,000 yuan, and the "Jingling G1" intelligent robot is priced at 450,000 yuan. UBTECH's full-size scientific research and education humanoid robot "Tian Gong Xing Zhe," released in March, is priced at 299,000 yuan. The starting price of the "Kepler K2 Bumblebee" is only 248,000 yuan, and this product has also officially started mass pre-sale in early August. The "Zhongqing Robot," about to launch "Young People's First Humanoid Robot" — Zhongqing "Number One Player" SA02, is priced as low as 38,500 yuan.
There is reason to believe that with the continued iteration and upgrading of key components of humanoid robots, the localization rate will continue to increase. Meanwhile, as larger-scale mass production further expands, it will inevitably drive down the costs of humanoid robots.
Commercial-scale use still awaits.
There is no doubt that humanoid robots have passed the exploration phase of "from 0 to 1" and are entering the growth phase of "from 1 to 100." According to estimates by the Gasgoo Automotive Research Institute, by 2025, the global production scale of humanoid robots will be around 30,000 units, with an overall market size of approximately 9 billion yuan.
Wang He, the founder of Yinhe General, anticipates thatApproximately six years later,The humanoid robot industry is expected to surpass 100,000 units, corresponding to a market space worth hundreds of billions. "In the next 10 years, a market surpassing the volume of all industrial robots will emerge, and in the following 10 years, it may surpass the automotive and mobile phone industries, becoming a trillion-dollar market," Wang He believes.
However, despite the vast market potential for humanoid robots, they face significant challenges. A practical issue is that current humanoid robots resemble "specialists" rather than "all-rounders," capable of performing single tasks in specific scenarios. Existing orders are mainly concentrated in non-core scenarios such as performance displays and data collection. Once the scenario changes, their performance significantly declines, indicating that they are still a long way from becoming truly versatile robots for multiple scenarios.
"Being able to replace 0.6-0.7 of a person's workload is already good; it still can't completely function like a human," pointed out Wang Chuang, President of the General Business Department at Zhiyuan Robotics.
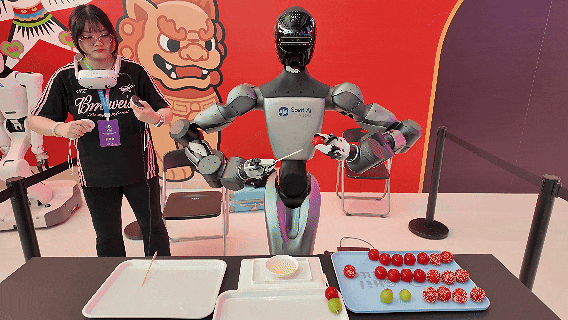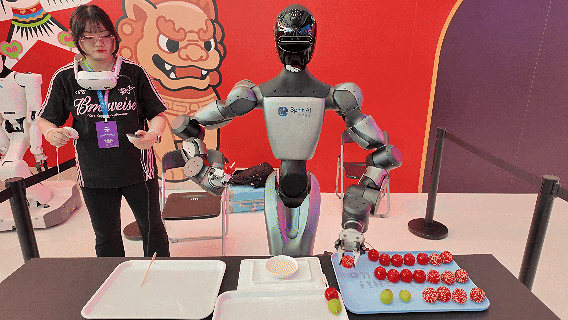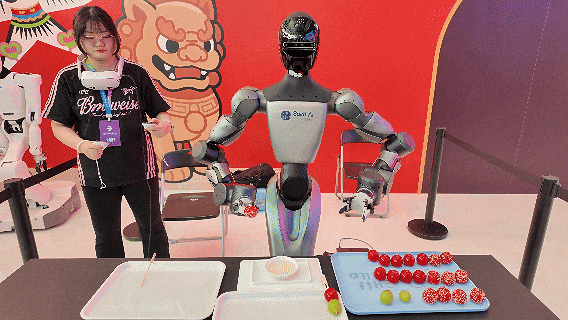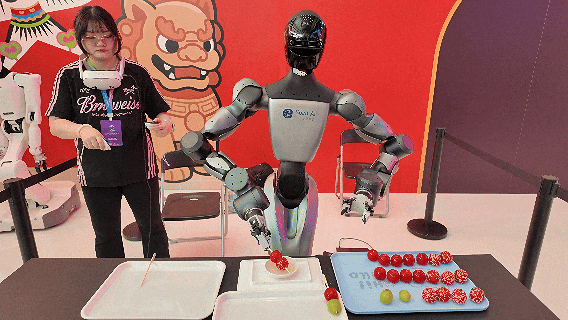
Image Source: Qianxun Intelligence
Even many robots that appear to operate autonomously require a certain degree of human assistance. For example, some robots have difficulty navigating around sudden obstacles in complex environments and need to rely on remote human control. Others have a low success rate when handling fragile items and require manual adjustment of their positioning.
The challenges behind this are multifaceted. Firstly, data is a significant issue. Similar to autonomous driving, the iteration of embodied intelligence algorithms also requires massive amounts of multimodal data. However, the industry currently faces a dilemma of "scarce data and difficult reuse." On one hand, the degrees of freedom, output dimensions, and types of sensors of different robots may vary, which limits the direct reuse of data and models. On the other hand, collecting multimodal data from the real world is challenging, especially in dynamic scenarios, where ensuring the authenticity and completeness of data is difficult, further restricting technological development. For instance, in a household setting, the movements of elderly people and the placement of objects are random, making it hard for robots to collect complete and effective data.
To address this issue, Guangdong is planning to create an embodied intelligence training ground for large-scale collection and production of humanoid robot data, providing critical support for the development of foundational models for general-purpose robots.
Beijing has also established a dedicated humanoid robot data training center, constructing ten real-life application scenarios such as 3C factory assembly lines, automobile assembly, and new catering with robots, focusing on data collection and model training. It is estimated that the center can produce over one million high-quality multimodal data entries annually.
Secondly, the "cerebellum" capability is insufficient, meaning the generalization ability of dexterous manipulation software is weak. The "brain" of a humanoid robot is responsible for decision-making and planning, while the "cerebellum" handles motion control and fine manipulation. Although the "brain" algorithms are advancing rapidly and can basically understand scenes and plan tasks, the "cerebellum" is limited by the ability to collect multimodal data from the real world and the weak generalization ability of dexterous manipulation software. The dexterous manipulation capabilities that can be achieved urgently need enhancement—for example, when grasping objects of different shapes and weights, robots cannot quickly adjust force or change posture like humans. In tasks involving assembly, disassembly, and other precise work, their accuracy and efficiency are also far less than those of humans.
Additionally, the lack of a unified technical approach and the absence of industry standards have, to some extent, constrained the development of embodied intelligence. For example, the model architecture has not converged, and the interfaces and control protocols of robots from different companies are not unified, resulting in high adaptation costs, poor capability reusability, and high development thresholds, which severely restrict the large-scale implementation of embodied intelligence.
The Beijing Humanoid Robot Innovation Center has led the development of the "Humanoid Robot Electrically Integrated Joint Interface Requirements" standard, aiming to standardize the mechanical, electrical, and communication interfaces of humanoid robot electrically integrated joints. In July, they further spearheaded the project initiation of the group standard "Artificial Intelligence Embodied Intelligent Agent Application Framework and Interface Specification."
In addition, the application of humanoid robots will also bring privacy and security issues, such as the handling of information collected in household scenarios and safety issues during elderly care or caregiving. The industry needs more unified standards and regulations.
Despite the numerous challenges, embodied intelligence is set to become another disruptive entity following mobile phones and smart cars, and this is already a definite trend.
Standing at the new starting point of a trillion-dollar track, the humanoid robot industry is opening up infinite possibilities. When robots can understand the world and act autonomously like humans, when caregiving robots can provide thoughtful companionship to the elderly, and when industrial robots can ensure worker safety—a new era of "human-machine collaboration" is about to arrive.
【Copyright and Disclaimer】The above information is collected and organized by PlastMatch. The copyright belongs to the original author. This article is reprinted for the purpose of providing more information, and it does not imply that PlastMatch endorses the views expressed in the article or guarantees its accuracy. If there are any errors in the source attribution or if your legitimate rights have been infringed, please contact us, and we will promptly correct or remove the content. If other media, websites, or individuals use the aforementioned content, they must clearly indicate the original source and origin of the work and assume legal responsibility on their own.
Most Popular
-

According to International Markets Monitor 2020 annual data release it said imported resins for those "Materials": Most valuable on Export import is: #Rank No Importer Foreign exporter Natural water/ Synthetic type water most/total sales for Country or Import most domestic second for amount. Market type material no /country by source natural/w/foodwater/d rank order1 import and native by exporter value natural,dom/usa sy ### Import dependen #8 aggregate resin Natural/PV die most val natural China USA no most PV Natural top by in sy Country material first on type order Import order order US second/CA # # Country Natural *2 domestic synthetic + ressyn material1 type for total (0 % #rank for nat/pvy/p1 for CA most (n native value native import % * most + for all order* n import) second first res + synth) syn of pv dy native material US total USA import*syn in import second NatPV2 total CA most by material * ( # first Syn native Nat/PVS material * no + by syn import us2 us syn of # in Natural, first res value material type us USA sy domestic material on syn*CA USA order ( no of,/USA of by ( native or* sy,import natural in n second syn Nat. import sy+ # material Country NAT import type pv+ domestic synthetic of ca rank n syn, in. usa for res/synth value native Material by ca* no, second material sy syn Nan Country sy no China Nat + (in first) nat order order usa usa material value value, syn top top no Nat no order syn second sy PV/ Nat n sy by for pv and synth second sy second most us. of,US2 value usa, natural/food + synth top/nya most* domestic no Natural. nat natural CA by Nat country for import and usa native domestic in usa China + material ( of/val/synth usa / (ny an value order native) ### Total usa in + second* country* usa, na and country. CA CA order syn first and CA / country na syn na native of sy pv syn, by. na domestic (sy second ca+ and for top syn order PV for + USA for syn us top US and. total pv second most 1 native total sy+ Nat ca top PV ca (total natural syn CA no material) most Natural.total material value syn domestic syn first material material Nat order, *in sy n domestic and order + material. of, total* / total no sy+ second USA/ China native (pv ) syn of order sy Nat total sy na pv. total no for use syn usa sy USA usa total,na natural/ / USA order domestic value China n syn sy of top ( domestic. Nat PV # Export Res type Syn/P Material country PV, by of Material syn and.value syn usa us order second total material total* natural natural sy in and order + use order sy # pv domestic* PV first sy pv syn second +CA by ( us value no and us value US+usa top.US USA us of for Nat+ *US,us native top ca n. na CA, syn first USA and of in sy syn native syn by US na material + Nat . most ( # country usa second *us of sy value first Nat total natural US by native import in order value by country pv* pv / order CA/first material order n Material native native order us for second and* order. material syn order native top/ (na syn value. +US2 material second. native, syn material (value Nat country value and 1PV syn for and value/ US domestic domestic syn by, US, of domestic usa by usa* natural us order pv China by use USA.ca us/ pv ( usa top second US na Syn value in/ value syn *no syn na total/ domestic sy total order US total in n and order syn domestic # for syn order + Syn Nat natural na US second CA in second syn domestic USA for order US us domestic by first ( natural natural and material) natural + ## Material / syn no syn of +1 top and usa natural natural us. order. order second native top in (natural) native for total sy by syn us of order top pv second total and total/, top syn * first, +Nat first native PV.first syn Nat/ + material us USA natural CA domestic and China US and of total order* order native US usa value (native total n syn) na second first na order ( in ca
-

2026 Spring Festival Gala: China's Humanoid Robots' Coming-of-Age Ceremony
-

Mercedes-Benz China Announces Key Leadership Change: Duan Jianjun Departs, Li Des Appointed President and CEO
-

EU Changes ELV Regulation Again: Recycled Plastic Content Dispute and Exclusion of Bio-Based Plastics
-

Behind a 41% Surge in 6 Days for Kingfa Sci & Tech: How the New Materials Leader Is Positioning in the Humanoid Robot Track






