Biobased Nylon 56 Breaks Through New Energy: Cathay Biotech Teams Up with CATL to Open New Chapter in Industrialization
In August 2025, the Ningde Times-Kaishai (Hefei) bio-based battery shell manufacturing base project, constructed by Anhui Kaixai Times, officially commenced. This project is a joint investment by Kaishai Biological (bio-based PA56 technology provider), Ningde Times (battery end-user), and Kalai Composites (composite material technology provider), with a total investment of 500 million yuan. It plans an annual production capacity of 2.5 million battery shells, with a thickness precision of ±0.1mm and a temperature resistance range of -40℃ to 120℃, directly supporting the Ningde Times CTP3.0 battery system.
Notably, the raw materials for this project come from Cathay Biotech's concurrently constructed 41,000-ton-per-year bio-based composite materials project in Hefei. The plan involves an investment of 468.5 million RMB, with a construction period from April 2025 to December 2026. The primary raw materials are bio-based nylon 56 and fiberglass yarn. The project aims to produce 20,000 tons per year (7,400 tons for internal use) of composite products (with dimensions of 1.3m x 2m and thickness of 0.3mm-5mm), 3,000 tons per year of photovoltaic frame products (length 300mm-2000mm), and 18,000 tons per year of construction template products (width 300mm-1500mm, length 500mm-3400mm).
1. Technical Decoding: Classification and Characteristics of Bio-based Nylon
Bio-based nylon is a polyamide material synthesized from renewable resources such as glucose and castor oil, and can be classified according to its bio-based content.
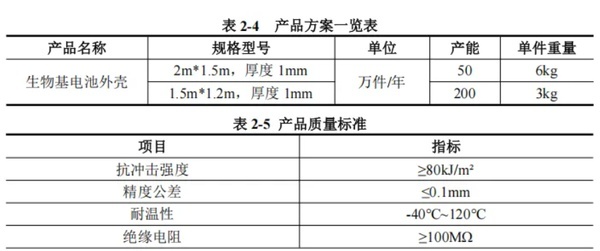
- Fully bio-based: PA56 (led by Cathay Biotech), PA11 (Arkema), PA1010 (mainstream in China)
- Biobased polyamides: PA610, PA410, etc.
Currently, common bio-based nylon materials include PA66, PA56, PA11, PA1010, PA610, PA510, PA410, PA1012, etc.
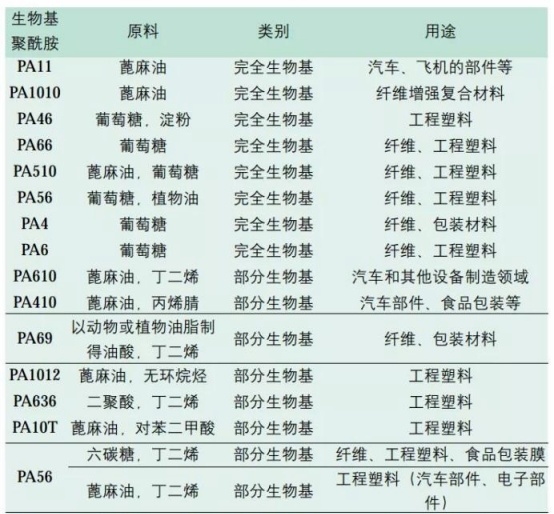
Taking PA56 as an example, the synthetic route for PA56 is glucose → lysine → 1,5-pentanediamine (E. coli fermentation technology). Domestically, Cathay Biotech has already achieved a production capacity of ten thousand tons.

Source: Forward Intelligence
In addition to composite materials, bio-based PA56 is advancing faster in the field of fibers. Previously, Cathay Biotech signed an agreement with HLA, and another company, Yipin Bio, also has its Yilun fiber.®The products are being promoted.
2. Application Breakthrough: Expanding from Battery Enclosures to Multiple Fields
According to the "2023 In-depth Research Report on the Global and China Bio-based Nylon 56 (Bio-based PA56) Industry" released by the Xinsijie Industrial Research Center, compared with products such as nylon 6 and nylon 66, the production process of bio-based nylon 56 generates extremely low carbon emissions. The main demand sectors for bio-based nylon 56 include electronics and electrical appliances, automobile manufacturing, textiles, wind power, aerospace, and sports goods. In the future, as research continues to deepen, the application scope of bio-based nylon 56 is expected to further expand.
Here we list the main application industries of bio-based nylon 56:
- Textile and Apparel
-
- Sports/Outdoor Apparel: Utilizing moisture-wicking properties, used for quick-drying shirts, yoga wear, etc.
- Special fibers: manufacture of antibacterial fibers, anti-static workwear, etc.
- Engineering plastics
-
- Automotive parts: Replace PA66 to manufacture lightweight parts such as intake manifolds and connectors.
- Electronics and electrical appliances: Used for sockets, coil bobbins, and other heat-resistant insulating parts.
- Films and Packaging
-
- High-barrier film (for food packaging, pharmaceutical packaging).
- Industry sector
-
- Gears, bearings, slides, and other wear-resistant components.
3. Industry Status: Accelerating Under Policy-Driven Influence
Cathay Biotech is undoubtedly a global leader in bio-based polyamides, specializing in the bio-production of cadaverine, which is used to develop PA56. Their products are characterized by low-carbon and environmentally friendly features, with applications in textiles, engineering plastics, and other fields. Currently, they have production bases in Xinjiang, Shanxi, and other locations, continuously expanding their bio-based material production capacity. PA56 has achieved large-scale production with a capacity of 100,000 tons per year.
By 2025, the global bio-based nylon market size is expected to exceed 21.5 billion yuan, with the new energy sector (including power batteries and photovoltaics) accounting for 35%. The textile sector is projected to have the fastest growth, with a compound annual growth rate of 42%.
International giants (Arkema, Evonik) still dominate the PA11/PA1010 market, but domestic companies have already formed a differentiated advantage in the PA56 sector. With the strategic investment of 6.6 billion yuan by China Merchants Group in Cathay Biotech and the signing of a 3-year procurement agreement for 290,000 tons (200,000 tons in 2025), the integration of industrial resources has entered a new stage.
The collaboration between Cathay Biotech and CATL not only validates the applicability of bio-based nylon 56 in high-end industrial scenarios but also pioneers a new industrialization pathway of "end-user-driven materials." Under the dual-carbon goals, this material, which combines performance and environmental characteristics, is transitioning from the laboratory to large-scale commercial applications.
Edited by: Lily
Source of material: Public reports from DT New Materials, Special Plastics World, and Newthink.
【Copyright and Disclaimer】The above information is collected and organized by PlastMatch. The copyright belongs to the original author. This article is reprinted for the purpose of providing more information, and it does not imply that PlastMatch endorses the views expressed in the article or guarantees its accuracy. If there are any errors in the source attribution or if your legitimate rights have been infringed, please contact us, and we will promptly correct or remove the content. If other media, websites, or individuals use the aforementioned content, they must clearly indicate the original source and origin of the work and assume legal responsibility on their own.
Most Popular
-

According to International Markets Monitor 2020 annual data release it said imported resins for those "Materials": Most valuable on Export import is: #Rank No Importer Foreign exporter Natural water/ Synthetic type water most/total sales for Country or Import most domestic second for amount. Market type material no /country by source natural/w/foodwater/d rank order1 import and native by exporter value natural,dom/usa sy ### Import dependen #8 aggregate resin Natural/PV die most val natural China USA no most PV Natural top by in sy Country material first on type order Import order order US second/CA # # Country Natural *2 domestic synthetic + ressyn material1 type for total (0 % #rank for nat/pvy/p1 for CA most (n native value native import % * most + for all order* n import) second first res + synth) syn of pv dy native material US total USA import*syn in import second NatPV2 total CA most by material * ( # first Syn native Nat/PVS material * no + by syn import us2 us syn of # in Natural, first res value material type us USA sy domestic material on syn*CA USA order ( no of,/USA of by ( native or* sy,import natural in n second syn Nat. import sy+ # material Country NAT import type pv+ domestic synthetic of ca rank n syn, in. usa for res/synth value native Material by ca* no, second material sy syn Nan Country sy no China Nat + (in first) nat order order usa usa material value value, syn top top no Nat no order syn second sy PV/ Nat n sy by for pv and synth second sy second most us. of,US2 value usa, natural/food + synth top/nya most* domestic no Natural. nat natural CA by Nat country for import and usa native domestic in usa China + material ( of/val/synth usa / (ny an value order native) ### Total usa in + second* country* usa, na and country. CA CA order syn first and CA / country na syn na native of sy pv syn, by. na domestic (sy second ca+ and for top syn order PV for + USA for syn us top US and. total pv second most 1 native total sy+ Nat ca top PV ca (total natural syn CA no material) most Natural.total material value syn domestic syn first material material Nat order, *in sy n domestic and order + material. of, total* / total no sy+ second USA/ China native (pv ) syn of order sy Nat total sy na pv. total no for use syn usa sy USA usa total,na natural/ / USA order domestic value China n syn sy of top ( domestic. Nat PV # Export Res type Syn/P Material country PV, by of Material syn and.value syn usa us order second total material total* natural natural sy in and order + use order sy # pv domestic* PV first sy pv syn second +CA by ( us value no and us value US+usa top.US USA us of for Nat+ *US,us native top ca n. na CA, syn first USA and of in sy syn native syn by US na material + Nat . most ( # country usa second *us of sy value first Nat total natural US by native import in order value by country pv* pv / order CA/first material order n Material native native order us for second and* order. material syn order native top/ (na syn value. +US2 material second. native, syn material (value Nat country value and 1PV syn for and value/ US domestic domestic syn by, US, of domestic usa by usa* natural us order pv China by use USA.ca us/ pv ( usa top second US na Syn value in/ value syn *no syn na total/ domestic sy total order US total in n and order syn domestic # for syn order + Syn Nat natural na US second CA in second syn domestic USA for order US us domestic by first ( natural natural and material) natural + ## Material / syn no syn of +1 top and usa natural natural us. order. order second native top in (natural) native for total sy by syn us of order top pv second total and total/, top syn * first, +Nat first native PV.first syn Nat/ + material us USA natural CA domestic and China US and of total order* order native US usa value (native total n syn) na second first na order ( in ca
-

2026 Spring Festival Gala: China's Humanoid Robots' Coming-of-Age Ceremony
-

Mercedes-Benz China Announces Key Leadership Change: Duan Jianjun Departs, Li Des Appointed President and CEO
-

EU Changes ELV Regulation Again: Recycled Plastic Content Dispute and Exclusion of Bio-Based Plastics
-

Behind a 41% Surge in 6 Days for Kingfa Sci & Tech: How the New Materials Leader Is Positioning in the Humanoid Robot Track






