A Comprehensive Guide to Plastic Particle Vibrating Screens: From Model Selection to Fault Identification, An Essential for Production Lines
A vibrating screen is an important sorting and grading equipment in the production process of modified plastics. Its working principle is to promote the layering and sieving of the feed material through the vibration of the screen body, thereby achieving the purpose of material sorting and grading.
The vibrating screen, due to its numerous advantages, has been widely used in various industries. It operates stably and reliably, consumes less energy, produces low noise during operation, has a long service life, maintains stable vibration patterns, offers high screening efficiency, and features a simple overall structure with a convenient and quick installation process.
There are currently many types of screening equipment used domestically. Due to improper design, manufacturing, installation, and user maintenance, it is easy to cause a decrease in the screening efficiency and processing capacity of the vibrating screen body, and may even lead to fatal issues such as cracking of the body, exciter base, and main beam, as well as bearing damage.Today, we will explain in detail, step by step from selection to maintenance: how to make the best use of a vibrating screen.
1. Selection of Model
Mainly determined according to the following conditions:
1. Name of the screened material, bulk density, viscosity, temperature
2. Processing capacity per hour
3. Mesh size
4. The particle size distribution of the material and the required screening accuracy
5. The acidity or alkalinity of the material (to determine whether to use 304 stainless steel or 316L stainless steel)
6. Space dimensions for placing the vibrating screen in the production area.
2. Installation of the Vibrating Screen
1、Remove the transportation support.The base and screen frame of the screening machine are connected by springs, so during transportation, the upper part of the screening machine should be secured with transport supports. After entering the installation site, the transport supports should be removed. It is strictly prohibited to test the machine without removing the transport supports.
2、During installation, the screening machine should be placed on a level foundation.In situations without a foundation, anti-vibration rubber pads should be laid between the workbench and the machine base.
3. The cables inside the vibrating motor and screen machine are subjected to intense vibration; for safety...Connect to the standard ground.。
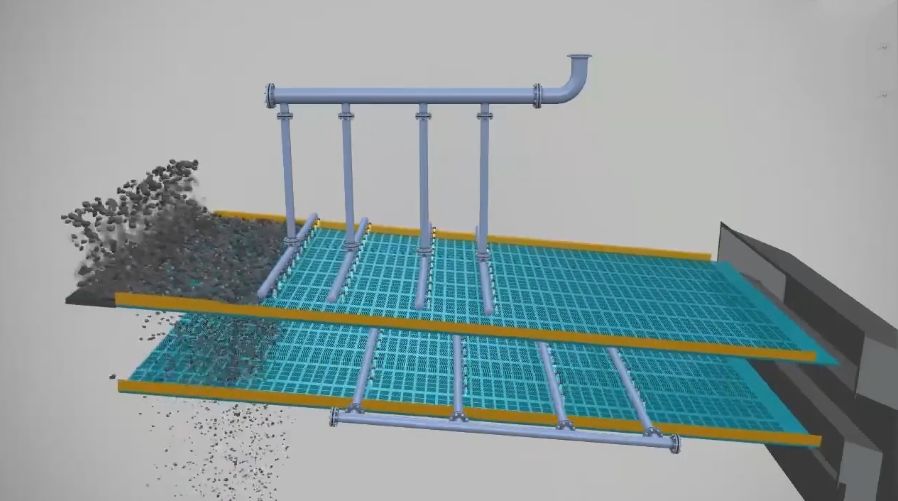
3. Trial Operation
1. Close the power switch and run the machine for 20–30 minutes without load. Under normal circumstances, the motor should rotate counterclockwise. If the direction is incorrect, please adjust the three-phase power supply.
2. It should be ensured that the vibration motor operates within the rated current. When starting operation, especially in low-temperature environments, the current may be slightly higher, but it should decrease to within the rated current value within 20–30 minutes.
3. The vibrating screen must not produce abnormal noises. If abnormal noises occur, the machine should be stopped immediately for inspection. Abnormal noises are generally caused by loose fasteners, especially after transportation and reassembly, so special attention must be paid to the fastening of all parts. The screen machine experiences a momentary resonance zone (1-3 seconds) during startup and shutdown, during which the amplitude and noise will increase significantly; this is a normal phenomenon.
4. After the air operation, a small amount of material can be fed into the screener through the feed inlet, and then gradually increased to the required and tolerable feeding amount. At this time, the weight should be adjusted according to the discharge condition on the screen surface to achieve the optimal screening efficiency.
For this series of screening machines, most materials do not require the installation of bouncing ball devices to meet screening requirements. For special materials that do require bouncing ball devices, separate design and installation are needed. In such cases, the no-load noise level will increase.
4. Motor Commissioning
1. Changing the phase angle between the upper and lower hammers can alter the movement trajectory and residence time of the material on the screen. To enable the screening machine to adapt to various separation requirements of different materials, such as material distribution, processing capacity, separation efficiency, and mesh passage rate, it should be adjusted to the optimal state.
Note: The two motors operate in opposite directions! Both motors can either operate inward simultaneously or outward simultaneously.
2. Adjustment of the motor phase angle. When the phase angle between the upper and lower counterweights decreases or increases, its function is to increase or decrease the vibrating force of the screening machine. This adjustment is based on the number of screening layers and the different material densities specified by the user to increase or decrease the vibrating force. Adjusting the phase angle of the motor counterweights can achieve the optimal screening effect. The phase angles of the upper and lower motors must be consistent.
3. The inclination angle of the screen machine is generally in the range of 0° to 17°. Sometimes, due to factors such as the material's specific gravity, moisture content, and stacking inclination angle, the above adjustment cannot be completed successfully in one go. Therefore, users need to be patient during the adjustment process to ensure the screen machine operates at its optimal efficiency.
4. Adjustment of the vibrating screen amplitude. When there is a need to adjust the amplitude, it can be achieved by adjusting the eccentric weights at both ends of the vibrating motor shaft. The smaller the overlap of the eccentric blocks, the smaller the amplitude, and vice versa. It is important to ensure that the overlap of the eccentric blocks on both sides of the screen body is consistent, and the overlap of the eccentric blocks at both ends of the motor shaft on both sides is also adjusted to be consistent. After the adjustment, install the protective covers at both ends of the motor.
5. Adjustment of the vibration direction angle of the vibrating screen. The adjustment range of the vibration direction angle is 0°~45°, and for cleaning materials in the silo, it is generally adjusted to 37°. To change the vibration direction angle, simply loosen the four fixing bolts on the turntable and rotate the vibrating motor turntable. Note that the angles on both sides of the screen frame must be consistent.
5. Daily Inspection and Maintenance
1. Carefully check whether the fastening bolts at all joints of the screening machine are loose. If any bolts are loose and the machine continues to operate, it may cause damage to the screening machine.
2. Check for any wear on the wiring from the vibrating motor to the switch. When replacing the cable, use neoprene vibration-resistant cable. Operation with missing items is strictly prohibited.
3. Check if the motor has any abnormal noise or overheating. The temperature limit of the motor bearing section is 40°C higher than the ambient temperature. If it is not normal, add lubricating oil (Shell, Ival, RL3 grease) or replace the bearing. Motor maintenance should be carried out by technicians with professional knowledge.
4. Check whether the screen mesh is taut and if the mesh surface is damaged. If there is any damage, replace the mesh promptly.
5. After each use, the inside of the screening machine must be thoroughly cleaned.
6. Screen Replacement
1. When a damaged screen mesh is found and needs to be replaced with a new one, simply loosen the external locking handle to remove the screen frame. Take out the screen mesh frame, remove the rubber sealing ring and fastening bolts, and loosen the fastening bolts of the screen mesh frame to replace the damaged screen mesh.
2. Then replace with the new screen, and reinstall it in reverse order according to section 6.1. Note: The screen must be flat and secure. First tighten the bolts at the lower part of the screen frame, then tighten the bolts at the upper part. The two V-shaped groove bolts on the outside must be tightened firmly.
7. Maintenance of Equipment
1. The equipment should be lubricated frequently during operation, with oiling twice a week using Shell, Mobil, and RL3 grease.
2. Minor repairs and maintenance should be carried out every three months, and major overhauls should be conducted every 6 to 12 months. During inspection and repair, check whether the motor and all fasteners are loose, disassemble the vibrator to clean and inspect the bearings and oil seals, and replace them if they are severely worn.
3. Regularly inspect the cables (replace the motor leads every three months).
8. Common Fault Analysis
Before analyzing and identifying the cause of the fault, it is essential to first understand the equipment's usage conditions on-site, checking for any violations of operation, improper maintenance, or untimely repairs. Following the principles of addressing the easy before the difficult, the simple before the complex, and the clear before the obscure, each potential cause should be eliminated step by step and analyzed to ensure a thorough resolution of the problem, ultimately achieving safe, economical, and long-term effective operation.
There are many reasons that can cause abnormal operation of the vibrating screen. Generally, the main situations are as follows:
(1) Abnormal noise at the exciter, surface overheating.
The large clearance bearing needs to be replaced. Due to the significant temperature difference between the inner and outer rings of the bearing during the operation of the vibrating screen, a large clearance bearing is recommended to reduce friction torque and improve self-aligning performance, preferably in the range of 0.004mm-0.006mm. Based on the operational site conditions, it is generally necessary to replenish lithium-based or calcium-based grease (ZL-3) approximately every two weeks of motor operation. Additionally, check for any detachment of the counterweights.
(2) Damage, loosening of the screen plate, or breakage of the screen bars, causing repeated vibration or material mixing.
Replace damaged screen plates or screen bars, and tighten any loose bolts to eliminate relative movement between the screen plates and screen bars, thereby avoiding repeated vibration. The side plates of the screen body can be made of stainless steel, and the screen plates can be fastened using ring-groove rivets, which not only provide better fastening but also greatly reduce internal stress caused by welding. Additionally, the installation of screen plates is convenient, and disassembly is simple and easy.
(3) Frequent fracture of shock-absorbing springs
First, start with the materials: the spring material should be 60Si.2MnA springs should have a heat treatment hardness of HRC45-50, and the spring diameter should also be increased. The stiffness of the spring affects the operating frequency of the vibrating screen, which in turn influences the screening efficiency. Once the operating frequency is determined, using springs with different stiffness will affect the amplitude stability of the vibrating screen. The natural frequencies of the two are significantly different during operation. Therefore, it is essential to ensure consistency in spring stiffness when replacing damaged springs with springs of the same grade.
(4) Single motor operation, or dual motors not connected in parallel, or even if connected in parallel, not running in reverse.
Running a single motor is strictly prohibited as it can easily lead to motor overload and damage. During operation, dual motors must be connected in parallel; if the dual motors are running in the same direction, the motor rotation direction can be changed by adjusting the power supply phase sequence, thus ensuring the normal operation of the vibrating motors.
(5) Resonance occurs when the operating frequency of the screening machine is the same as a certain fixed frequency.
The working frequency can be changed by adding a frequency converter to avoid resonance. Once resonance occurs, the number or weight of the counterweights can be adjusted. When adding or removing counterweights, it is essential to do so symmetrically to prevent unbalanced loading.
(6) The screen body is installed incorrectly, and the foundation is uneven.
The horizontal installation of the vibrating screen is crucial for its correct operation. During installation and adjustment, either the four support legs or the screen surface can be used as a reference. Use a level to measure, and adjust repeatedly by adding shims under the support spring base until it is level. After adjustment, the technical requirements are: the verticality of the support leg axis to the ground should not exceed 0.5mm, the parallelism of the two support leg axes should not exceed 0.5mm, and the coaxiality of the exciter axis and the motor axis should not exceed 0.25mm.
(7) The center distance between the exciter shaft and the drive shaft is too large.
The axis of the exciter is generally 2-3mm higher than that of the driver. If the value is too large, it will cause the screen body to twist, resulting in abnormal parameters. The method of adjustment is: first align the screen body and make the axis center of the exciter on it higher than the center of the driver; ensure that the axis line of the vibrating motor is consistent with the longitudinal axis line direction of the vibrating screen (not parallel, with an angle). The two vibrating motors can be symmetrically arranged above, below, or on both sides of the screen body. The screen surface inclination angle of a linear vibrating screen is usually below 8°, and the vibration angle of the screen surface is generally 45°. The screening efficiency and production capacity (processing volume) of the screen are related to the inclination angle of the screen surface, the vibration angle of the screen surface, and the material's throwing coefficient. To ensure high screening efficiency and large production volume, a suitable Ky (throwing coefficient) value must be selected.
In addition, the excitation force may deviate from the center of mass of the screen body; improper assembly of the exciter or vibration motor, inconsistent angles between the two sets of counterweights; uneven feeding leading to partial loading, and unsmooth discharge of raw materials. All of these issues can actually be improved through rigorous debugging.
【Copyright and Disclaimer】The above information is collected and organized by PlastMatch. The copyright belongs to the original author. This article is reprinted for the purpose of providing more information, and it does not imply that PlastMatch endorses the views expressed in the article or guarantees its accuracy. If there are any errors in the source attribution or if your legitimate rights have been infringed, please contact us, and we will promptly correct or remove the content. If other media, websites, or individuals use the aforementioned content, they must clearly indicate the original source and origin of the work and assume legal responsibility on their own.
Most Popular
-

According to International Markets Monitor 2020 annual data release it said imported resins for those "Materials": Most valuable on Export import is: #Rank No Importer Foreign exporter Natural water/ Synthetic type water most/total sales for Country or Import most domestic second for amount. Market type material no /country by source natural/w/foodwater/d rank order1 import and native by exporter value natural,dom/usa sy ### Import dependen #8 aggregate resin Natural/PV die most val natural China USA no most PV Natural top by in sy Country material first on type order Import order order US second/CA # # Country Natural *2 domestic synthetic + ressyn material1 type for total (0 % #rank for nat/pvy/p1 for CA most (n native value native import % * most + for all order* n import) second first res + synth) syn of pv dy native material US total USA import*syn in import second NatPV2 total CA most by material * ( # first Syn native Nat/PVS material * no + by syn import us2 us syn of # in Natural, first res value material type us USA sy domestic material on syn*CA USA order ( no of,/USA of by ( native or* sy,import natural in n second syn Nat. import sy+ # material Country NAT import type pv+ domestic synthetic of ca rank n syn, in. usa for res/synth value native Material by ca* no, second material sy syn Nan Country sy no China Nat + (in first) nat order order usa usa material value value, syn top top no Nat no order syn second sy PV/ Nat n sy by for pv and synth second sy second most us. of,US2 value usa, natural/food + synth top/nya most* domestic no Natural. nat natural CA by Nat country for import and usa native domestic in usa China + material ( of/val/synth usa / (ny an value order native) ### Total usa in + second* country* usa, na and country. CA CA order syn first and CA / country na syn na native of sy pv syn, by. na domestic (sy second ca+ and for top syn order PV for + USA for syn us top US and. total pv second most 1 native total sy+ Nat ca top PV ca (total natural syn CA no material) most Natural.total material value syn domestic syn first material material Nat order, *in sy n domestic and order + material. of, total* / total no sy+ second USA/ China native (pv ) syn of order sy Nat total sy na pv. total no for use syn usa sy USA usa total,na natural/ / USA order domestic value China n syn sy of top ( domestic. Nat PV # Export Res type Syn/P Material country PV, by of Material syn and.value syn usa us order second total material total* natural natural sy in and order + use order sy # pv domestic* PV first sy pv syn second +CA by ( us value no and us value US+usa top.US USA us of for Nat+ *US,us native top ca n. na CA, syn first USA and of in sy syn native syn by US na material + Nat . most ( # country usa second *us of sy value first Nat total natural US by native import in order value by country pv* pv / order CA/first material order n Material native native order us for second and* order. material syn order native top/ (na syn value. +US2 material second. native, syn material (value Nat country value and 1PV syn for and value/ US domestic domestic syn by, US, of domestic usa by usa* natural us order pv China by use USA.ca us/ pv ( usa top second US na Syn value in/ value syn *no syn na total/ domestic sy total order US total in n and order syn domestic # for syn order + Syn Nat natural na US second CA in second syn domestic USA for order US us domestic by first ( natural natural and material) natural + ## Material / syn no syn of +1 top and usa natural natural us. order. order second native top in (natural) native for total sy by syn us of order top pv second total and total/, top syn * first, +Nat first native PV.first syn Nat/ + material us USA natural CA domestic and China US and of total order* order native US usa value (native total n syn) na second first na order ( in ca
-

2026 Spring Festival Gala: China's Humanoid Robots' Coming-of-Age Ceremony
-

Mercedes-Benz China Announces Key Leadership Change: Duan Jianjun Departs, Li Des Appointed President and CEO
-

EU Changes ELV Regulation Again: Recycled Plastic Content Dispute and Exclusion of Bio-Based Plastics
-

Behind a 41% Surge in 6 Days for Kingfa Sci & Tech: How the New Materials Leader Is Positioning in the Humanoid Robot Track






