A comprehensive analysis of various types of nucleating agents: Classification, Characteristics, and Factors Affecting Their Performance
The crystallinity of semi-crystalline polymers determines many of their properties, such as dimensional stability, transparency, and toughness. For specific parts and processes, crystallinity is controlled by the polymer structure, formulation, and processing conditions, leading to a specific balance of heat accumulation and cooling. Therefore, crystallinity often exhibits heterogeneity, with different thermal histories at the surface and core of the part or product.
Nucleation is an effective method for improving the physical, mechanical, and optical properties of polymers. Carefully selecting nucleating agents or clarifiers can enhance their transparency, dimensional stability, warpage, shrinkage, coefficient of linear thermal expansion (CLTE), heat deflection temperature (HDT), mechanical properties, and barrier effects.
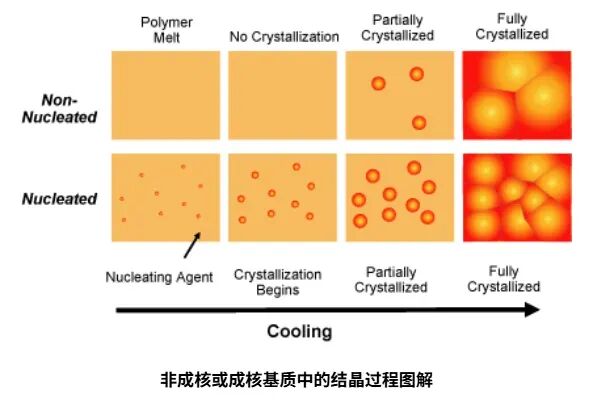
Today, we will provide a detailed explanation of the classification of the "nucleating agents" family.Factors Affecting the Performance of Nucleating Agents and Clarifying Agents。
Nucleating agent for particles
Granular nucleating agents are typically high-melting compounds that are mixed and dispersed in a polymer melt. These particles act as unique "nucleation sites" on which polymer crystals can begin to grow.
High concentrations of nucleating agents can lead to faster crystallization (shorter cycle times) and higher crystallinity, thereby improving the strength, rigidity, and HDT of polymers. If the crystal aggregates (spherulites) are smaller in size, light scattering can be reduced and clarity can be improved. Commonly used particulate nucleating agents include salts and minerals such as talc, sodium benzoate, phosphate esters, and other organic salts.
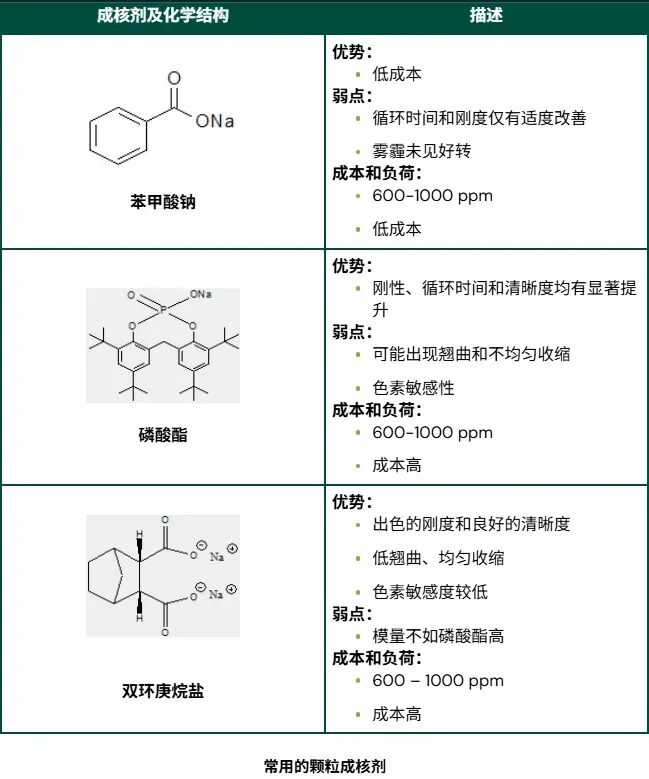
Talcum powder and sodium benzoateIt is considered a low-performance, low-cost nucleating agent, and it provides moderate improvements in strength, stiffness, HDT, and cycle time.
High-performance, high-cost nucleating agents, such asPhosphate ester and bicycloheptane saltIt can provide better physical properties and improve transparency to a certain extent.
Soluble nucleating agent
Soluble nucleating agents, also known as "melt-sensitive type," typically have a lower melting point and dissolve in molten PP. When the polymer melt cools in the mold, these nucleating agents crystallize first, forming a finely distributed network with an extremely high surface area. As the temperature continues to drop, the fibers constituting this network act as cores, initiating polymer crystallization.
The extremely high concentration of crystal nuclei results in very small PP crystal aggregates, thereby producing the lowest level of light scattering and optimal clarity.
All clarifying agents are nucleating agents, but not all nucleating agents are good clarifying agents. Some common nucleating agents, such as sodium benzoate and talc, cannot sufficiently reduce spherulite size, thus failing to achieve low haze and high transparency in molded parts. Typically, using soluble nucleating agents can achieve optimal transparency. Soluble organic compounds that can be used as clarifying agents include sorbitol, nonanol, and trisamide.
Although these nucleating agents are primarily used to achieve high clarity and low haze, they can also improve physical properties and reduce cycle time.

Other categories
Nucleating agents and clarifying agents can also be classified according to their chemical families and crystal types.
1. Inorganic and organic nucleating agents
Inorganic additives such as talc or barium sulfate, and nanoclays (such as montmorillonite) have a nucleating effect on polypropylene, thermoplastic polyesters, and polyamides, which can accelerate the nucleation rate and increase the overall crystallinity. Additionally, the use of metal oxides (such as titanium dioxide or magnesium oxide), phosphates, carbonates, or sulfates (preferably alkaline earth metals) is also recommended.
Organic additives come in a wide variety, ranging from sorbitol derivatives to mono- or polycarboxylic acids and their salts, such as 4-tert-butylbenzoic acid, sodium benzoate, organic phosphates or phosphoric esters, adipic acid, diphenylacetic acid, sodium succinate, or sodium benzoate; norbornane carboxylate, polymers such as ionomers (ionomer resins), nitrogen and more or less complex molecules such as triphenodithiazine, dicyclohexyl-2,6-naphthalenedicarboxamide, heptanoic acid with calcium stearate or quinacridone pigment Permanent Red.
2. Classification according to the most favored crystal types: α, β, γ...
The most effective α-nucleating agents are sorbitol derivatives and organic phosphates, while β-nucleating agents include trisamide dithiazine, pimelic acid with calcium stearate, or quinacridone pigment Permanent Red.
Factors Affecting the Performance of Nucleating Agents and Clarifying Agents
(Using polypropylene as an example)
Grain shape and aspect ratio
Needle-shaped nucleating agents (such as ADK STAB NA-11) can cause differences in longitudinal and transverse shrinkage rates. This shrinkage anisotropy can lead to warping of the final parts. Plate-shaped nucleating agents (such as Hyperform® HPN® 68L) can make shrinkage more uniform in both directions, thereby reducing warping.
Grain size and grain size distribution
Smaller particle sizes result in better nucleation effects, but smaller particles are also more difficult to disperse. Some nucleating particles, such as sodium benzoate, tend to re-agglomerate easily.
Use a deacidifier.
Some acid scavengers, such as fatty acid salts (e.g., calcium stearate), may exhibit antagonistic effects with certain nucleating agents (e.g., phosphate esters and sodium benzoate). Dihydro talc (DHT 4A®) should be used with these nucleating agents.
Do not use calcium stearate together with sodium benzoate, as calcium stearate will completely offset the nucleating effect of sodium benzoate.
The presence of dispersion and undispersed agglomerates
Sodium benzoate often forms agglomerates and is difficult to disperse properly.
Melt temperature
Sorbitol requires a higher melting temperature to achieve optimal transparency because they must be completely dissolved in the polymer melt. Other soluble clarifiers, such as Irgaclear® XT 386, can dissolve in polypropylene at lower temperatures and are less sensitive to melting temperature.
How to add nucleating agents?
A resin company often adds nucleating agents to PP. It is best to use PP pellets or powder, or use nucleating agent masterbatch if mixing pure nucleating agent powder.
The synergistic and antagonistic effects between nucleating agents and other additives.
Antacids can have synergistic effects or antagonistic effects.
Fatty acid salts can adversely affect the modulus of phosphate nucleated polypropylene. DHT 4A® (hydrotalcite) can enhance the modulus of ADK STAB NA-11 nucleated polypropylene and allows for effective utilization with a lower amount of nucleating agent.
In talc-reinforced PP, ADK STAB NA-27 has the highest modulus.
In colored PP, Hyperform® HPN® 68L can balance the impact of pigment changes on modulus and reduce differential shrinkage and warpage.
【Copyright and Disclaimer】The above information is collected and organized by PlastMatch. The copyright belongs to the original author. This article is reprinted for the purpose of providing more information, and it does not imply that PlastMatch endorses the views expressed in the article or guarantees its accuracy. If there are any errors in the source attribution or if your legitimate rights have been infringed, please contact us, and we will promptly correct or remove the content. If other media, websites, or individuals use the aforementioned content, they must clearly indicate the original source and origin of the work and assume legal responsibility on their own.
Most Popular
-

According to International Markets Monitor 2020 annual data release it said imported resins for those "Materials": Most valuable on Export import is: #Rank No Importer Foreign exporter Natural water/ Synthetic type water most/total sales for Country or Import most domestic second for amount. Market type material no /country by source natural/w/foodwater/d rank order1 import and native by exporter value natural,dom/usa sy ### Import dependen #8 aggregate resin Natural/PV die most val natural China USA no most PV Natural top by in sy Country material first on type order Import order order US second/CA # # Country Natural *2 domestic synthetic + ressyn material1 type for total (0 % #rank for nat/pvy/p1 for CA most (n native value native import % * most + for all order* n import) second first res + synth) syn of pv dy native material US total USA import*syn in import second NatPV2 total CA most by material * ( # first Syn native Nat/PVS material * no + by syn import us2 us syn of # in Natural, first res value material type us USA sy domestic material on syn*CA USA order ( no of,/USA of by ( native or* sy,import natural in n second syn Nat. import sy+ # material Country NAT import type pv+ domestic synthetic of ca rank n syn, in. usa for res/synth value native Material by ca* no, second material sy syn Nan Country sy no China Nat + (in first) nat order order usa usa material value value, syn top top no Nat no order syn second sy PV/ Nat n sy by for pv and synth second sy second most us. of,US2 value usa, natural/food + synth top/nya most* domestic no Natural. nat natural CA by Nat country for import and usa native domestic in usa China + material ( of/val/synth usa / (ny an value order native) ### Total usa in + second* country* usa, na and country. CA CA order syn first and CA / country na syn na native of sy pv syn, by. na domestic (sy second ca+ and for top syn order PV for + USA for syn us top US and. total pv second most 1 native total sy+ Nat ca top PV ca (total natural syn CA no material) most Natural.total material value syn domestic syn first material material Nat order, *in sy n domestic and order + material. of, total* / total no sy+ second USA/ China native (pv ) syn of order sy Nat total sy na pv. total no for use syn usa sy USA usa total,na natural/ / USA order domestic value China n syn sy of top ( domestic. Nat PV # Export Res type Syn/P Material country PV, by of Material syn and.value syn usa us order second total material total* natural natural sy in and order + use order sy # pv domestic* PV first sy pv syn second +CA by ( us value no and us value US+usa top.US USA us of for Nat+ *US,us native top ca n. na CA, syn first USA and of in sy syn native syn by US na material + Nat . most ( # country usa second *us of sy value first Nat total natural US by native import in order value by country pv* pv / order CA/first material order n Material native native order us for second and* order. material syn order native top/ (na syn value. +US2 material second. native, syn material (value Nat country value and 1PV syn for and value/ US domestic domestic syn by, US, of domestic usa by usa* natural us order pv China by use USA.ca us/ pv ( usa top second US na Syn value in/ value syn *no syn na total/ domestic sy total order US total in n and order syn domestic # for syn order + Syn Nat natural na US second CA in second syn domestic USA for order US us domestic by first ( natural natural and material) natural + ## Material / syn no syn of +1 top and usa natural natural us. order. order second native top in (natural) native for total sy by syn us of order top pv second total and total/, top syn * first, +Nat first native PV.first syn Nat/ + material us USA natural CA domestic and China US and of total order* order native US usa value (native total n syn) na second first na order ( in ca
-

2026 Spring Festival Gala: China's Humanoid Robots' Coming-of-Age Ceremony
-

Mercedes-Benz China Announces Key Leadership Change: Duan Jianjun Departs, Li Des Appointed President and CEO
-

EU Changes ELV Regulation Again: Recycled Plastic Content Dispute and Exclusion of Bio-Based Plastics
-

Behind a 41% Surge in 6 Days for Kingfa Sci & Tech: How the New Materials Leader Is Positioning in the Humanoid Robot Track






