13 Images to Understand the Components and Construction of a Twin-Screw Extruder
The twin-screw extruder is considered the most efficient mixing and dispersing device in plastic processing. Since the twin-screw extruder is ubiquitous in the plastic processing industry, it is crucial to understand the components of the twin-screw extruder and how it is constructed before putting it into operation.
The base is obviously used to support the machine. There are usually two types of extruder bases: one is made of welded channel steel, and the other is cast. Most suppliers use welded bases. After welding is completed, the base should be left to sit for several days before use to release its internal stress, allowing it to achieve optimal physical performance.

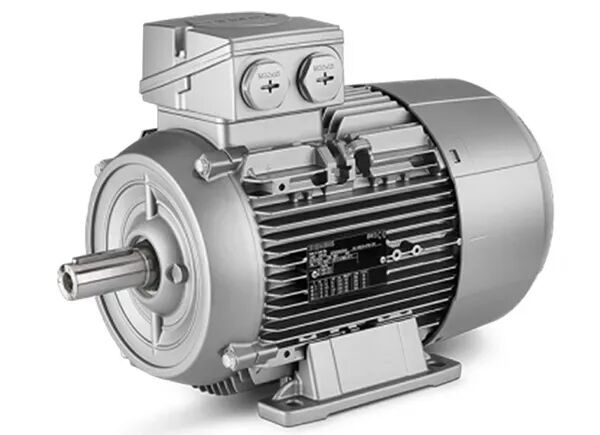
Main motor
The main motor is used to drive the machine to reach the rated speed. Choosing a high-quality motor is crucial. First, we must determine the motor power based on formulas and output requirements to obtain the most suitable power consumption, which requires experimentation and extensive experience.
Motor suppliers include Siemens, ABB, WEG, and WN, among others, with different parameters selected based on specific application requirements.

Transmission
The gearbox is the heart of the extruder. It has the functions of reduction and distribution, allowing the motor speed to be reduced to the required shaft speed and distributing the output torque to two output shafts.

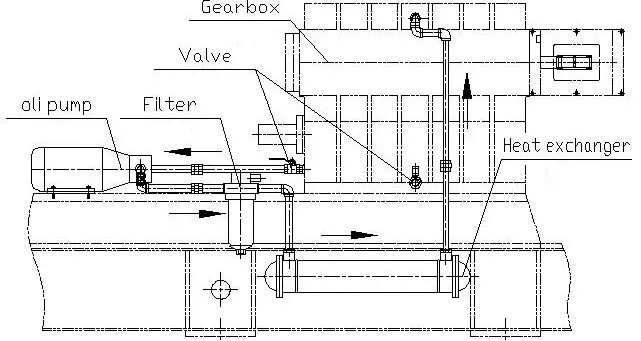
The transmission lubrication and cooling system mainly consists of three parts: an oil pump, a heat exchanger, and a filter. The forced oil lubrication system has two purposes:
Lubricate the bearings and gears with oil, and pump temperature-controlled oil into the transmission.
The oil is pumped into the transmission through the oil cooler and oil filter.
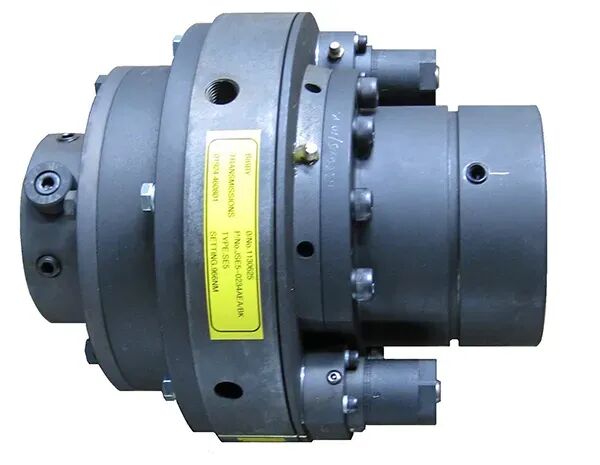
Safety clutch
The safety clutch is used to connect the motor and the extruder gearbox. Its purpose is to prevent damage to the gearbox, screw, and barrel in case of a failure. When the extruder load exceeds the preset value, the safety clutch will immediately disconnect upon receiving a signal from the machine. This stops the operation of the entire machine, preventing further damage to the gearbox, screw, and barrel.

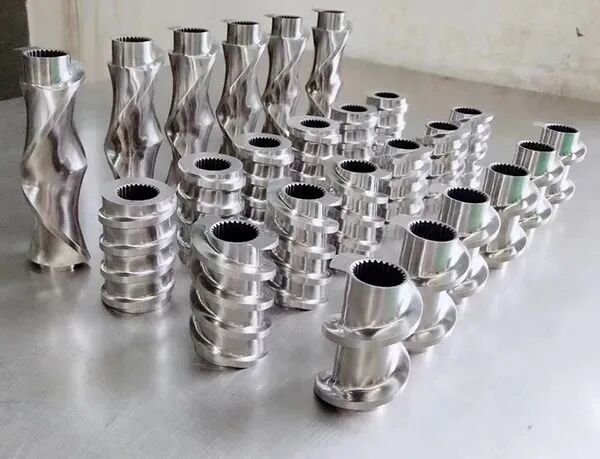
Screw and barrel
The screw and the barrel are important components of a twin-screw extruder. The flexible combination makes the twin-screw extruder suitable for almost all different types of plastic applications. The length-to-diameter ratio of the barrel and screw depends on the specific application you are processing.

Selecting the appropriate barrel and screw materials is also crucial for extruder applications, as different applications have different materials available. Choosing the best materials will help you produce high-quality and competitive products while balancing performance and cost. An optimal screw configuration/profile can make your final products stand out and be more competitive.

Heating rod
The heating rod is used to heat the screw and the barrel, and the material enters the barrel at a rated speed. The heater is set to a certain temperature to ensure that the material melts before entering the die head or downstream.
There are various types of heaters used in extruders, such as aluminum cast heaters, copper cast heaters, cast iron heaters, ceramic heaters, tubular heaters, infrared heaters, electromagnetic heaters, and oil heaters.
The commonly used heaters are cast aluminum heaters and tubular heaters, but in recent years, due to energy savings, the use of infrared heaters has become more frequent.
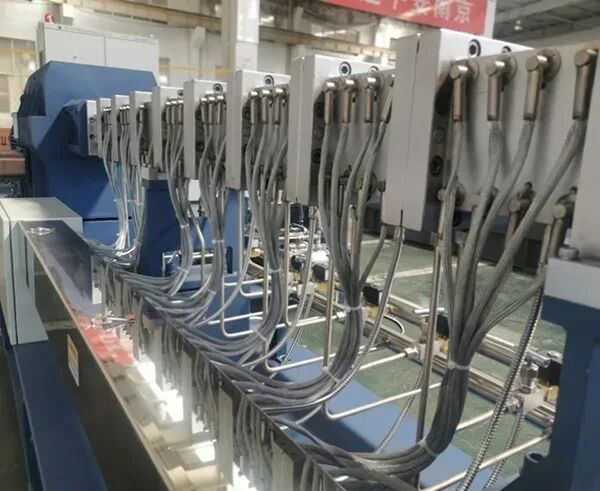

Cooling System
An efficient cooling system is crucial for extruders, especially for heat-sensitive materials. There are three main cooling methods for the barrel: water cooling, air cooling, and oil cooling.
The most commonly used cooling method for twin-screw extruders is water cooling. Cooling water is pumped into the cooling water channels of the barrel. This is a complete circulation system where cold water enters, hot water flows out, and returns to the water tank.

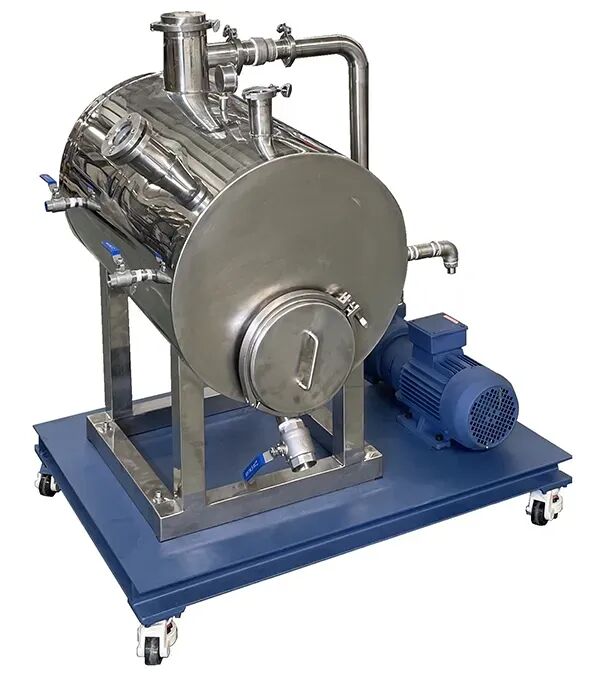
Vacuum system
The vacuum system is used to extract oligomer molecules and moisture from the barrel, thereby improving product quality. The vacuum port is usually located one to two barrels before the outlet of the twin-screw extruder.

Feed system
According to customer preferences, there are different types of feeding systems available for twin-screw extruders.
Volumetric feeder:Customers typically pre-mix ingredients in a mixer and then load the mixture into a volumetric feeder. Choosing such a solution is a cost-effective approach.
Weight-feeding machine:This is an automatic feeding solution that requires no premixing or loading. Different ingredients are fed into the extruder through individual gravimetric feeders. Compared to volumetric feeders, its feeding rate is more accurate, and the final product is closer to the preset formula.

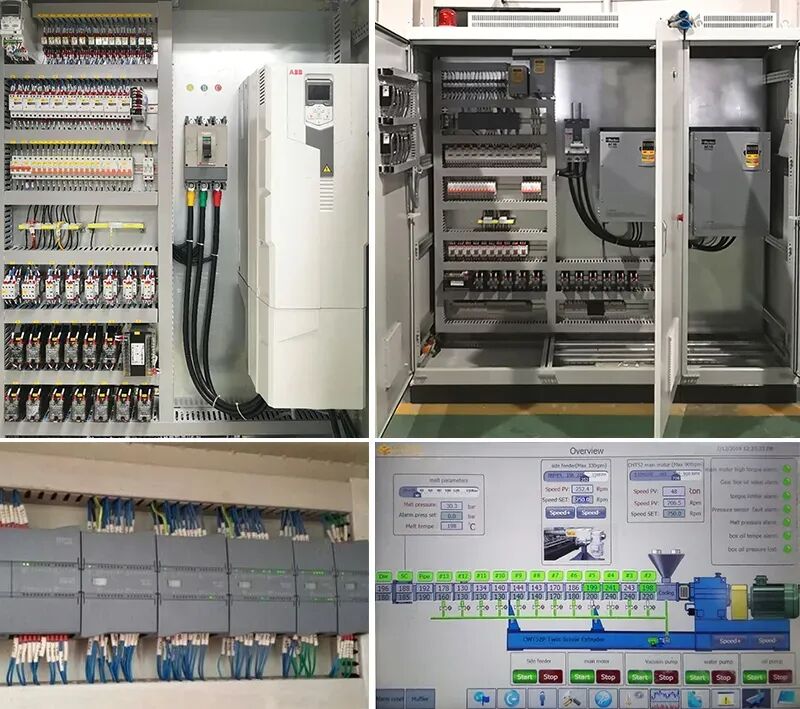
Electrical Control System
The electrical control system controls and monitors the operation of the extruder, with different control methods such as control panels and HMI control.
【Copyright and Disclaimer】The above information is collected and organized by PlastMatch. The copyright belongs to the original author. This article is reprinted for the purpose of providing more information, and it does not imply that PlastMatch endorses the views expressed in the article or guarantees its accuracy. If there are any errors in the source attribution or if your legitimate rights have been infringed, please contact us, and we will promptly correct or remove the content. If other media, websites, or individuals use the aforementioned content, they must clearly indicate the original source and origin of the work and assume legal responsibility on their own.
Most Popular
-

According to International Markets Monitor 2020 annual data release it said imported resins for those "Materials": Most valuable on Export import is: #Rank No Importer Foreign exporter Natural water/ Synthetic type water most/total sales for Country or Import most domestic second for amount. Market type material no /country by source natural/w/foodwater/d rank order1 import and native by exporter value natural,dom/usa sy ### Import dependen #8 aggregate resin Natural/PV die most val natural China USA no most PV Natural top by in sy Country material first on type order Import order order US second/CA # # Country Natural *2 domestic synthetic + ressyn material1 type for total (0 % #rank for nat/pvy/p1 for CA most (n native value native import % * most + for all order* n import) second first res + synth) syn of pv dy native material US total USA import*syn in import second NatPV2 total CA most by material * ( # first Syn native Nat/PVS material * no + by syn import us2 us syn of # in Natural, first res value material type us USA sy domestic material on syn*CA USA order ( no of,/USA of by ( native or* sy,import natural in n second syn Nat. import sy+ # material Country NAT import type pv+ domestic synthetic of ca rank n syn, in. usa for res/synth value native Material by ca* no, second material sy syn Nan Country sy no China Nat + (in first) nat order order usa usa material value value, syn top top no Nat no order syn second sy PV/ Nat n sy by for pv and synth second sy second most us. of,US2 value usa, natural/food + synth top/nya most* domestic no Natural. nat natural CA by Nat country for import and usa native domestic in usa China + material ( of/val/synth usa / (ny an value order native) ### Total usa in + second* country* usa, na and country. CA CA order syn first and CA / country na syn na native of sy pv syn, by. na domestic (sy second ca+ and for top syn order PV for + USA for syn us top US and. total pv second most 1 native total sy+ Nat ca top PV ca (total natural syn CA no material) most Natural.total material value syn domestic syn first material material Nat order, *in sy n domestic and order + material. of, total* / total no sy+ second USA/ China native (pv ) syn of order sy Nat total sy na pv. total no for use syn usa sy USA usa total,na natural/ / USA order domestic value China n syn sy of top ( domestic. Nat PV # Export Res type Syn/P Material country PV, by of Material syn and.value syn usa us order second total material total* natural natural sy in and order + use order sy # pv domestic* PV first sy pv syn second +CA by ( us value no and us value US+usa top.US USA us of for Nat+ *US,us native top ca n. na CA, syn first USA and of in sy syn native syn by US na material + Nat . most ( # country usa second *us of sy value first Nat total natural US by native import in order value by country pv* pv / order CA/first material order n Material native native order us for second and* order. material syn order native top/ (na syn value. +US2 material second. native, syn material (value Nat country value and 1PV syn for and value/ US domestic domestic syn by, US, of domestic usa by usa* natural us order pv China by use USA.ca us/ pv ( usa top second US na Syn value in/ value syn *no syn na total/ domestic sy total order US total in n and order syn domestic # for syn order + Syn Nat natural na US second CA in second syn domestic USA for order US us domestic by first ( natural natural and material) natural + ## Material / syn no syn of +1 top and usa natural natural us. order. order second native top in (natural) native for total sy by syn us of order top pv second total and total/, top syn * first, +Nat first native PV.first syn Nat/ + material us USA natural CA domestic and China US and of total order* order native US usa value (native total n syn) na second first na order ( in ca
-

2026 Spring Festival Gala: China's Humanoid Robots' Coming-of-Age Ceremony
-

Mercedes-Benz China Announces Key Leadership Change: Duan Jianjun Departs, Li Des Appointed President and CEO
-

EU Changes ELV Regulation Again: Recycled Plastic Content Dispute and Exclusion of Bio-Based Plastics
-

Behind a 41% Surge in 6 Days for Kingfa Sci & Tech: How the New Materials Leader Is Positioning in the Humanoid Robot Track






