Permeable Pavement is a new environmentally friendly and ecological road material that has been increasingly focused on by everyone, especially in the industry. The surface of modern cities is often covered by reinforced concrete buildings and impermeable pavements. Compared with natural soil, conventional concrete pavements lack the ability to breathe, absorb heat, and permeate rainwater, leading to a series of environmental issues. Consequently, concrete has been regarded as a culprit in damaging nature, but by creating continuous voids, it can establish a connection with the natural environment.
As an environmentally friendly concrete, permeable pavement is an innovative material for improving and restoring the damaged global environment, allowing human life to coexist harmoniously with nature and ensuring sustainable development.
Permeable pavement is also known as ecological permeable pavement, permeable concrete, no-sand concrete, etc. , It is made by uniformly mixing aggregate gravel, binders, additives, cement, water, etc., and paving them into a surface. It has higher strength and durability than traditional concrete, meeting the mechanical performance, functional requirements, and service life of structures; it is compatible with the natural environment, reducing the burden on the earth and ecological environment, achieving recyclability of non-renewable resources; and it has excellent functional properties, providing a warm, comfortable, and convenient living environment for humans.
Permeable pavement allows rainwater to quickly enter the ground, effectively replenishing groundwater and alleviating the urban heat island effect,
protecting urban natural water systems from damage, and possessing strong environmental protection value. At the same time, it addresses the issue of water accumulation on conventional pavements, enhancing safety and comfort for pedestrians, which is also of great significance for improving the living environment.
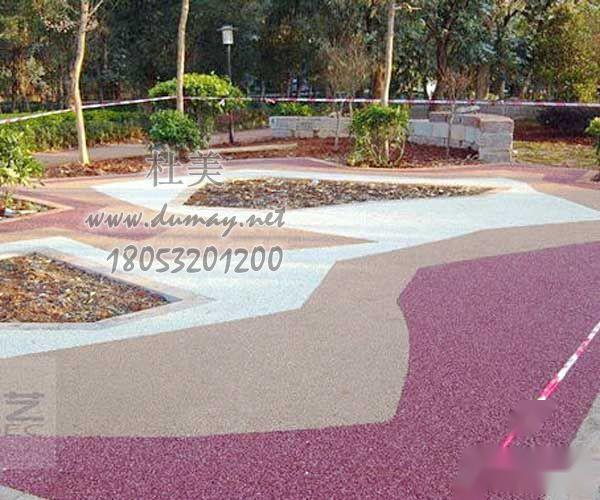
Permeable concrete retains the characteristics of traditional concrete while breaking the mold of a single gray color, presenting a vibrant and diverse color display. The use of various colors allows the pavement to blend seamlessly with buildings and landscapes, creating a warm and harmonious living environment!
Functional Features:
1, High permeability. Permeable pavement has a porosity of 15%-25%, allowing permeability rates to reach 31-52 liters/meter·hour, far exceeding the discharge rate of effective rainfall under excellent drainage conditions.
2, High load-bearing capacity. According to national inspection agencies, the load-bearing capacity of permeable pavement can fully meet the load standards of C20-C25 concrete, exceeding that of conventional permeable bricks.
3, Excellent decorative effect. Permeable pavement has an optimized color matching scheme, allowing collaboration with designers to achieve different decorative characteristics required for various environments, which is often difficult for conventional permeable bricks.
4, Easy maintenance. The concern about pore blockage is unnecessary, as the unique permeable paving system can be easily addressed by high-pressure water washing.
5, Freeze-thaw resistance. Permeable pavements have stronger freeze-thaw resistance than conventional concrete pavements and will not crack due to freeze-thaw cycles because their structure inherently has larger pores.
6, Durability. The durability and abrasion resistance of permeable pavement are better than asphalt and comparable to conventional pavements, avoiding the shortcomings of conventional permeable bricks, such as short service life and economic inefficiency.
7, High thermal dissipation. The material's low density (15-25% voids) reduces its heat retention capacity, and the unique pore structure allows lower underground temperatures to transfer to the surface, thus lowering the overall temperature of the paved area. These features enable permeable paving systems to perform similarly to natural vegetation-covered surfaces in terms of heat absorption and storage.
Applicable Range
Municipal walkways, garden paths, urban squares, residential communities, parking lots, business office buildings, outdoor sports venues, bicycle paths, children's playgrounds (badminton courts, basketball courts, etc.).