PVC
PVC is actually a polymer of vinyl, and the material is an amorphous substance. In practical applications, PVC materials are often mixed with stabilizers, lubricants, processing aids, colorants, impact modifiers, and other additives. It is characterized by non-flammability, high strength, resistance to weather changes, and excellent geometric stability. PVC has strong resistance to oxidizing agents, reducing agents, and strong acids. However, it can be corroded by concentrated oxidizing acids such as concentrated nitric acid and is not suitable for contact with aromatic hydrocarbons and chlorinated hydrocarbons. Additionally, the term "person vs computer" in games is abbreviated as PVC, and PVC figures are often referred to simply as PVC.
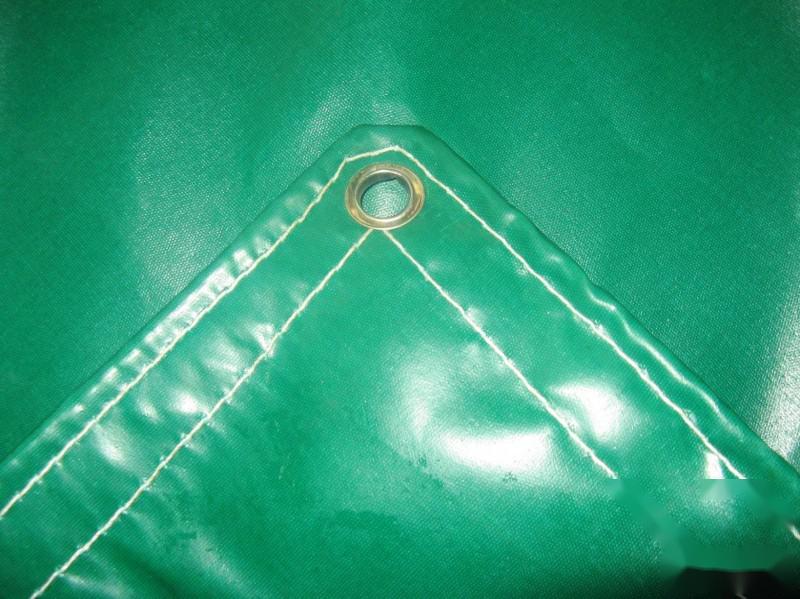
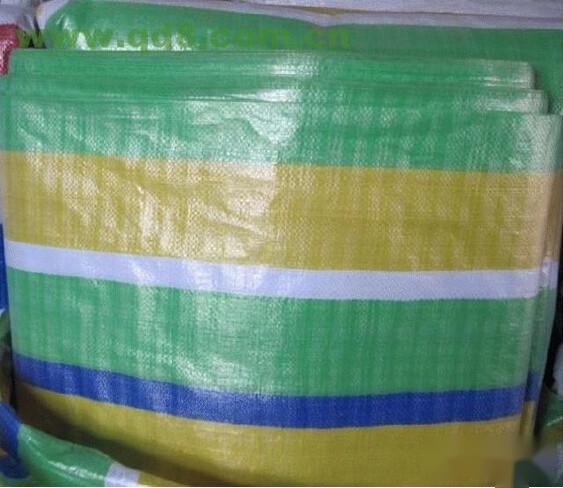
PVC coated fabric is made by applying PVC-containing glue onto the canvas substrate, making its surface smoother and more waterproof. It is now widely used in automotive tarpaulins, train covers, ship covers, outdoor cargo tarps, and in agriculture and industry; it is used in glass factories, timber mills, fertilizer plants, steel structure factories, mechanical hardware factories, feed factories, grain storage, container factories, oil refineries, packaging factories, paper factories, air conditioning factories, logistics companies, ore factories, fleets, railways, maritime transport, pig farms, and more.
Properties
Edit
It has excellent mildew resistance, significant waterproof properties, is relatively more waterproof compared to other canvases, has good low-temperature flexibility, high strength, strong tensile strength, and is relatively lightweight; its applications are very broad, including foreign trade, granaries, oil fields, docks, tents, drilling rig covers, railway and road transportation, storage, coal mines, and outdoor tarpaulin products.