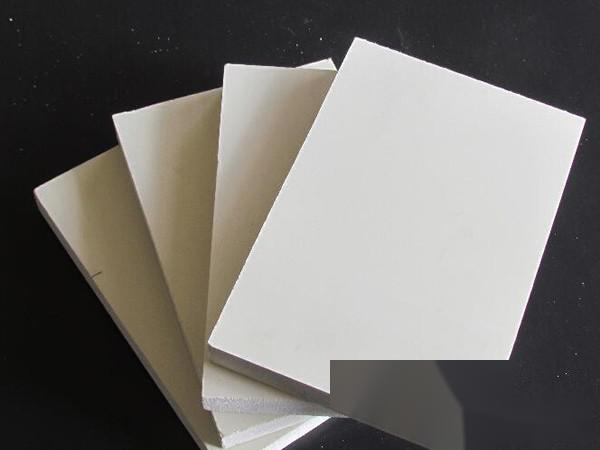
Length: 9m Manufacturer: Baoding Lida Thickness: 9mm
Weight per piece: 0.919kg Application: Industrial corrosion resistance, chemical, electronic, machinery, medicine Width: 1.5m
Pure PP board: Low density, easy to weld and process, with excellent chemical resistance, heat resistance, and impact resistance. Non-toxic and odorless, it is one of the engineering plastics that meet environmental protection requirements. The main colors are white and milky color, and other colors can be customized according to customer needs.
Modified PP board (Calcium-Plastic Board): With good dimensional stability, low price, and improved rigidity and heat resistance compared to pure PP. The colors are generally green, white, and beige. It is mainly used to make water tanks and three-phase separators.
Fiber-reinforced PP board (FRPP board): After being reinforced with 20% glass fiber, it maintains its original excellent properties while having its strength and rigidity doubled compared to PP. It also has good heat resistance, low-temperature impact resistance, corrosion resistance, arc resistance, and low shrinkage rate. It is especially suitable for applications in chemical fiber, chlor-alkali, petroleum, dyeing, food, medicine, light industry, metallurgy, and wastewater treatment.
PP board is a semi-crystalline material. It is harder than PE and has a higher melting point. Because the homopolymer type of PP is very brittle at temperatures above 0°C, many commercial PP materials are random copolymers with 1-4% ethylene or block copolymers with a higher ethylene content. Copolymer type PP materials have a lower heat distortion temperature (100°C), low transparency, low gloss, and low rigidity, but have higher impact strength. The strength of PP increases with the ethylene content. The Vicat softening temperature of PP is 150°C. Due to its high crystallinity, this material has excellent surface rigidity and scratch resistance. PP does not have issues with environmental stress cracking. Typically, PP is modified by adding glass fibers, metal additives, or thermoplastic rubber. The melt flow rate (MFR) of PP ranges from 1 to 40. Low MFR PP materials have better impact properties but lower tensile strength. For materials with the same MFR, copolymer type PP has higher strength than homopolymer type. Due to crystallization, PP has a relatively high shrinkage rate, generally between 1.8% and 2.5%. Additionally, the uniformity of the shrinkage rate is much better than that of materials like PE-HD. Adding 30% glass additives can reduce the shrinkage rate to 0.7%. Both homopolymer and copolymer types of PP materials have excellent moisture resistance, acid and alkali corrosion resistance, and solubility resistance. However, they have no resistance to aromatic hydrocarbon solvents and chlorinated hydrocarbon solvents. Unlike PE, PP does not exhibit antioxidant properties at high temperatures.
Application range: Acid and alkali resistant equipment, environmental protection equipment, wastewater and exhaust gas discharge equipment, washing towers, clean rooms, semiconductor factories and related industrial equipment, also used as materials for manufacturing plastic water tanks. Among them, thick PP sheets are widely used in stamping plates, punch pads, and others.