Optimizing Screw Combination and Feeding to Significantly Improve Impact Strength of Modified ABS (with Solution)
Co-rotating twin-screw extruder is a large category within the twin-screw extruder family, and it is widely usedApplied to polymer blending, filling modification, fiber reinforcement, and reactive extrusion.。
Compared to single-screw extruders, co-rotating twin-screw extruders haveEasy feeding, short material residence time in the screw, excellent mixing and plasticizing effect, and superior venting performance.In the production of modified plastics, co-rotating twin-screw extruders are the core equipment for achieving efficient compounding and enhanced modification. Compared to single-screw extruders, they offer distinct advantages in mixing effectiveness, venting, and feeding flexibility. However, if the complex screw configurations and feeding processes are not optimized, they can lead to a decline in the performance of heat-sensitive materials (such as ABS).
ABS resin is widely used due to its excellent comprehensive properties, but its molecular structure dictates that it is highly susceptible to degradation under high temperature and high shear conditions. When processing ABS using a general-purpose twin-screw extruder with a large length-to-diameter ratio (L/D=40), optimizing the screw "recipe" and feeding strategy becomes crucial for protecting material performance and ensuring product quality. However, there are many operational variables, such as feeding amount, feeding method, and screw configuration. Therefore, in addition to optimizing the product formulation and processing conditions (screw speed, temperature of each screw zone), optimizing the screw combination and feeding process is essential to produce plastic products with excellent mechanical properties.
Acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene (ABS) copolymer is currently one of the engineering plastics with the largest production volume and most extensive applications. It organically combines the various properties of polystyrene (PS), acrylonitrile-styrene (AS) copolymer, and polyacrylonitrile (PAN). It not only possesses balanced mechanical properties of toughness, hardness, and rigidity, but also exhibits good...Chemical resistance, dimensional stability, surface gloss, low-temperature resistance, colorability, and processing flow. etc. ABS has developed extremely rapidly and is widely used inMechanical and Electrical, Home Appliances, TransportationABS is widely used in various fields to manufacture gears, pump impellers, bearings, instrument housings, home appliance housings, and automotive wheel covers. However, due to its susceptibility to degradation under high temperatures or high shear conditions, its mechanical properties are often severely affected during processing by improper screw L/D ratio, screw configuration selection, or unreasonable process control. Typically, extruders for processing ABS have a smaller screw L/D ratio. Our center does not have a low L/D ratio extruder suitable for ABS processing and can only utilize the existing 58 mm co-rotating twin-screw extruder with an L/D ratio of 40.
To ensure product quality and address the issue of decreased mechanical properties during the processing and modification of ABS, the author investigated a 58 mm co-rotating twin-screw extruder. Screw configuration and feeding method Research and optimization were conducted, and analysis was performed. Effects of Optimizing Screw Configuration and Feeding Process on the Mechanical Properties of Modified ABS。
Faced with the above contradiction, our optimization experiment starts with the screw configuration, a core variable. The mainstream modular screw design allows us to combine different screw threads and kneading block elements, like building with Legos, specifically tailored to the characteristics of ABS.
1Influence of Different Screw Configurations on the Mechanical Properties of Modified ABS
Currently, co-rotating twin-screw extruders adopt a modular design, allowing for optimized combinations based on different polymers, formulations, and additive components. Additionally, considering the characteristics of the materials and additives, such as their conveying, melting, and mixing properties, as well as the desired final mechanical performance of the modified polymer, feeding can be done separately through the main feed port of the extruder and downstream feed ports after the plasticizing section. This approach can reduce specific energy input, achieve low-temperature extrusion, and prevent material degradation. The screw combination elements used are two-head conveying elements and kneading elements.
Transport element
Currently, the most commonly used conveying elements for co-rotating intermeshing twin-screw extruders are screw-grooved elements designed based on the principle of relative motion, such as forward screw elements and reverse screw elements, as shown in Figure 1.
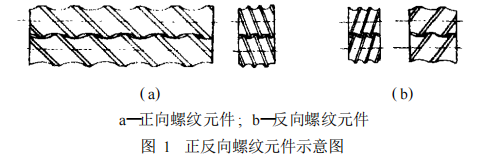
Conveying screw elements are self-wiping, longitudinally open and transversally closed, providing strong conveying action. They have a short material residence time, good self-cleaning properties, and can establish high pressure within a short axial distance. To promote material melting, increase pressure, enhance mixing, and increase material residence time and shear energy input, reverse screw elements should be placed upstream of the venting zone.
(2) Shear Element
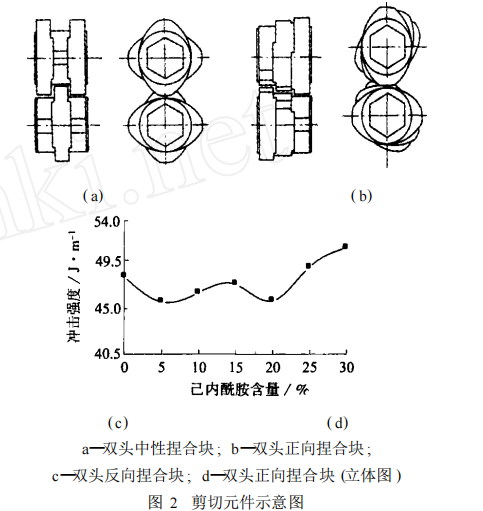
Shear elements mainly refer to kneading block elements commonly used in co-rotating twin-screw extruders. Their primary function is to provide high shear, thereby enabling good dispersive mixing and distributive mixing. Based on their stagger angle, they can be classified into neutral kneading blocks, forward kneading blocks, and reverse kneading blocks. A kneading block with a stagger angle of 90° is called a neutral kneading block. A forward kneading block refers to kneading discs installed in a staggered manner, with the resulting helix angle matching the helix direction of forward screw elements. A reverse kneading block refers to kneading discs installed in a staggered manner, with the resulting helix angle matching the helix direction of reverse screw elements. Figure 2 shows various types of shear elements (kneading blocks).
As can be seen from Table 2, screw configuration 1# has the poorest extrusion performance.
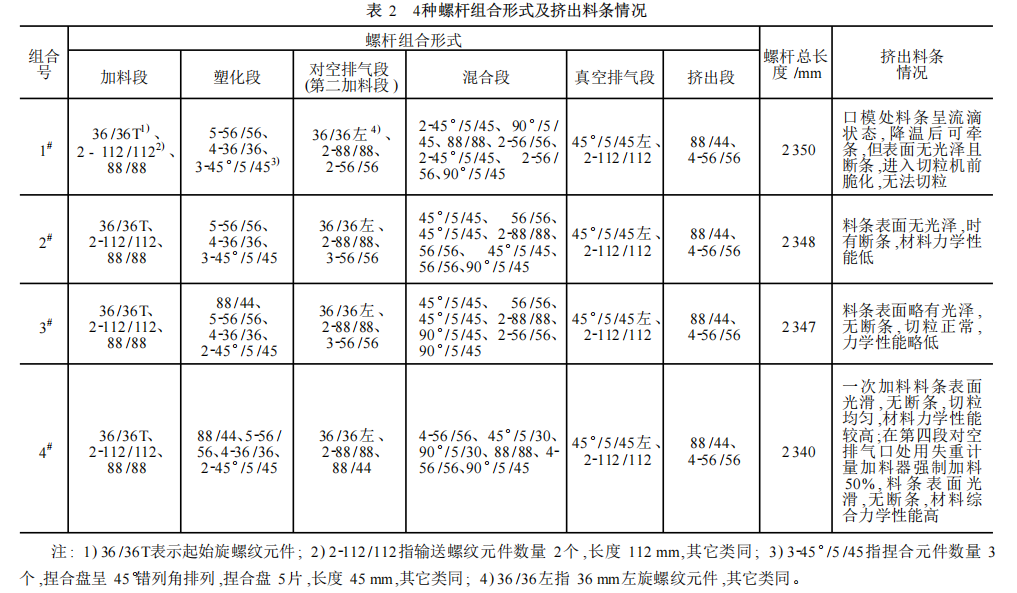
Therefore, under the condition of identical ABS formula, the influence of the 2#~4# screw combination and feeding process on the mechanical properties of modified ABS was investigated, and the results are listed in Table 3.
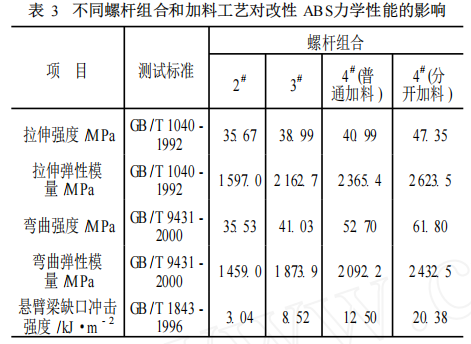
As can be seen from Table 3, different screw combinations have a significant impact on the mechanical properties of modified ABS. From screw combination 2# to 4#, the tensile strength, flexural strength, and notched impact strength of the modified ABS increased significantly, especially the notched impact strength increased the most. The modified ABS extruded with screw combination 4# has the best comprehensive performance, followed by screw combination 3#, and screw combination 2# is slightly lower than screw combination 3#.
The lower comprehensive mechanical properties of modified ABS caused by screw combinations #2 and #3 are mainly due to their excessive pursuit of material dispersion and distributive mixing effects, increasing the number of kneading blocks, while neglecting the impact of a large screw L/D ratio and high shear strength on the performance of modified ABS. Because ABS is a non-Newtonian fluid, its melt viscosity is related to processing temperature and shear rate, especially sensitive to shear rate. Screw combination #4 reduces one 45° kneading block in the plasticizing section and replaces thick kneading block elements with two thin kneading block elements in the mixing section, and also reduces the number of kneading block elements, thus significantly improving the comprehensive mechanical properties of the modified ABS.
2The Impact of Different Feeding Processes on the Mechanical Properties of Modified ABS
Since ABS is extremely sensitive to shear stress and shear rate of the screw, although the screw configuration has been optimized to reduce kneading block elements, the large L/D ratio of the screw itself results in a long residence time of the material within the screw. This leads to repeated compression, backflow, stretching, and shearing, causing a decline in the material's mechanical properties. Therefore, the author installed a loss-in-weight feeder at the downstream glass fiber feeding port to quantitatively add 50% of the material. This portion of the material experiences 1/3 less shear and residence time in the screw, reducing the opportunity for the material's mechanical properties to degrade due to excessive shear and residence time. This significantly improves the overall mechanical properties of the modified ABS.
The modified ABS produced using a #4 screw configuration and a split feeding process exhibited improved mechanical properties, meeting user requirements. Furthermore, this feeding process and optimized screw configuration have similar effects on processing glass fiber reinforced ABS, flame-retardant modified ABS, and other products.
In conclusion, through this system's process optimization, we have not only found a viable solution for processing ABS on specific equipment, but also validated... Refined process control for enhancing the performance of modified plastics: general value. :
Through optimized experiments, a screw configuration suitable for processing modified ABS has been identified. This screw configuration provides gentle shearing of ABS, excellent plasticization, and uniform filler distribution, resulting in improved mechanical properties of the modified ABS.
The comprehensive mechanical properties of modified ABS produced using optimized screw configurations paired with downstream loss-in-weight feeders for material addition are significantly improved.
The screw configuration of a co-rotating twin-screw extruder has a significant impact on the mechanical properties of modified ABS and other modified engineering plastics. Using a reasonable screw configuration is a necessary condition for obtaining modified engineering plastics with excellent comprehensive performance.
Separate feeding can achieve higher extrusion rates, reduce material residence time in the screw, lower shear rates, and realize low-temperature extrusion, which is an effective way to improve the mechanical properties of modified engineering plastics.
【Copyright and Disclaimer】The above information is collected and organized by PlastMatch. The copyright belongs to the original author. This article is reprinted for the purpose of providing more information, and it does not imply that PlastMatch endorses the views expressed in the article or guarantees its accuracy. If there are any errors in the source attribution or if your legitimate rights have been infringed, please contact us, and we will promptly correct or remove the content. If other media, websites, or individuals use the aforementioned content, they must clearly indicate the original source and origin of the work and assume legal responsibility on their own.
Most Popular
-

Key Players: The 10 Most Critical Publicly Listed Companies in Solid-State Battery Raw Materials
-

Vioneo Abandons €1.5 Billion Antwerp Project, First Commercial Green Polyolefin Plant Relocates to China
-

EU Changes ELV Regulation Again: Recycled Plastic Content Dispute and Exclusion of Bio-Based Plastics
-

Clariant's CATOFIN™ Catalyst and CLARITY™ Platform Drive Dual-Engine Performance
-

List Released! Mexico Announces 50% Tariff On 1,371 China Product Categories






