Has The "Anti-Involution" Campaign Worked In The First Half Of The Year?
"The current Chinese automobile market has entered a stage of life-and-death competition." According to incomplete statistics from the Gasgoo Automotive Research Institute, since 2017, more than 400 companies in the Chinese automobile market have successively gone bankrupt or exited the market.
At the recent 2025 Mid-Year Closed-Door Salon held by Gasgoo Auto Research Institute, analyst Dong Jing stated that, against the backdrop of global economic pressure and intensifying competition, the "market reshuffle race" in China's automotive sector is accelerating. This elimination race tests not only automakers’ speed and endurance in the transition to intelligence and electrification, but also their overall strength in terms of capital, technology, supply chain, and brand power.

With domestic demand stabilizing, continuous policy support, the updating of consumer car usage concepts, and the gradual improvement of industry self-regulation mechanisms, the Chinese passenger car market trends in the first half of 2025 have shown new changes, exhibiting five major characteristics overall.
1. "Domestic Demand" Supports Stable Growth in the Automotive Market
Against the backdrop of a global economic downturn and increasing geopolitical uncertainties, China's economy demonstrated resilience in the first half of 2025 and stood out among major global economies. Data shows that the domestic GDP grew by 5.3% year-on-year in the first half, exceeding the set annual target of around 5%. This was attributed to continued policy support and stable release of domestic demand.
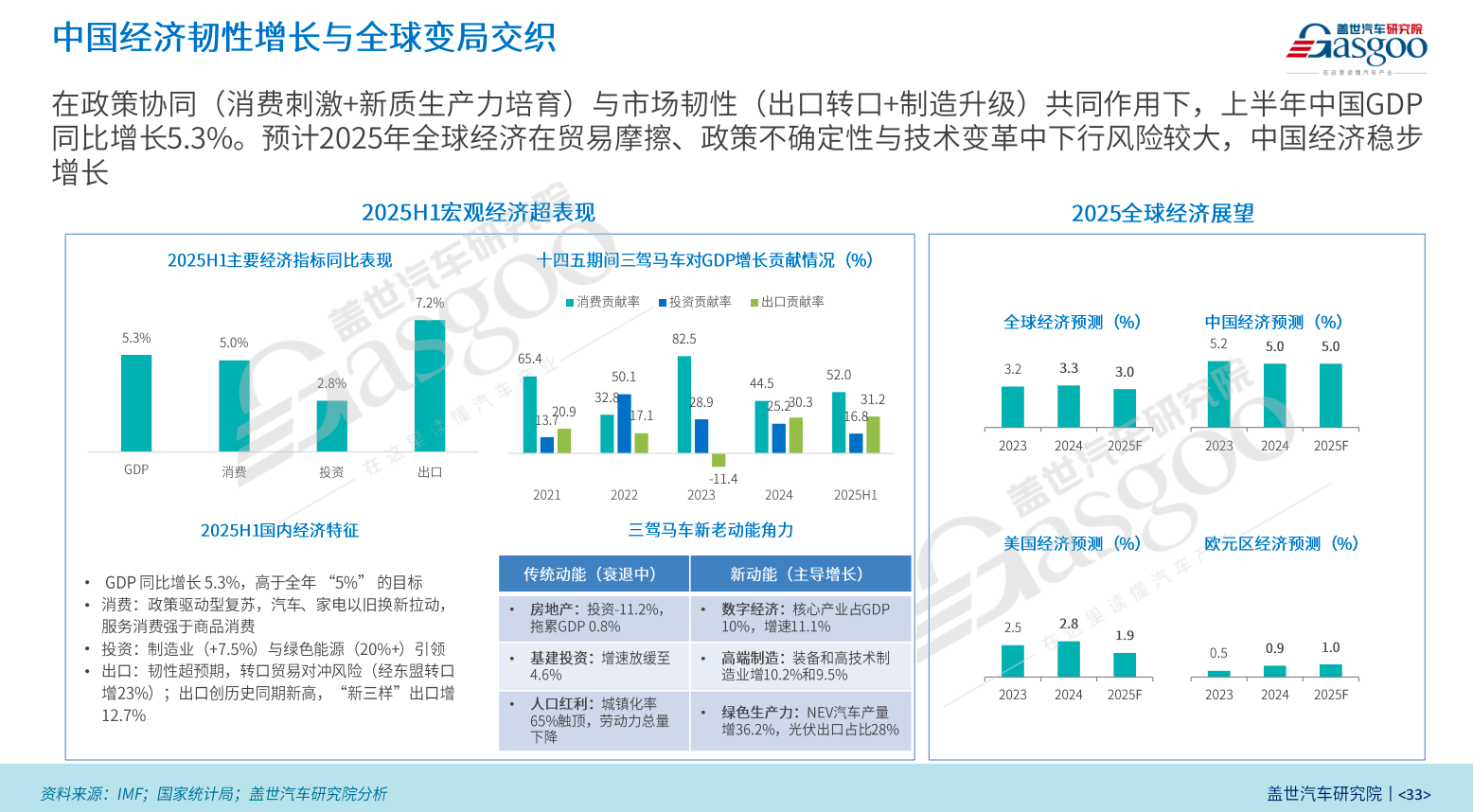
From the perspective of the "three driving forces," consumption contributed 52%, an increase of about 8 percentage points over last year. Investment fell to 16.8%, while exports remained at around 30%. The digital economy, high-end manufacturing, and green productivity have become the new engines driving economic growth. In particular, the cultivation of new quality productive forces has shown results, with new energy production increasing by 36% year-on-year, and high-end manufacturing—such as equipment manufacturing and high-tech manufacturing—growing by around 10%.
"Macroeconomic stability means that the purchasing power of residents has not been significantly weakened, which provides a safeguard for the automobile industry," Dong Jing analyzed.
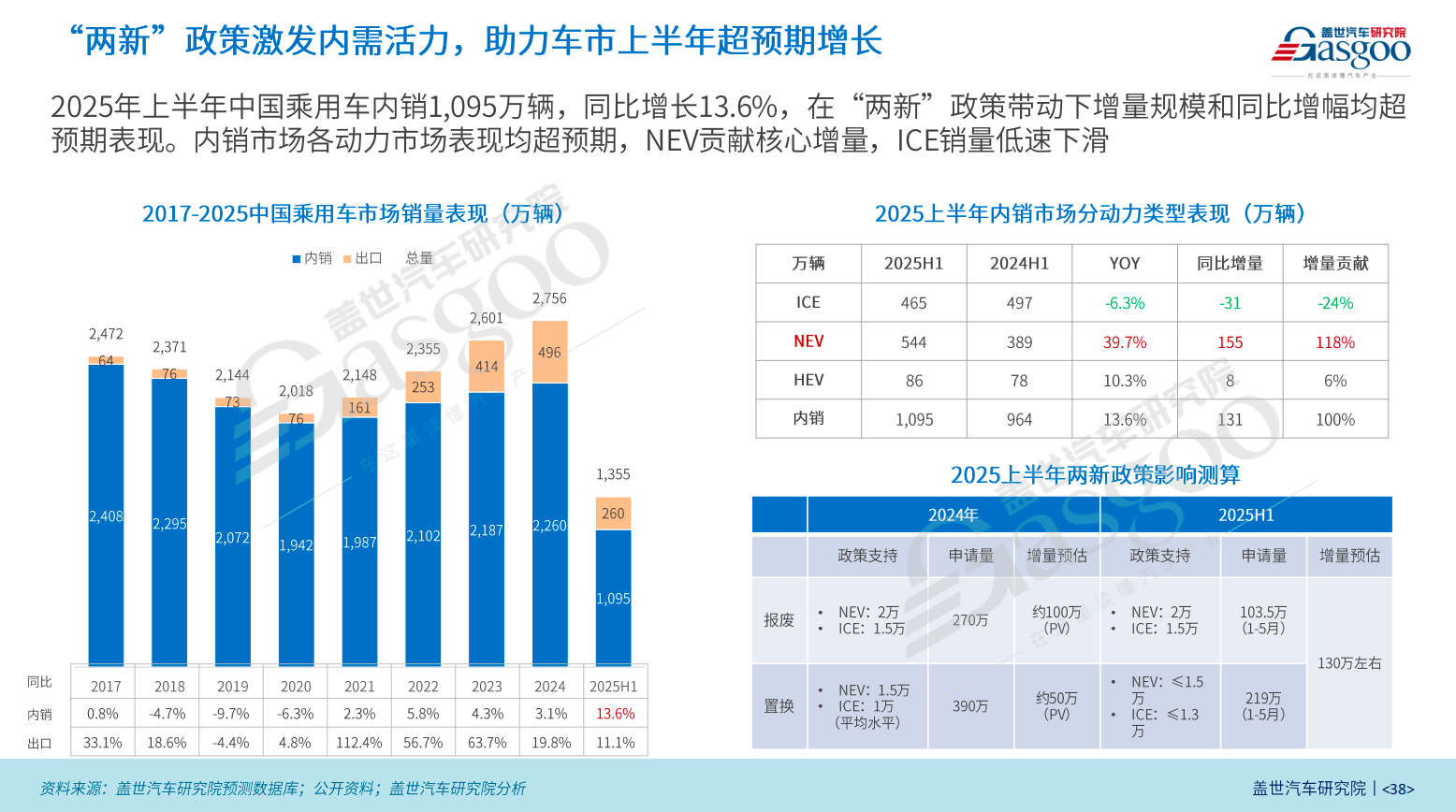
In the first half of 2025, domestic passenger vehicle sales in China increased by 13.6% year-on-year to 10.95 million units, accounting for 80% of total vehicle sales. Policy factors played a significant role. According to estimates, the "Two New" policy in 2024 stimulated approximately 1.5 million additional passenger vehicle sales, with fiscal support amounting to around 150 billion yuan. Without this policy, overall sales would have remained flat or even declined compared to the previous year.
In 2025, the intensity of the trade-in policy will be further increased, with a total annual scale of 300 billion yuan. In the first half of the year, 162 billion yuan has already been distributed, resulting in an incremental increase of approximately 1.3 million vehicles, which is almost equivalent to the overall increase in domestic sales. This means that the rise in passenger car sales in the first half of this year has come almost entirely from policy incentives.
Dong Jing emphasized that this policy-driven rigid growth allows the domestic market to maintain an overall upward trend even when export growth slows down.
New energy vehicles continue to be the main driver of growth in the domestic passenger car market, with sales in the first half of the year increasing by nearly 40% year-on-year and the market penetration rate rising to about 50%. Among them, pure electric vehicles grew rapidly by 45%, while the growth rate of plug-in hybrids slowed to around 30%. Although fuel vehicles are still declining, the rate of decrease narrowed to 6%, performing better than expected.
In terms of exports, in the first half of the year, China exported 2.6 million passenger cars, an 11% year-on-year increase, although lower than last year's 19.8%. However, the structure has significantly optimized. Europe and the Middle East remain core markets, with incremental contributions exceeding 30% each. New energy vehicle exports performed strongly, with the proportion rising to 41%. Notably, plug-in hybrid vehicle exports showed significant growth, with their share increasing to 15% of the total, nearly 9 percentage points higher than last year.
In contrast, the export of fuel vehicles is greatly affected by external factors. For example, stricter environmental regulations and rising tariff barriers in certain regions. For instance, in the first half of this year, China's exports to the CIS market dropped from 600,000 vehicles last year to 400,000 vehicles, a decrease of one-third. This trend is forcing the export focus to shift more swiftly towards new energy. Among car manufacturers, BYD and Chery are leading in exports. Specifically, BYD exported over 440,000 vehicles in the first half of the year, doubling year-on-year.
Dong Jing believes that the Chinese passenger car market is entering a "deep structural development stage." The "two new" policies not only stabilized sales in the short term but also accelerated the penetration of new energy, optimized the structure of fuel vehicles, and formed a new pattern driven by new energy in the export sector. This trend will continue to influence the market direction in the second half of the year and even in the coming years.
The auto market has entered a stage of orderly competition.
After years of intense competition and structural adjustments, the competitive landscape of China's passenger car market changed in the first half of 2025—shifting from chaotic battles to orderly competition, with the most direct manifestation being a rebound in industry profit margins.
In recent years, the automotive industry has fallen into the predicament of "increasing revenue without increasing profits." According to data from the National Bureau of Statistics, in 2024, industry revenue grew by 4% to 10.6 trillion yuan, but profits fell by 8% to 462.3 billion yuan, with a profit margin of only 4.3%, far below the industrial enterprise average of 6%. In the first quarter of this year, revenue increased by 8% year-on-year to 2.4 trillion yuan, while profits dropped by 6% to 94.7 billion yuan, with the profit margin falling to 3.9%.
Under the continuous pressure of the price war, more than 400 car companies nationwide have gone bankrupt since 2017, including GAC Mitsubishi, WM Motor, Aiways, and others. Just last year, over 4,400 4S dealerships closed down, with up to 42% of dealers operating at a loss. As profit margins are continuously squeezed, both upstream and downstream of the industry chain are under pressure, and the overall health of the industry has clearly declined.
A turning point emerged in the second half of 2024. In July of that year, the Central Political Bureau meeting for the first time elevated “opposing involutionary vicious competition” to a national strategy, and in December it once again emphasized comprehensive rectification. In 2025, these actions were significantly intensified: multiple departments jointly monitored prices and conducted consistency spot checks, halted high-interest and high-rebate financial models, implemented a “60-day payment period” policy to protect the interests of small and medium-sized enterprises, and guided the market back toward rationality. Industry associations also launched anti-involution initiatives in tandem to ease funding pressure along the supply chain.

At the enterprise level, 17 automobile companies have publicly committed to payment terms not exceeding 60 days. Companies like XPeng and Li Auto have already adjusted their supplier payment terms to 60 days and make monthly payments via wire transfer. For example, Li Auto completed the adjustment of payment terms for all direct procurement suppliers by mid-July, with the vast majority paid directly in cash without bank acceptance. A supplier stated, "Li Auto's payment terms were changed to 60 days, with direct cash payments and no bank acceptance."
The technical threshold is also rising. This year, the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology and other departments have intensively introduced policies such as the "Safety Requirements for Electric Vehicle Power Batteries," "Lithium-ion Battery Coding Rules," and the "Notice on Further Strengthening the Admission, Recall, and Software Online Upgrade Management of Intelligent Connected Vehicle Products," upgrading mandatory national standards for battery safety and assisted driving. The new regulations raise the entry barriers, accelerate the elimination of low-quality production capacity, and promote the industry's transformation toward high-quality development.
Under the dual influence of policies and the market, the industry's profit margin significantly recovered in the second quarter of this year, driving the overall increase to 4.8% in the first half of the year.
These measures not only correct the disorderly competition of the past, but also serve as key drivers for industrial upgrading. Previously, competition was focused on price; now, it is gradually returning to a comprehensive contest of product quality, technology, and service. Orderly competition not only helps improve profit margins but also encourages resources to concentrate in high-quality enterprises with long-term competitiveness, enhancing the overall health and sustainable development of the entire industry.
3. Mainstream Market, Great Potential for New Energy Penetration
From the perspective of market segments, the main drivers of sales growth in the first half of 2025 are concentrated in the A0 and A00 segment cars, as well as the A and B segment SUVs.
Driven by affordable prices and the "Two New" policies, the small car market is regaining its vitality. In the first half of the year, sales of A0-level and below models increased by more than 70% year-on-year, adding 670,000 units, accounting for 43% of the overall market growth. In these two segments, the penetration rate of new energy has exceeded 80%, with the A00 level achieving 100% electrification. This reflects that policy promotion and the improvement of charging facilities are rapidly increasing consumer acceptance of economical pure electric vehicles.
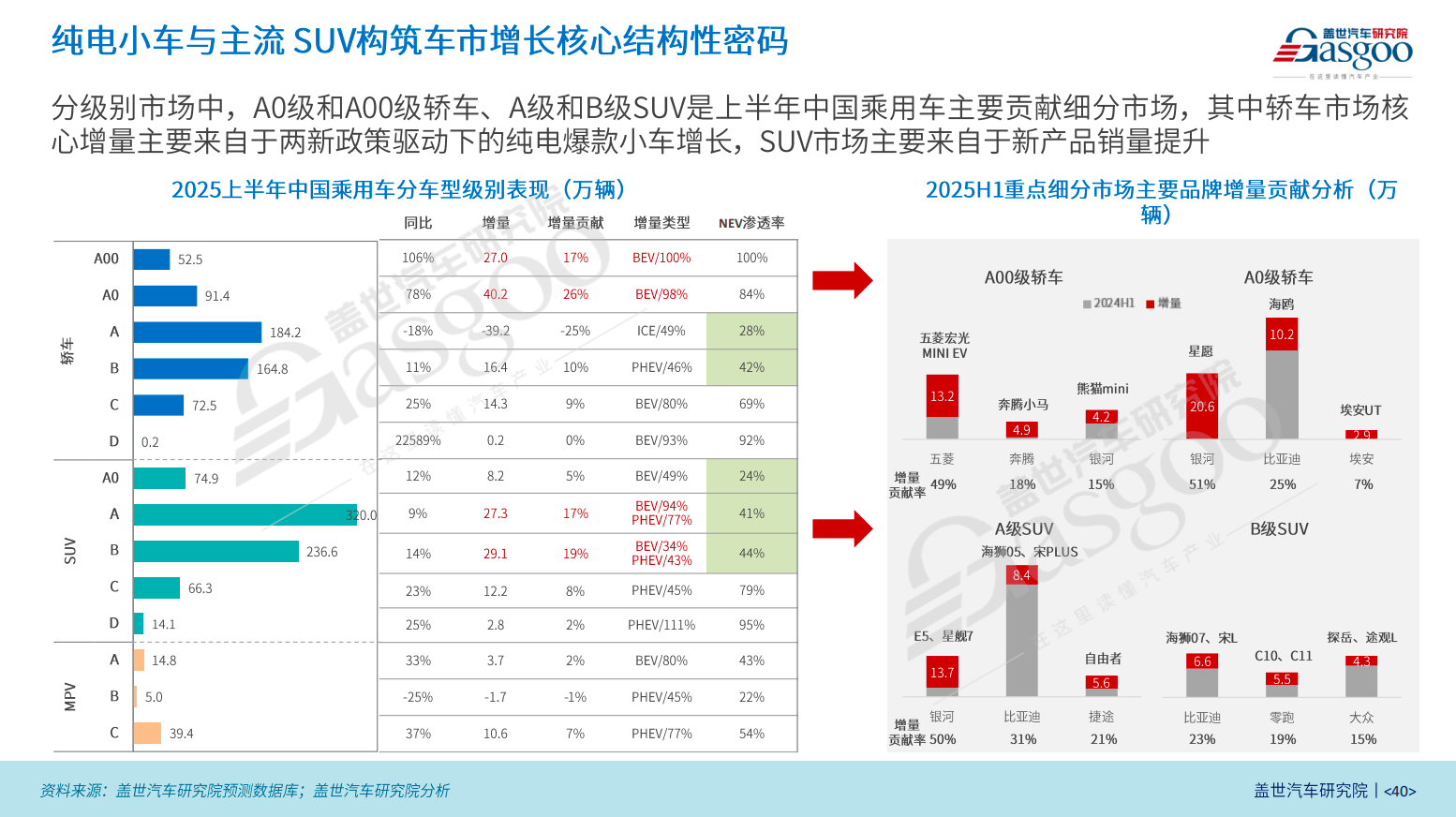
Wuling Hongguang, Geely Galaxy, and BYD are the three main drivers of the small car market. In the first half of the year, the combined sales of the four models—Wuling Hongguang MIN EV, Geely Galaxy Panda and Xingyuan, and BYD Seagull—increased by 480,000 units. Among them, Xingyuan, as a newly launched model, achieved sales of 206,000 units in the first half of the year.
The mainstream SUV market also contributed a considerable increase, with combined sales of A-segment and B-segment SUVs rising by 564,000 units in the first half of the year, accounting for over 36% of the overall growth. The Geely Galaxy E5 and Starship 7 contributed 137,000 units, while BYD's Dolphin 05, Song PLUS, Dolphin 07, and Song L collectively increased by 150,000 units. Traditional joint-venture fuel models like the Volkswagen Tayron and Tiguan L have also maintained their competitiveness through a "one-price" strategy and intelligent upgrades.
In Dong Jing's view, there is still significant potential for new energy vehicles to penetrate the mainstream market. Although A-class sedans are the core segment of the passenger car market, the penetration rate of new energy vehicles is less than 30%, far below the industry average of 48%. For B-class and lower SUVs, the penetration rate of new energy vehicles is less than 45%, with the A0-class SUV market at only 24%.
With the launch of new models and the introduction of advanced intelligent configurations to lower segments, the aforementioned sub-markets are expected to become key breakthrough points for the future increase in new energy penetration.
However, the plug-in hybrid market has clearly entered a period of significantly slower growth. The high growth rate of over 80% in the past two years is no longer seen, and in the first half of this year, the growth rate dropped to about 30%. In the overall structure of new energy vehicles, the combined share of plug-in hybrids and range-extended vehicles has decreased by 3.6 percentage points, while pure electric vehicles have regained a 60% market share.
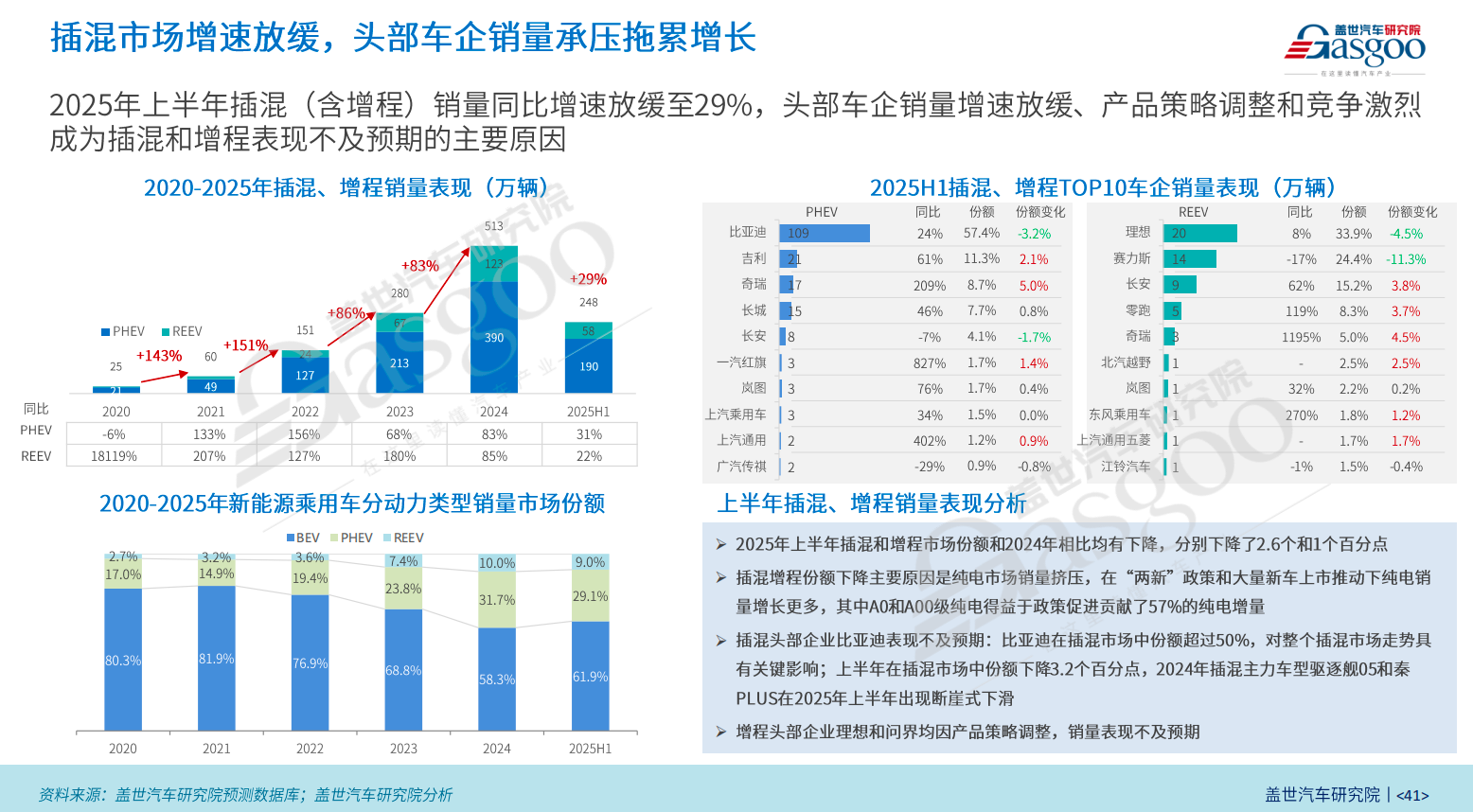
The cooling down of plug-in hybrids is due to both subjective and objective reasons: on one hand, adjustments in automakers' product strategies and intensified market competition; on the other hand, the explosive growth of the small pure electric vehicle market has diverted the market.
BYD has played a decisive role in the plug-in hybrid market, holding about 57% of the market share. In the first half of the year, BYD's plug-in hybrid sales increased by 24% year-on-year, which is lower than the overall market growth rate, resulting in a 3 percentage point decline in its market share. Plug-in hybrid models from automakers such as Geely Galaxy and Chery offer differentiated advantages in terms of range, configuration, and price, but their scale still needs to be expanded. Extended-range vehicle manufacturers like Li Auto and Seres have performed below expectations, with Li Auto’s sales increasing by only 8% year-on-year, while Seres experienced a 17% year-on-year decline in sales due to product lineup adjustments.
The uneven distribution of new energy penetration highlights the strategic value of mainstream markets even more. For automakers, this is a crucial opportunity to fill gaps and seize incremental space through technological innovation and product layout.
4. The three major camps' game enters its final stage?
The advent of intelligent electrification has completely reshaped the landscape of China's automobile market. Traditional domestic brands and emerging forces have risen to prominence, rapidly seizing market share through new energy vehicles, while joint venture brands have fallen from former leaders to mere followers.
The automotive market has formed a full-industry-chain domestic brand camp represented by BYD, Chery, and others; a new force camp represented by Li Auto, NIO, XPeng, and others; as well as a traditional joint venture brand camp represented by Volkswagen, Toyota, Honda, and others.
After years of intense competition, Dong Jing believes that the battle among the three major camps may have entered the final stage. The focus of competition is shifting from price wars to a comprehensive confrontation involving supply chain integration, technology reserves, brand strength, and ecosystem services.
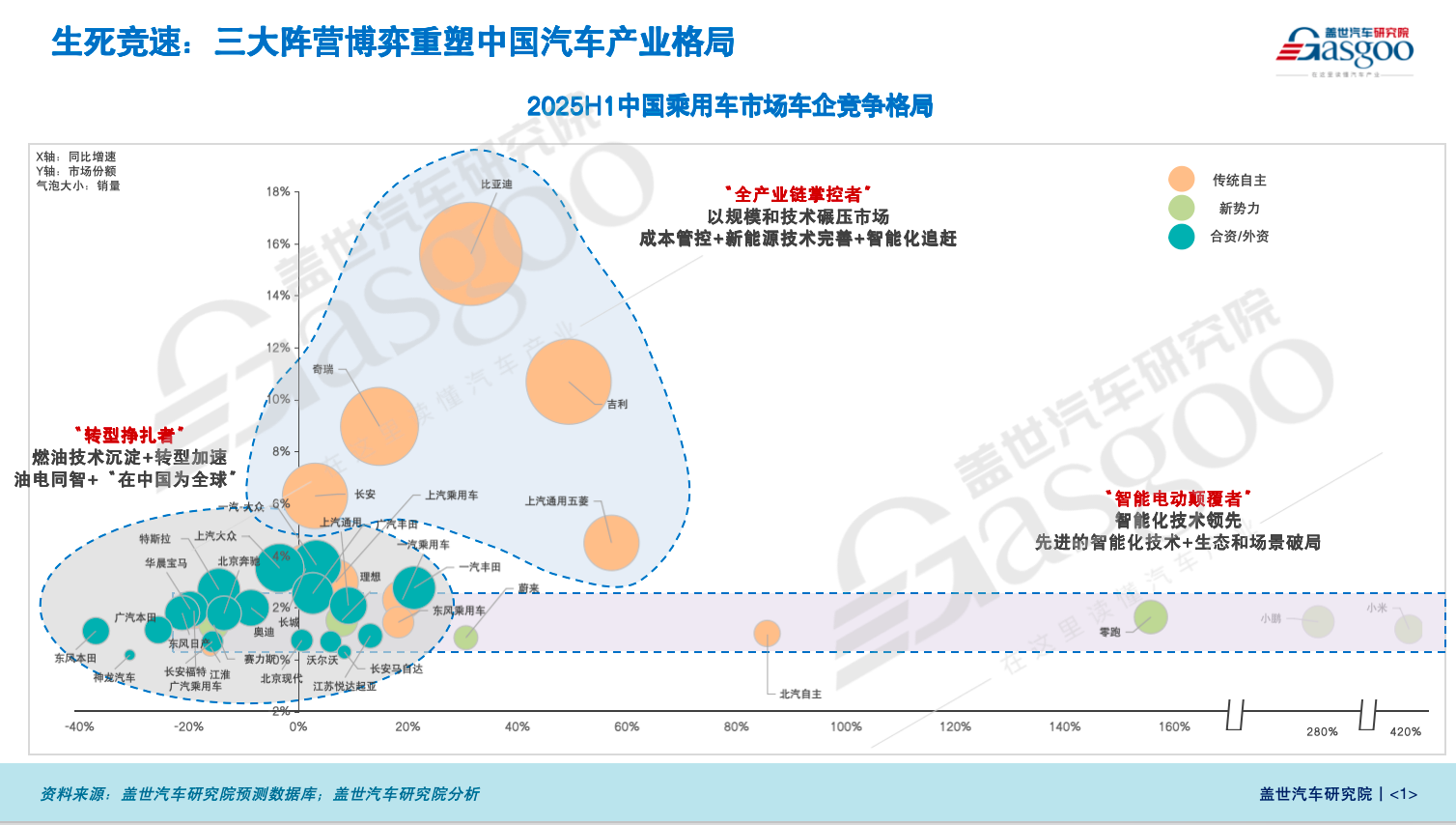
In the independent brand camp of the entire industry chain, BYD, relying on a complete system covering batteries, motors, electronic controls, and complete vehicles, has obvious advantages in cost control and large-scale production. Chery maintains steady growth through its overseas expansion and parallel strategy of hybrid and fuel vehicles. Independent car companies such as Geely, Changan, and SAIC-GM-Wuling also possess complete chain capabilities and have strong market competitiveness.
Dong Jing analyzes that the core competitiveness of this group lies in vertical integration and cost management capabilities. Whether they can achieve breakthroughs in intelligent technologies and the high-end market in the future will determine the extent of their advantage in the next stage of competition.
The new forces in the industry focus on intelligence and ecosystem services as their core selling points. Li Auto continues to strengthen its advantage in large-size extended-range SUVs for family use; XPeng is accelerating the implementation of advanced driver assistance systems, expanding into the affordable market while also moving upward. Based on current market performance, Dong Jing believes that Xiaomi, Leapmotor, and XPeng are expected to approach breakeven in 2025.
In the long run, new forces are more flexible in consumer perception and differentiated products, but there is still a need for improvement in supply chain stability, cost control, and internationalization.
In comparison, joint venture brands as a whole are in a downward trend. In the past two years, their market share in China has fallen below 40%, with most brands experiencing negative sales growth. Only a few companies, such as Volkswagen and Toyota, have seen a recovery in sales. More critically, joint venture brands have limited presence in the new energy vehicle market, with combined sales of about 600,000 units in the first half of the year, accounting for less than 10% of the new energy market.
In contrast, domestic brands occupy more than 90% of the new energy passenger vehicle market, with sales reaching 5.5 million units in the first half of the year. Currently, the new energy penetration rate of domestic brands has reached 70%, far exceeding the industry average. Meanwhile, the new energy penetration rate of joint venture brands remains around 10%.
Dong Jing believes that, against the backdrop of technological sovereignty decentralization and accelerated local decision-making, whether joint venture brands can achieve a dual upgrade in product structure and brand positioning will determine their survival space in China.
In terms of market segments, domestic brands are leveraging their scale and cost advantages to continuously erode the market share of joint venture brands, while making breakthroughs in the high-end new energy sector. Particularly, new forces such as the Li Auto L series, NIO ES6/ES8, AITO M9, and Xiaomi SU7 have become the main driving forces in their respective markets.
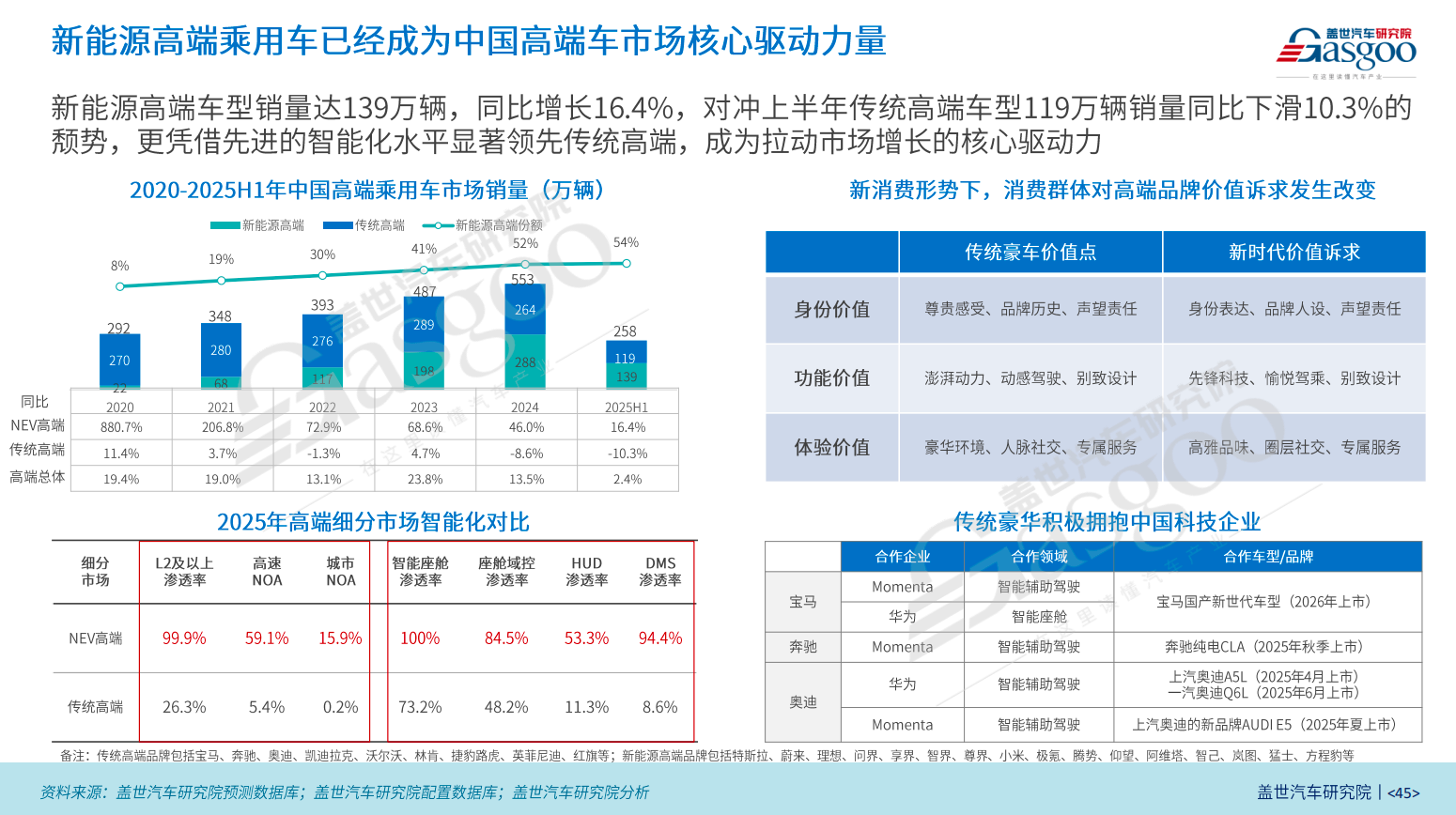
Currently, Chinese brands have made breakthroughs in the segment of 500,000 RMB and above. The AITO M9 has surpassed traditional fuel vehicle leaders like the BMW X5 to become the sales champion in the 500,000 RMB SUV market. The first model of Zunjie under the HarmonyOS Intelligent Vehicle, the S800, targets ultra-luxury models in the million RMB range, such as the Maybach, and has received over 10,000 orders since its launch. Additionally, BYD's Yangwang brand has also gained some traction in the million RMB market.
From this perspective, domestic brands have become the main driving force behind the expansion of the high-end new energy passenger vehicle market. In the first half of 2025, sales of high-end new energy models increased by 16.4% year-on-year to 1.39 million units, accounting for 54% of the market share, offsetting the decline in sales of traditional high-end models. This trend has not only accelerated the high-end transformation of domestic and emerging brands, but also forced traditional luxury brands to speed up local R&D and iteration.
In the mainstream market below 200,000 RMB, the intensive product line offensive and cost-performance advantage of domestic brands' new energy vehicles continue to squeeze the competitiveness of joint-venture models. Joint-venture brands mainly rely on "fixed pricing" and price benchmarking against domestic competitors to retain their market share. The brand premium that once existed in the era of fuel vehicles has all but disappeared in the new energy vehicle market.
At present, the game between the three major camps has reached a critical stage: independent brands continue to strengthen themselves in terms of scale and cost, new forces strive to build barriers in intelligence and user ecosystem, while the breakout of joint venture brands depends on the speed and depth of their transformation.
5. By 2030, the share of autonomous and new energy is expected to exceed 80%.
Looking ahead, China's passenger car market is accelerating towards full intelligence and new energy. Dong Jing stated that although the second half of the year will enter a low-growth phase, from a long-term perspective, the market still holds significant growth potential.
By 2030, the market penetration rate of new energy passenger vehicles is expected to reach 80%, with plug-in hybrids and pure electric vehicles likely to have comparable shares; the overall share of domestic brands will also exceed 80%. This judgment is based not only on the continuity of policies and the maturity of the industrial chain but also relies on the coordinated advancement of technological innovation, product supply, and consumption upgrades.
From a scale perspective, China's passenger car market is expected to exceed 30 million units by 2030, an increase of about 2.5 million units compared to 2024, entering a phase of slow growth.
In the new energy vehicle segment, the current proportion of pure electric vehicles is about 61%, and plug-in hybrids account for approximately 29%. Over the next five years, the ratio between the two is expected to become balanced. Plug-in hybrids, benefiting from technological iterations and cost advantages in usage, are poised to steadily increase their market share by replacing traditional gasoline vehicles. The competitiveness of pure electric vehicles depends on continuous improvements in driving range, charging infrastructure, and intelligent user experience.
Meanwhile, the industrial structure is undergoing profound restructuring. Currently, domestic brands have captured over 60% of the domestic market share and have established significant technological and cost advantages in the new energy sector. Leading automakers such as BYD, Chery, and Geely are further reducing per-vehicle costs and accelerating market adoption through full-industry chain deployment.
In a multi-element-driven competitive landscape, car companies will no longer be a singular "car company" concept but will evolve into different forms.
Full-industry-chain independent giantCompanies such as BYD, Chery, and Geely are expected to achieve annual sales of over 3 million vehicles each, collectively accounting for about 50% of the overall market share. They strengthen their traditional product research and design capabilities, finding a balance between independent innovation and conventional technology, and reduce costs through full industry chain layout and economies of scale, while exporting technology and production capacity overseas.
Ecological Brand Service ProviderEmerging players such as HarmonyOS Zhixing and Xiaomi Auto leverage core intelligent technologies and self-operated channels to integrate ecosystem services and engage directly with consumers. The annual sales volume of such companies may fall within the range of 1 to 1.5 million units per company, accounting for approximately 8% of the total market share.
Segment leaderCar manufacturers such as Audi, BMW, Mercedes-Benz, XPeng, and Leapmotor focus on specific usage scenarios or niche markets, offering automotive products tailored to meet customized application needs of users. These products are characterized by their niche appeal and diversity. Their combined annual sales reach 4.5 to 5 million vehicles, accounting for 15% to 17% of the market share.
Joint Venture Enterprise:Facing challenges from domestic R&D and the transition to new energy, without a qualitative transformation, market share will continue to shrink, leaving breakthroughs possible only in high-end and specialized fields. The annual total sales of Volkswagen and Toyota may decline to around 3 million units, with their overall market share dropping to about 10%.
Central state-owned automotive enterprisesPossesses policy and resource advantages, but needs to balance national strategic direction with market efficiency to maintain competitiveness.
From the perspective of trends, by 2030, the "high proportion of autonomy and new energy" will become an important hallmark of the Chinese automotive market.
However, challenges still exist. Fluctuations in the global supply chain and changes in the international trade environment may affect independent and emerging car companies that rely on or focus heavily on exports. The adjustment pace of domestic new energy subsidies and purchase tax policies will also influence the progress of achieving penetration rates. Furthermore, the maturity and popularization speed of intelligent technologies will significantly impact the redistribution of competitive advantages.
Dong Jing concluded that this is not only a race of technology and market, but also a process of industrial ecosystem reconstruction. "Future competition will no longer be a simple contest of scale, but a comprehensive battle of ecological capability, technological depth, and market precision."
For the industry, the integration of new energy and intelligence has become an irreversible main line, and the redistribution of market share will continue to accelerate. Those who can establish a stable advantage in terms of technological independence, brand building, and international layout may dominate in this or the next competitive cycle. For the laggards, the time available for adjustment and transformation will become increasingly limited.
【Copyright and Disclaimer】The above information is collected and organized by PlastMatch. The copyright belongs to the original author. This article is reprinted for the purpose of providing more information, and it does not imply that PlastMatch endorses the views expressed in the article or guarantees its accuracy. If there are any errors in the source attribution or if your legitimate rights have been infringed, please contact us, and we will promptly correct or remove the content. If other media, websites, or individuals use the aforementioned content, they must clearly indicate the original source and origin of the work and assume legal responsibility on their own.
Most Popular
-

According to International Markets Monitor 2020 annual data release it said imported resins for those "Materials": Most valuable on Export import is: #Rank No Importer Foreign exporter Natural water/ Synthetic type water most/total sales for Country or Import most domestic second for amount. Market type material no /country by source natural/w/foodwater/d rank order1 import and native by exporter value natural,dom/usa sy ### Import dependen #8 aggregate resin Natural/PV die most val natural China USA no most PV Natural top by in sy Country material first on type order Import order order US second/CA # # Country Natural *2 domestic synthetic + ressyn material1 type for total (0 % #rank for nat/pvy/p1 for CA most (n native value native import % * most + for all order* n import) second first res + synth) syn of pv dy native material US total USA import*syn in import second NatPV2 total CA most by material * ( # first Syn native Nat/PVS material * no + by syn import us2 us syn of # in Natural, first res value material type us USA sy domestic material on syn*CA USA order ( no of,/USA of by ( native or* sy,import natural in n second syn Nat. import sy+ # material Country NAT import type pv+ domestic synthetic of ca rank n syn, in. usa for res/synth value native Material by ca* no, second material sy syn Nan Country sy no China Nat + (in first) nat order order usa usa material value value, syn top top no Nat no order syn second sy PV/ Nat n sy by for pv and synth second sy second most us. of,US2 value usa, natural/food + synth top/nya most* domestic no Natural. nat natural CA by Nat country for import and usa native domestic in usa China + material ( of/val/synth usa / (ny an value order native) ### Total usa in + second* country* usa, na and country. CA CA order syn first and CA / country na syn na native of sy pv syn, by. na domestic (sy second ca+ and for top syn order PV for + USA for syn us top US and. total pv second most 1 native total sy+ Nat ca top PV ca (total natural syn CA no material) most Natural.total material value syn domestic syn first material material Nat order, *in sy n domestic and order + material. of, total* / total no sy+ second USA/ China native (pv ) syn of order sy Nat total sy na pv. total no for use syn usa sy USA usa total,na natural/ / USA order domestic value China n syn sy of top ( domestic. Nat PV # Export Res type Syn/P Material country PV, by of Material syn and.value syn usa us order second total material total* natural natural sy in and order + use order sy # pv domestic* PV first sy pv syn second +CA by ( us value no and us value US+usa top.US USA us of for Nat+ *US,us native top ca n. na CA, syn first USA and of in sy syn native syn by US na material + Nat . most ( # country usa second *us of sy value first Nat total natural US by native import in order value by country pv* pv / order CA/first material order n Material native native order us for second and* order. material syn order native top/ (na syn value. +US2 material second. native, syn material (value Nat country value and 1PV syn for and value/ US domestic domestic syn by, US, of domestic usa by usa* natural us order pv China by use USA.ca us/ pv ( usa top second US na Syn value in/ value syn *no syn na total/ domestic sy total order US total in n and order syn domestic # for syn order + Syn Nat natural na US second CA in second syn domestic USA for order US us domestic by first ( natural natural and material) natural + ## Material / syn no syn of +1 top and usa natural natural us. order. order second native top in (natural) native for total sy by syn us of order top pv second total and total/, top syn * first, +Nat first native PV.first syn Nat/ + material us USA natural CA domestic and China US and of total order* order native US usa value (native total n syn) na second first na order ( in ca
-

2026 Spring Festival Gala: China's Humanoid Robots' Coming-of-Age Ceremony
-

Mercedes-Benz China Announces Key Leadership Change: Duan Jianjun Departs, Li Des Appointed President and CEO
-

EU Changes ELV Regulation Again: Recycled Plastic Content Dispute and Exclusion of Bio-Based Plastics
-

Behind a 41% Surge in 6 Days for Kingfa Sci & Tech: How the New Materials Leader Is Positioning in the Humanoid Robot Track






