Guo baohua et al.: Production, Application, Issues, and Recommendations of Biodegradable Mulch Film
Title: Classification and Research and Development Application Status of Biodegradable Mulch Film
Source: Journal of Agricultural Environmental Sciences, 2024, 43(6): 1278-1287.
Authors: Zhang Mingming, Zhou Yingxin, Chen Jingwen, Xu Jun, Xu Jing, Sun Chitao, Weng Yunxuan, Tan Zhijian, Xu Lei, Mi Qinghua*, Guo Baohua*
Note: This article is an excerpt published in June 2024, and the related data may be outdated.
1. Production situation of biodegradable films
Currently, China is the largest producer, seller, and user of biodegradable films in the world.
In the first half of 2023, China had more than ten thousand tons of biodegradable film production and sales, with seven companies producing over one thousand tons. These companies are Shanghai Hongrui Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Shandong Jinan Xin San Plastic Industry Co., Ltd., Henan Yinfeng Plastic Co., Ltd., Qingdao Haiyi Plastic Co., Ltd., Gansu Lanzhou Xinyin Huan Rubber and Plastic Products Co., Ltd., Yunnan Kedi Plastic Co., Ltd., and Jinan Tianyi Plastic Co., Ltd. The company with the highest production and sales is Shanghai Hongrui Biotechnology Co., Ltd., and the province with the highest production and sales is Shandong Province. After 2024,Shandong Blue Ocean Crystal Technology Co., Ltd.A newcomer in the agricultural film industry, the company has received orders exceeding 10 million yuan for agricultural film in the first half of 2025.
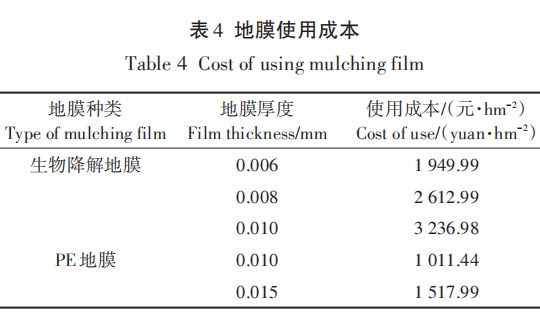
The main raw material PBAT for biodegradable film is priced at 12,000 to 13,500 yuan per ton, while the special blow film material is priced at 15,000 to 18,000 yuan per ton. The factory price for different specifications of film ranges from 21,000 to 25,000 yuan per ton, and the market retail price ranges from 24,100 to 26,800 yuan per ton. Based on the above factory prices and retail prices, the cost of using the film for farmers is shown in the table below.
Currently, the production capacity of hemp mulch made from plant fibers in China exceeds 50,000 tons. Its derivative seedling film has shown significant promotional effects in the cultivation of rice and rapeseed seedlings, with low investment and high output. However, in recent years, the rising prices of hemp fiber raw materials have led to increased production costs, which in turn limits its application in mulch. Paper mulch and other plant fiber mulches are mostly still in the research and development or initial promotion stages. The main factors restricting their application include high production costs, poor resistance to wind and rain, and high water vapor permeability.
2. Application of biodegradable film
Biodegradable plastic film has been widely tested and demonstrated in the country. According to the research team from the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs on the "Current Status and Characteristics of Research and Application of Degradable Plastic Film,"
In the first half of 2023, the demonstration and promotion area of biodegradable film has exceeded 100,000 hectares. The main crops demonstrated include potatoes, sweet potatoes, taro, corn, rice, peanuts, sunflowers, cotton, vegetables (cucumbers, bitter gourds, loofahs, tomatoes, eggplants, garlic, peppers, green beans, kidney beans, radishes, cabbages, asparagus, etc.), tobacco, melons, pineapples, and others.
The region with the largest demonstration application area is Inner Mongolia.
Biodegradable plastic film generally increases yield compared to PE plastic film in the application of medium- and short-growth-cycle crops. The use of black biodegradable plastic film on crops like rice has shown significant effects in terms of weed control and yield increase. It has also shown notable yield improvements in underground tuber crops. Research by Cheng Wanli et al. indicates that, compared to PE film, the use of biodegradable plastic film in the Hexi irrigation area increased potato yield by 13.64%. He Pengcheng et al. compared the effects of different biodegradable films on potato yield, and the results showed that the yield increase with biodegradable plastic film compared to PE film could reach 15.76%.
3. Existing Problems
Biodegradable mulch films have made significant contributions to ensuring the safe supply of agricultural products in China and protecting the ecological environment. However, in the process of practical promotion and application, biodegradable mulch films still face a series of challenges and issues.
(1) Insufficient research on adaptive matching. The performance of biodegradable mulching film is influenced by various factors, including material composition and application environmental conditions. Different regions, crops, and seasons have varying functional requirements for mulching films, such as moisture retention, temperature maintenance, breathability, weed suppression, and pest repellent. Currently, there is a lack of crop-specific biodegradable mulching films that precisely match performance and functionality.
(2) The low-cost modification and performance regulation technology needs to be improved. Compared to traditional polyethylene (PE) film, the cost of biodegradable film is about twice as high, and its moisture retention, thermal insulation, and weather resistance properties still need enhancement. There is an urgent need to develop high-performance, low-cost biodegradable materials and modification technologies.
(3) The technical standards for the entire chain are urgently needed to be improved. Although China has established product standards for fully biodegradable agricultural ground cover films, the comprehensive technical standard system that covers the entire chain—from the production, sales, and use of biodegradable films to degradation monitoring and residue treatment—is still in need of improvement. At the same time, there is a lack of product and application technology standards for biodegradable films that are specific to certain regions and crops.
(4) The awareness of scientific applications is not high. The application of biodegradable film not only addresses the issue of film pollution at the source but also reduces the costs associated with film recovery. However, the awareness and acceptance of the scientific application technology of biodegradable film among the majority of farmers still need to be improved. There is a need to further strengthen the training, publicity, and promotion of biodegradable film application technology.
(5) Supporting policies, regulations, and management measures are still not sound. At the national level, relevant policies and regulations have been established to encourage and support the research, production, and use of biodegradable plastic films, but local supporting regulations and policies are not yet sound, including ecological subsidies, tax incentives, and other incentive mechanisms, as well as strict quality control of biodegradable plastic films and supervision systems for non-standard films.
4. Countermeasures and Suggestions
The promotion and use of biodegradable film in our country has received full recognition from society and has achieved important phased results. However, it is necessary to further improve policies, regulations, and systems, as well as the demonstration and promotion system. We should increase innovation and demonstration support, enhance promotion training and publicity efforts, expand the pilot scope based on the existing pilot provinces and cities, and take the following relevant measures:
(1) Improve policies, regulations, and management measures. It is recommended that relevant departments enhance support policies for biodegradable film, strengthen market supervision of non-standard films, and regulate the main raw materials, relative biodegradation rates, thickness, tensile properties, light transmittance, ecological toxicity tests, and field usage of biodegradable films; establish management measures and work mechanisms for regular inspections of product production, field applications, and soil health; prohibit the use and promotion of photodegradable films; strengthen the precise matching of scientific usage funding for plastic films with local crop needs; implement management measures such as a production license or access system for biodegradable film, a factory sales usage ledger system, and a government promotion subsidy tendering system; ensure traceability of products through coding; standardize the use of national financial project funds, enhance the timeliness and supervision of fund allocation, and avoid additional costs and price differences due to delays in fund disbursement.
(2) Strengthen the investment in the production capacity of new biodegradable film. In response to the issues of mismatched coverage needs of biodegradable film products with crops, seasons, and regional characteristics, optimize resource allocation, enhance research and development of specialized materials for biodegradable film, low-cost modification, and processing innovation technologies. Conduct supporting research on the scientific application of biodegradable film in different regions, for different crops, and in different seasons, continuously extending the innovation chain and improving the industrial chain; establish a scientific and effective monitoring and evaluation system for the application of biodegradable film, and strengthen the scientific application of evaluation results; enhance the investment from governments at all levels and enterprises in the research and development and application demonstration of biodegradable film technology. In pilot projects for the scientific application of film, support research on film functions and agronomic machinery matching, regional application technologies, etc., at a certain percentage of the funding; guide enterprises to independently invest in related technology research and development and application demonstration work, forming new productive forces brought by the application of biodegradable film technology.
(3) Establish a full-chain technical standard and application regulations. Improve national standards for special materials for biodegradable film, product industry standards, and local application standards. Encourage and guide enterprises to formulate product enterprise standards in the production of film, establish a product traceability system, and standardize the preparation of product usage manuals. In the packaging and storage phase, develop corresponding requirements based on the performance characteristics of different biodegradable films. In the field application phase, establish application guidance manuals and technical regulations for film usage in different regions and for different crops, to guide the scientific and standardized application of biodegradable films.
(4) Strengthen popular science and publicity efforts. Multiple departments should work together to utilize radio, television, and new media to enhance the promotion of the significance and technology of biodegradable film applications; agricultural technology promotion departments at all levels and research and production units should collaborate to develop training lesson plans and promotional materials for the scientific use of film, actively conducting training and experience exchange activities for planting enterprises, cooperatives, large-scale farmers, and agricultural technicians on the application of biodegradable film, to improve the awareness and acceptance of relevant personnel regarding biodegradable film.
【Copyright and Disclaimer】The above information is collected and organized by PlastMatch. The copyright belongs to the original author. This article is reprinted for the purpose of providing more information, and it does not imply that PlastMatch endorses the views expressed in the article or guarantees its accuracy. If there are any errors in the source attribution or if your legitimate rights have been infringed, please contact us, and we will promptly correct or remove the content. If other media, websites, or individuals use the aforementioned content, they must clearly indicate the original source and origin of the work and assume legal responsibility on their own.
Most Popular
-

Key Players: The 10 Most Critical Publicly Listed Companies in Solid-State Battery Raw Materials
-

Vioneo Abandons €1.5 Billion Antwerp Project, First Commercial Green Polyolefin Plant Relocates to China
-

EU Changes ELV Regulation Again: Recycled Plastic Content Dispute and Exclusion of Bio-Based Plastics
-

Clariant's CATOFIN™ Catalyst and CLARITY™ Platform Drive Dual-Engine Performance
-

List Released! Mexico Announces 50% Tariff On 1,371 China Product Categories






