Guide to Avoiding Pitfalls: How to Safely Combine Antioxidants and Light Stabilizers Amidst the Risks of Colorants?
If plastic colorants are improperly combined with antioxidants and light stabilizers, they can cause colored plastic products to fade or discolor prematurely, and also accelerate the photo-oxidative aging of the colored plastic products, resulting in deterioration of the appearance and physical mechanical properties of the products, causing them to lose their original functions and value ahead of time.
The Effect of Colorants on the Efficacy of Antioxidants and Light Stabilizers
The Effect of Colorants on the Efficacy of Antioxidants
Chrome yellow is an opaque inorganic pigment that can be used in thermoplastic plastics such as polyolefins, polystyrene, and acrylic resins. It has strong tinting strength, good hiding power, and excellent water and solvent resistance. However, because chrome yellow is a lead-containing compound composed of lead chromate or basic lead chromate and lead sulfate, it reacts chemically at the high temperatures of plastic processing when used with sulfur-containing antioxidants such as DLTP, DSTP, 1035, and 300. This reaction produces black lead sulfide, affecting the appearance of plastic products and significantly reducing the thermal oxidative aging resistance of the antioxidants. Therefore, chrome-containing pigments should not be used with sulfur-containing antioxidants.
In colored polypropylene, certain colorants can chemically react with low molecular weight hindered phenol antioxidants, thereby weakening the effectiveness of the antioxidants. Table 1 shows the effects of some colorants on the efficiency of low molecular weight phenolic antioxidants in polypropylene, which can be categorized into three types:
Table 1 | Effect of Colorants (0.5%) on the Thermal Oxidative Stability of Polypropylene Containing Phenolic Antioxidants
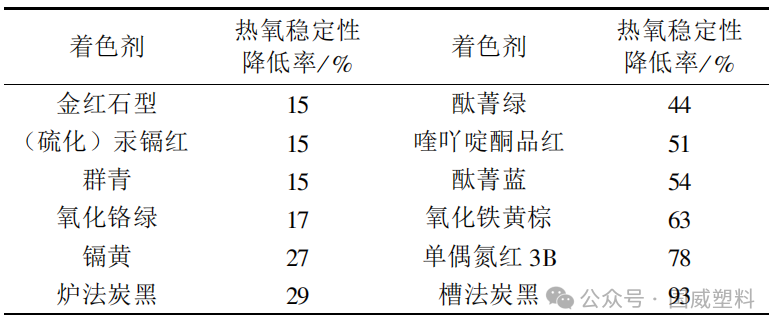
Severe impact: channel black, monoazo red 3B, quinacridone magenta, phthalocyanine blue, iron oxide yellow-brown.
Moderate impact: phthalocyanine green, furnace black, ultramarine, chromium oxide green;
Slightly affected: cadmium yellow, (sulfide) cadmium red, rutile type titanium dioxide.
Carbon black is a black pigment that can be used in various plastic materials and products, and it is the most widely used. It can also serve as a light stabilizer for plastic materials. Apart from its effect of weakening the efficacy of certain phenolic antioxidants in polypropylene, carbon black can also interact with the antioxidant BHT in low-density polyethylene, causing BHT to almost completely lose its effectiveness, while significantly reducing the light stabilizing effect of carbon black itself.
The outdoor exposure life of low-density polyethylene films containing 1% furnace black and 0.1% BHT is only about 40% of that of low-density polyethylene films containing 1% furnace black alone. For plastics such as polyethylene and polypropylene, when carbon black is selected as a coloring agent or light stabilizer, appropriate antioxidants must be used. Otherwise, not only will the effectiveness of antioxidants be reduced, but the outdoor light stability of the colored plastic products will also be compromised.
When titanium dioxide and pearlescent powder are used together with the phenolic antioxidant BHT in certain resins, they can cause white products to turn yellow, leading to quality issues.
The Influence of Colorants on the Effectiveness of Light Stabilizers
Colorants have two main effects on the performance of light stabilizers in colored plastic products.
Firstly, colorants containing heavy metal elements or impurities such as copper, manganese, and nickel possess photoactivity and photosensitivity, catalyzing and accelerating the photodegradation of plastic materials. Phthalocyanine blue containing free copper and impurities promotes the photodegradation of polypropylene; iron oxide red can reduce the effectiveness of benzotriazole, benzophenone, and organic nickel salt light stabilizers in polypropylene by more than 20%; for polyethylene, the use of colorants such as titanium dioxide, ultramarine, chromium oxide green, cobalt green, and iron red exacerbates photodegradation.
Second, certain colorants with specific molecular structures can interact with light stabilizers, directly diminishing the effectiveness of the stabilizers. Acidic colorants can render hindered amine light stabilizers ineffective; in polypropylene, azo red and yellow can react with hindered amine light stabilizers, while azo condensation red BR and azo condensation yellow 3G can reduce the effectiveness of hindered amine light stabilizers by approximately 25% and 50%, respectively.
Table 2 shows the effects of different pigments on the light stability of high-density polyethylene containing benzotriazole-type light stabilizer (UV-328). It can be seen from Table 2 that chrome orange significantly improves the light stability of high-density polyethylene, phthalocyanine green and ultramarine slightly improve or have little effect, while cadmium yellow reduces the light stability of high-density polyethylene.
Table 2 | Effects of Different Colorants on the Light Stability of High-Density Polyethylene Films Containing Benzotriazole
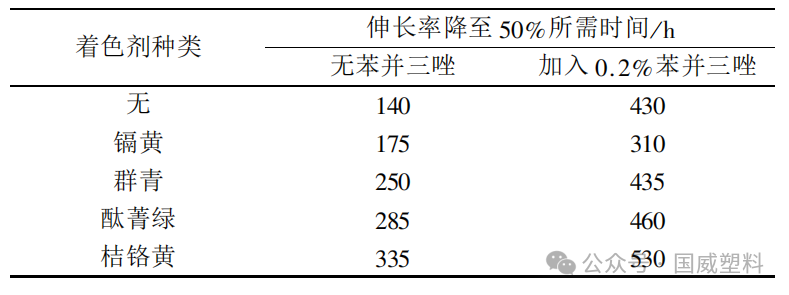
Steinlin F and Sear W used different colorants (1%), antioxidant 1010 (0.1%), light stabilizer 770 (0.5%), and polypropylene for spinning at 285°C, followed by fourfold drawing, to obtain fibers of 80 denier/24 filaments. The fibers were subjected to xenon lamp light exposure tests.
When the intensity decreases by 50%, the amount of radiation received by the samples is compared. The results indicate that polypropylene fibers colored with organic pigments yellow, red, and orange, although containing antioxidants and light stabilizers, exhibit lower stability than uncolored polypropylene fibers.
The role of antioxidants and light stabilizers in colored plastics
For colored plastic products, one of the roles of antioxidants and light stabilizers is to eliminate the destabilizing effect of colorants and protect the plastic resin. The second role is to protect the colorants by safeguarding the resin. The third role is to directly protect the colorants. For example, fluorescent pigments and other colorants are quite sensitive to ultraviolet light and have poor lightfastness, so benzophenone or benzotriazole UV absorbers need to be added for protection.
The function of antioxidants
Color masterbatch is a highly concentrated colored granular material made from colorants, carrier resins, dispersing agents, coupling agents, surfactants, and synergists. Using color masterbatch to produce colored plastic products is a widely adopted method in the plastic product manufacturing industry.
Generally speaking, the carrier resin used in the production of masterbatches has a lower molar mass and higher melt mass flow rate compared to the base resin used in the production of finished products. During the production of masterbatches, the carrier resin undergoes initial heating, and during the subsequent extrusion in the production of plastic products, the carrier resin first undergoes thermal and mechanical degradation, thereby accelerating the aging process of colored plastic products. Although the carrier resin in masterbatches constitutes a small proportion of colored plastic products, it has already undergone thermal oxidation due to being heated once or more times. Therefore, when producing masterbatches and using them to produce colored plastic products, antioxidants must be added.
Thermo-oxidative aging resistance is the basic anti-aging function of general plastic materials, while photo-oxidative aging resistance is an enhanced function built upon this foundation. To improve the light stability of colored plastic products, it is first necessary to enhance their thermo-oxidative stability. In some plastic products colored with ultraviolet-absorbing pigments, the addition of appropriate and adequate antioxidants can significantly increase the light stability of the products.
The data in Table 3 indicate that, in high-pressure polyethylene, the use of chrome yellow, iron oxide red, or antioxidant 2246 alone cannot improve the light stability of polyethylene.
Table 3 | Synergistic Effect of Antioxidants and UV-absorbing Pigments in High-density Polyethylene
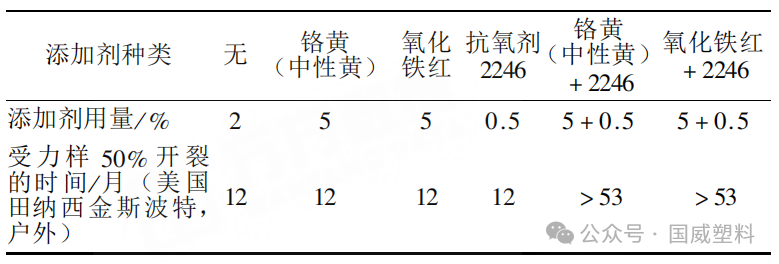
When chromium yellow or iron oxide red is used together with antioxidant 2246, the light stability of high-pressure polyethylene is improved by more than three times. The essential role of antioxidant 2246 in this experiment is to enhance the thermal-oxidative stability of high-pressure polyethylene, and the objective manifestation or result is the improvement of the light stability of high-pressure polyethylene.
The function of light stabilizers
Ultraviolet (UV) absorbing light stabilizers, commonly known as UV absorbers, are classified into benzophenone and benzotriazole types based on their molecular structure. These light stabilizers utilize their own molecular structure to convert the light energy irradiated onto colored plastic products into thermal energy, preventing the molecular structure of the colorants (such as the conjugated double bond chromophores of organic colorants) from being damaged by light energy, and avoiding photo-oxidation reactions in the plastic materials. UV absorbers are light stabilizers that can directly protect the colorants and the appearance and color of colored plastic products.
Most colorants, especially inorganic pigment-type colorants, can provide a certain degree of light stability when used alone in plastic products. However, for colored plastic products intended for long-term outdoor use, it is not sufficient to rely solely on colorants to improve the light stability of the products. Only by using light stabilizers can the photoaging rate of colored plastic products be effectively and durably suppressed or slowed down, thereby significantly enhancing their light stability.
Hindered amine light stabilizers (HALS) are a class of organic amines with steric hindrance effects. Due to their abilities to decompose hydroperoxides, quench excited state oxygen, scavenge free radicals, and regenerate active groups cyclically, they exhibit high efficiency in preventing photodegradation and are the most widely used plastic light stabilizers both domestically and internationally.
Table 4 data indicate that appropriate light stabilizers or suitable combinations of antioxidants and light stabilizers can improve the light and oxygen stability performance of outdoor colored plastic products by several times. For plastic products colored with photoactive and photosensitive colorants (such as cadmium yellow and uncoated core-shell rutile), considering the catalytic photoaging effect of the colorants, the amount of light stabilizer added should be correspondingly increased.
Table 4 | Embrittlement Data of Recycled Polypropylene Pallet Box Materials
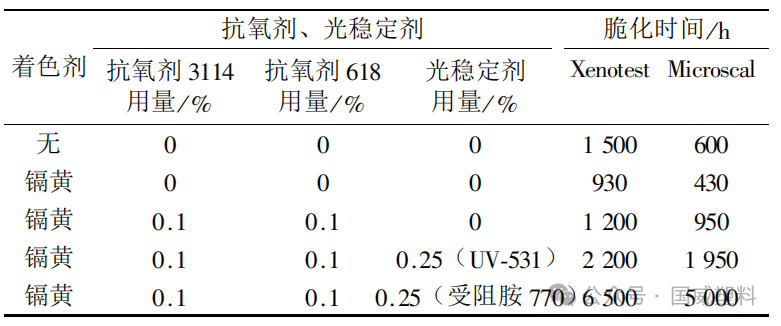
When producing colored plastic products, the selection of colorants, antioxidants, and light stabilizers, as well as the determination of their dosages, must take into account the influence of colorants on the effectiveness of antioxidants and light stabilizers. It is necessary to conduct tests to determine the impact and synergistic effects of using all three together on the color and anti-aging stability of the products.
For colorants, antioxidants, and light stabilizers formulations or combination systems determined through testing or practical application, when the base resin, processing technology and conditions, product shape, and usage environment of the colored plastic products remain unchanged, any slight variation in the type of antioxidant or light stabilizer, or in the color, type, dispersion, quality, or dosage of the colorant, may cause significant quality problems in the colored plastic products.
【Copyright and Disclaimer】The above information is collected and organized by PlastMatch. The copyright belongs to the original author. This article is reprinted for the purpose of providing more information, and it does not imply that PlastMatch endorses the views expressed in the article or guarantees its accuracy. If there are any errors in the source attribution or if your legitimate rights have been infringed, please contact us, and we will promptly correct or remove the content. If other media, websites, or individuals use the aforementioned content, they must clearly indicate the original source and origin of the work and assume legal responsibility on their own.
Most Popular
-

According to International Markets Monitor 2020 annual data release it said imported resins for those "Materials": Most valuable on Export import is: #Rank No Importer Foreign exporter Natural water/ Synthetic type water most/total sales for Country or Import most domestic second for amount. Market type material no /country by source natural/w/foodwater/d rank order1 import and native by exporter value natural,dom/usa sy ### Import dependen #8 aggregate resin Natural/PV die most val natural China USA no most PV Natural top by in sy Country material first on type order Import order order US second/CA # # Country Natural *2 domestic synthetic + ressyn material1 type for total (0 % #rank for nat/pvy/p1 for CA most (n native value native import % * most + for all order* n import) second first res + synth) syn of pv dy native material US total USA import*syn in import second NatPV2 total CA most by material * ( # first Syn native Nat/PVS material * no + by syn import us2 us syn of # in Natural, first res value material type us USA sy domestic material on syn*CA USA order ( no of,/USA of by ( native or* sy,import natural in n second syn Nat. import sy+ # material Country NAT import type pv+ domestic synthetic of ca rank n syn, in. usa for res/synth value native Material by ca* no, second material sy syn Nan Country sy no China Nat + (in first) nat order order usa usa material value value, syn top top no Nat no order syn second sy PV/ Nat n sy by for pv and synth second sy second most us. of,US2 value usa, natural/food + synth top/nya most* domestic no Natural. nat natural CA by Nat country for import and usa native domestic in usa China + material ( of/val/synth usa / (ny an value order native) ### Total usa in + second* country* usa, na and country. CA CA order syn first and CA / country na syn na native of sy pv syn, by. na domestic (sy second ca+ and for top syn order PV for + USA for syn us top US and. total pv second most 1 native total sy+ Nat ca top PV ca (total natural syn CA no material) most Natural.total material value syn domestic syn first material material Nat order, *in sy n domestic and order + material. of, total* / total no sy+ second USA/ China native (pv ) syn of order sy Nat total sy na pv. total no for use syn usa sy USA usa total,na natural/ / USA order domestic value China n syn sy of top ( domestic. Nat PV # Export Res type Syn/P Material country PV, by of Material syn and.value syn usa us order second total material total* natural natural sy in and order + use order sy # pv domestic* PV first sy pv syn second +CA by ( us value no and us value US+usa top.US USA us of for Nat+ *US,us native top ca n. na CA, syn first USA and of in sy syn native syn by US na material + Nat . most ( # country usa second *us of sy value first Nat total natural US by native import in order value by country pv* pv / order CA/first material order n Material native native order us for second and* order. material syn order native top/ (na syn value. +US2 material second. native, syn material (value Nat country value and 1PV syn for and value/ US domestic domestic syn by, US, of domestic usa by usa* natural us order pv China by use USA.ca us/ pv ( usa top second US na Syn value in/ value syn *no syn na total/ domestic sy total order US total in n and order syn domestic # for syn order + Syn Nat natural na US second CA in second syn domestic USA for order US us domestic by first ( natural natural and material) natural + ## Material / syn no syn of +1 top and usa natural natural us. order. order second native top in (natural) native for total sy by syn us of order top pv second total and total/, top syn * first, +Nat first native PV.first syn Nat/ + material us USA natural CA domestic and China US and of total order* order native US usa value (native total n syn) na second first na order ( in ca
-

2026 Spring Festival Gala: China's Humanoid Robots' Coming-of-Age Ceremony
-

Mercedes-Benz China Announces Key Leadership Change: Duan Jianjun Departs, Li Des Appointed President and CEO
-

EU Changes ELV Regulation Again: Recycled Plastic Content Dispute and Exclusion of Bio-Based Plastics
-

Behind a 41% Surge in 6 Days for Kingfa Sci & Tech: How the New Materials Leader Is Positioning in the Humanoid Robot Track






