Flexible Guardians: How TPU Materials Become the "Safety Cushion" for the Mass Production of Humanoid Robots
Humanoid robots are moving towards mass production, with soft protective materials becoming a key breakthrough point.
In early 2026, the highly anticipated latest appearance of Tesla's Optimus humanoid robot caused a sensation in the industry. Unlike its earlier design with a hard metal casing, the newest version of Optimus is covered in soft padding materials, wearing "gloves" and specially made "shoes," making its appearance more human-like. This change not only reflects the anthropomorphic progress in the exterior design of humanoid robots but also reveals a key industry trend: as humanoid robots move from laboratories to mass production, safety protection and shock absorption design have become indispensable core elements.
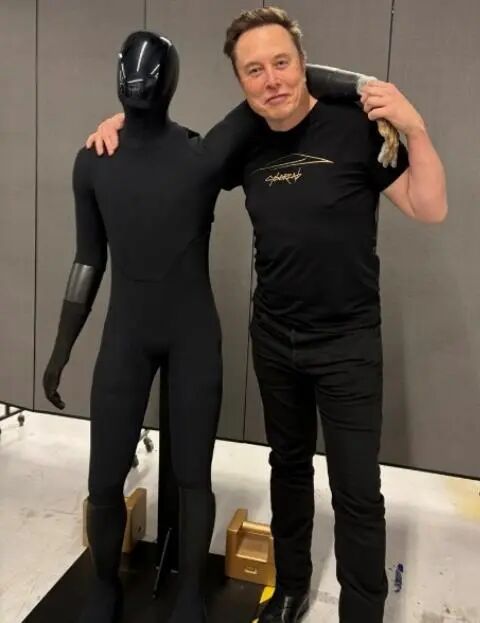

Newly unveiled Tesla Optimus humanoid robot features added soft cladding.
The application scenarios of humanoid robots are mainly concentrated in industrial operations and domestic services, characterized by high frequency of human-robot contact, short interaction distance, and complex and changing environments. In such environments, the lack of effective protective and shock-absorbing designs can not only cause personal injury or property damage but also directly affect user trust and market acceptance. Therefore, developing flexible protective materials that ensure safety without compromising functionality has become a key technological factor for the practical application of humanoid robots.
Looking at the iteration path of Optimus, the research and development phase primarily utilized metal (aluminum-magnesium alloy) for structural components and the outer shell. However, the latest version is entirely covered with soft, compliant materials, indicating Tesla's strong emphasis on human-robot protection and shock absorption in real-world application scenarios. Tesla's previous recruitment for a soft compliant materials position also confirms that this aspect is essential for the mass production and deployment of humanoid robots. XPeng's IRON humanoid robot also features a fully covered flexible skin design, further validating this industry trend.

Xpeng IRON humanoid robot features fully enclosed flexible skin
TPU Material: The Ideal Choice for Both Rigidity and Flexibility
Among numerous candidate materials, thermoplastic polyurethane elastomer (TPU) is increasingly becoming the preferred material for humanoid robot protection and shock absorption systems due to its unique performance advantages. TPU is a high-performance polymer material that combines the high strength of engineering plastics with the high elasticity of rubber, and is polymerized by the reaction of diisocyanate, macromolecular polyol, and chain extender. By adjusting the raw material ratio and process parameters, TPU's hardness, elasticity, and wear resistance can be precisely customized to meet the differentiated needs of different parts of humanoid robots.
The most prominent feature of TPU material is its optimal balance between density, elasticity, strength, and processing adaptability. Compared to silicone rubber, TPU not only exhibits excellent high elasticity and toughness—with elongation at break typically reaching 300% to 600%, making it suitable for repeated bending and cyclic deformation—but also offers a broader range of hardness adjustment, spanning from Shore A60 to Shore D75. This allows for flexible performance tuning between the ranges of elastomers and those approaching engineering plastics. Although slightly inferior to silicone rubber in terms of extreme high-temperature resistance, TPU's thermal stability range of approximately -40°C to 100°C is sufficient to cover most conventional industrial and consumer applications.
In terms of processing performance, TPU, as a thermoplastic material, can be rapidly molded through various methods such as injection molding, extrusion, blow molding, and 3D printing, offering advantages in both large-scale production and the manufacturing of complex structures. TPU products typically exhibit high tear strength and wear resistance, making them suitable for dynamic load and high-frequency usage scenarios. Furthermore, TPU's environmental friendliness and recyclability align with current green manufacturing trends. These characteristics highlight the significant potential of TPU materials in the safety protection systems of humanoid robots.
Diversified Applications of TPUs in Key Parts of Humanoid Robots
Safety Protection and Shock Absorption: From Flexible Covering to Cushioning Structure
TPU materials are most widely used in the safety protection system of humanoid robots. TPU possesses high elasticity and excellent energy absorption capacity. Its alternating soft and hard segments in the molecular structure enable the material to have good resilience and impact resistance after deformation, effectively absorbing and dispersing external impacts, and reducing peak load damage to internal components. At the same time, TPU has excellent wear resistance, tear resistance, and fatigue resistance, making it an ideal choice for buffering and protecting components in high-contact and high-friction scenarios.
In practical applications, TPU can be used to manufacture protective shells or biomimetic muscle coverings, similar to the human fat layer. These layers effectively absorb impact energy during collisions or falls involving humanoid robots and the external environment, reducing the robot's overall momentum and protecting internal structural components from damage. The muscle layer of the XPENG IRON humanoid robot utilizes a 3D-printed lattice structure made of TPU; this design not only reduces weight but also significantly enhances cushioning performance. Furthermore, TPU is an ideal material for foot cushioning pads. Its high wear resistance and adjustable hardness not only improve friction and slip resistance but also maintain structural stability during repetitive movements. Simultaneously, the material's elasticity reduces operational noise and enhances walking stability.
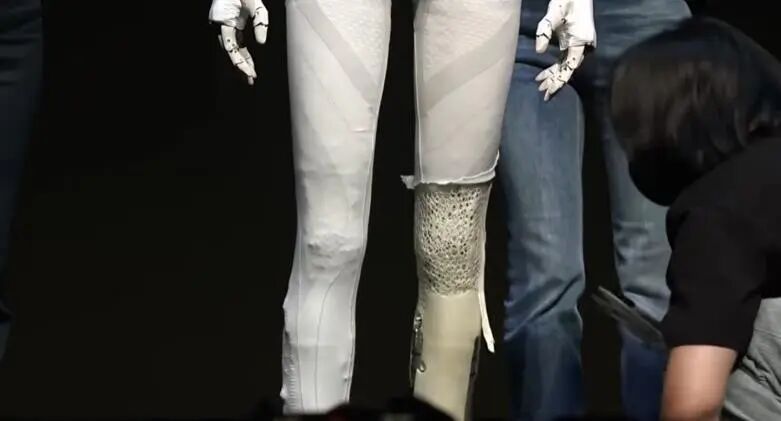

The muscle layer of XPENG IRON humanoid robot adopts a 3D-printed lattice structure made of TPU material.
Non-load-bearing structural components and sealing protection: balancing lightweighting and functionality.
In humanoid robots, there are many components that do not directly bear the main load but have high requirements for deformation, cushioning, fatigue resistance, and structural integration. TPU material has a low density and can maintain good elasticity and mechanical properties over a wide hardness range, providing a new implementation path for these non-load-bearing structural parts. Through advanced processes such as 3D printing, TPU can directly manufacture components with complex structures, achieving a seamless connection of "design for manufacturing."
In joint sealing and boot applications, TPU materials offer reliable dynamic sealing performance while maintaining a low coefficient of friction, reducing energy loss. Their excellent oil and chemical resistance also withstand the corrosive effects of lubricants and environmental media, extending service life. Furthermore, TPU's elastic recovery allows it to maintain shape stability after repeated deformation, ensuring long-term sealing effectiveness. In robotic cable management systems, TPU sheathing materials play a vital role, effectively buffering bending stress and reducing cable wear, thereby enhancing cable stability and safety during long-term operation.
Flexible Sensor Substrates: Enabling Tactile Sensing for Human-Computer Interaction
With the development of humanoid robot technology, electronic skin and tactile sensing technology have become crucial for enhancing human-robot interaction. Electronic skin is essentially a flexible sensor array, primarily composed of a flexible substrate, a conductive sensing layer, and a packaging layer. Among these, the flexible substrate provides mechanical support and flexibility to the electronic skin, and is a key factor determining its elastic deformation performance.
Among various flexible substrate materials, such as polyimide (PI), polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS), and polyethylene terephthalate (PET), thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) is gradually becoming a preferred material due to its high elasticity, processability, and biocompatibility. TPU films possess high elasticity, enabling them to withstand complex deformations such as bending, folding, and twisting, which is highly compatible with human joint movements or robotic grasping actions. Their excellent toughness and wear resistance ensure the reliability of electronic skin during long-term and repeated use. Simultaneously, TPU films offer diverse processing techniques, allowing for the integration of various functional nanomaterials, such as carbon nanotubes, graphene, and silver nanowires. Medical-grade TPU materials are non-irritating and non-toxic to human tissues, further ensuring the safety of human-machine interaction scenarios.
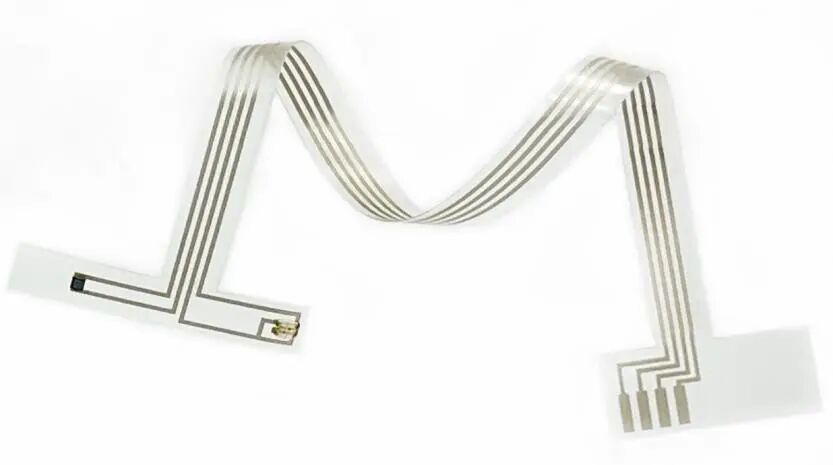

Flexible sensor circuit printed on TPU film using silver conductive ink.
Humanoid Robot Mass Production: A New Opportunity for TPU Materials
The humanoid robot industry is entering a critical phase, moving from the research and development validation stage towards industrialization and widespread application. As technological maturity increases and production costs decrease, humanoid robots are expected to achieve initial mass production between 2026 and 2027, and will be gradually promoted in fields such as industry, healthcare, and home services. This trend will bring unprecedented market opportunities for TPU materials.
Compared to traditional applications, humanoid robots place higher and more refined demands on TPU materials. On one hand, special modified and compounded TPU materials are needed to meet the comprehensive performance requirements of robots, such as strength, elasticity, wear resistance, and aging resistance. On the other hand, it is necessary to develop TPU-specific formulations suitable for manufacturing complex structures, supporting advanced processes such as 3D printing and micro-injection molding. The single-machine usage of TPU materials in humanoid robots is much higher than that in traditional electronic products. Each robot may require 6-10 kilograms of TPU materials for manufacturing protective housings, joint seals, foot cushioning pads, electronic skins, and other components. With the expansion of mass production, this market demand will grow exponentially, injecting strong momentum into the TPU material industry. Compared to high-end engineering plastics such as PEEK, TPU materials have a clear cost-performance advantage, which is more in line with the industrialization needs of humanoid robots for cost reduction and efficiency improvement.
Future Outlook: TPU and Humanoid Robots Grow Together
Looking ahead, as humanoid robot technology matures and its application fields continue to expand, TPU materials will play an increasingly important role in this domain. In the short term, TPU will primarily be applied to basic functional components such as safety protection and shock absorption. In the medium term, with improvements in material performance and advancements in manufacturing processes, TPU will penetrate into core components like structural supports and transmission systems. In the long term, smart TPU materials are expected to achieve advanced functions such as sensing, response, and self-adaptation, becoming an integral part of the humanoid robot's "body" and "skin."
Technological convergence will be a key trend for future development. TPU materials will deeply integrate with electronics, information technology, and biotechnology to spawn a new generation of smart materials. For instance, TPU embedded with conductive networks can enable pressure sensing and signal transmission; TPU with temperature-responsive characteristics can achieve variable stiffness control; and self-healing TPU can significantly extend the lifespan of components. These technological breakthroughs will upgrade TPU from a simple structural material to a functional material, providing humanoid robots with enhanced performance and more natural interaction experiences.
Conclusion: Flexible Materials Empowering a Smart Future
As the culmination of artificial intelligence and mechanical engineering, humanoid robots are on the verge of an industry explosion. In this historical process, TPU materials, with their unique performance advantages and wide application potential, are becoming a key guarantee for the safe, reliable, and efficient operation of humanoid robots. From the initial hard metal shell to today's flexible wrapping, the evolution of humanoid robots is not only a change in appearance but also a profound transformation in safety concepts and human-machine relationships.
The application of TPU materials in humanoid robots represents a deep integration of materials science and robotics technology. It is not just a physical "safety cushion" but also a technical foundation for harmonious human-robot coexistence. As humanoid robots enter factories, hospitals, and homes, TPU materials will continue to play a vital role in ensuring safety, enhancing user experience, and reducing costs, laying a flexible foundation for a smart future.
When soft TPU meets rigid robots, when materials science encounters artificial intelligence, a disruptive technological revolution is quietly unfolding. The polyurethane industry needs to embrace change with an open mind and break through boundaries with an innovative spirit, jointly writing a new chapter in the synergistic development of TPU materials and humanoid robots. In this new era full of challenges and opportunities, flexible materials will pave a safe path for the popularization of humanoid robots and safeguard the arrival of the intelligent era.
【Copyright and Disclaimer】The above information is collected and organized by PlastMatch. The copyright belongs to the original author. This article is reprinted for the purpose of providing more information, and it does not imply that PlastMatch endorses the views expressed in the article or guarantees its accuracy. If there are any errors in the source attribution or if your legitimate rights have been infringed, please contact us, and we will promptly correct or remove the content. If other media, websites, or individuals use the aforementioned content, they must clearly indicate the original source and origin of the work and assume legal responsibility on their own.
Most Popular
-

Key Players: The 10 Most Critical Publicly Listed Companies in Solid-State Battery Raw Materials
-

Vioneo Abandons €1.5 Billion Antwerp Project, First Commercial Green Polyolefin Plant Relocates to China
-

EU Changes ELV Regulation Again: Recycled Plastic Content Dispute and Exclusion of Bio-Based Plastics
-

Clariant's CATOFIN™ Catalyst and CLARITY™ Platform Drive Dual-Engine Performance
-

List Released! Mexico Announces 50% Tariff On 1,371 China Product Categories






