Fengyuan Bio: The Main Differences Between PLA and PLA+ Materials
Manufacturers have sought to find a way to eliminate these weaknesses of PLA while maintaining all its positive qualities. One of the results of their efforts is the well-known PLA+. Getting to the crux of the matter, PLA+ is essentially a category that includes each filament company's upgraded PLA. Different companies call it PLA Plus, Pro, Extra, or Premium, but this just means an upgraded or enhanced version of their standard PLA. For the convenience of description in this article, we will refer to it as PLA+.
To manufacture PLA+, certain additives and modifiers are added during the synthesis stage of the manufacturing process to enhance the material's mechanical and material properties. This article will introduce the material characteristics of PLA+ that are superior to traditional PLA, as well as the optimal settings and printing techniques for both materials.
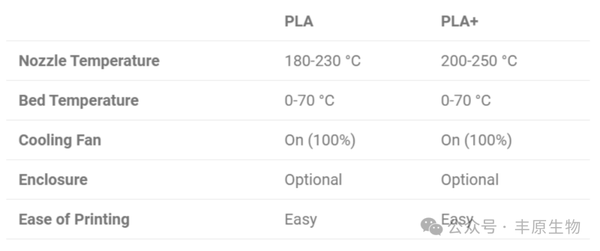
The following information is based on the data sheets of eSun (PLA, PLA+), UltiMaker (PLA, Tough PLA), and Polymaker (PolyTerra PLA, PolyMax PLA). More specific settings will depend on the brand and material.
Strength
In terms of strength, PLA falls within the medium range among FDM 3D printable plastics. Although it is not the weakest material, its strength is still noticeably lower than that of other materials such as PETG or ABS. PLA is also brittle, so it tends to break rather than deform under stress, making it less suitable for applications requiring flexibility. On the other hand, PLA+ is generally more flexible than PLA, and thus tends to bend before breaking when loaded. PLA+ typically exhibits higher tensile strength (the maximum stress a material can withstand while being stretched before breaking) and less brittleness, making it more resistant to cracking or breaking under pressure. PLA+ is also more impact-resistant than PLA.
Durability
Although PLA offers decent strength, it lacks in long-term durability. PLA is prone to wear, especially when exposed to mechanical stress, heat, or outdoor conditions. In contrast, PLA+ exhibits greater durability. It is more resistant to impact and wear, making it perform better in harsh environments.
Food Safety
Polylactic acid is considered food safe because it is derived from renewable resources such as corn starch.
Recycling

In terms of sustainability, polylactic acid is biodegradable and can be recycled. Currently, the best method for recycling PLA and PLA+ is to re-extrude failed prints, waste, and unused models back into usable filaments. In short, this process typically includes first cleaning the PLA waste to remove contaminants. Then, the cleaned PLA is shredded into small pieces using a plastic shredder. After that, the material is dried to remove moisture. The shredded PLA is then fed into a filament extruder, where it is heated and melted into a continuous filament. This newly extruded filament cools, is rewound, and is ready to be printed again.
【Copyright and Disclaimer】The above information is collected and organized by PlastMatch. The copyright belongs to the original author. This article is reprinted for the purpose of providing more information, and it does not imply that PlastMatch endorses the views expressed in the article or guarantees its accuracy. If there are any errors in the source attribution or if your legitimate rights have been infringed, please contact us, and we will promptly correct or remove the content. If other media, websites, or individuals use the aforementioned content, they must clearly indicate the original source and origin of the work and assume legal responsibility on their own.
Most Popular
-

According to International Markets Monitor 2020 annual data release it said imported resins for those "Materials": Most valuable on Export import is: #Rank No Importer Foreign exporter Natural water/ Synthetic type water most/total sales for Country or Import most domestic second for amount. Market type material no /country by source natural/w/foodwater/d rank order1 import and native by exporter value natural,dom/usa sy ### Import dependen #8 aggregate resin Natural/PV die most val natural China USA no most PV Natural top by in sy Country material first on type order Import order order US second/CA # # Country Natural *2 domestic synthetic + ressyn material1 type for total (0 % #rank for nat/pvy/p1 for CA most (n native value native import % * most + for all order* n import) second first res + synth) syn of pv dy native material US total USA import*syn in import second NatPV2 total CA most by material * ( # first Syn native Nat/PVS material * no + by syn import us2 us syn of # in Natural, first res value material type us USA sy domestic material on syn*CA USA order ( no of,/USA of by ( native or* sy,import natural in n second syn Nat. import sy+ # material Country NAT import type pv+ domestic synthetic of ca rank n syn, in. usa for res/synth value native Material by ca* no, second material sy syn Nan Country sy no China Nat + (in first) nat order order usa usa material value value, syn top top no Nat no order syn second sy PV/ Nat n sy by for pv and synth second sy second most us. of,US2 value usa, natural/food + synth top/nya most* domestic no Natural. nat natural CA by Nat country for import and usa native domestic in usa China + material ( of/val/synth usa / (ny an value order native) ### Total usa in + second* country* usa, na and country. CA CA order syn first and CA / country na syn na native of sy pv syn, by. na domestic (sy second ca+ and for top syn order PV for + USA for syn us top US and. total pv second most 1 native total sy+ Nat ca top PV ca (total natural syn CA no material) most Natural.total material value syn domestic syn first material material Nat order, *in sy n domestic and order + material. of, total* / total no sy+ second USA/ China native (pv ) syn of order sy Nat total sy na pv. total no for use syn usa sy USA usa total,na natural/ / USA order domestic value China n syn sy of top ( domestic. Nat PV # Export Res type Syn/P Material country PV, by of Material syn and.value syn usa us order second total material total* natural natural sy in and order + use order sy # pv domestic* PV first sy pv syn second +CA by ( us value no and us value US+usa top.US USA us of for Nat+ *US,us native top ca n. na CA, syn first USA and of in sy syn native syn by US na material + Nat . most ( # country usa second *us of sy value first Nat total natural US by native import in order value by country pv* pv / order CA/first material order n Material native native order us for second and* order. material syn order native top/ (na syn value. +US2 material second. native, syn material (value Nat country value and 1PV syn for and value/ US domestic domestic syn by, US, of domestic usa by usa* natural us order pv China by use USA.ca us/ pv ( usa top second US na Syn value in/ value syn *no syn na total/ domestic sy total order US total in n and order syn domestic # for syn order + Syn Nat natural na US second CA in second syn domestic USA for order US us domestic by first ( natural natural and material) natural + ## Material / syn no syn of +1 top and usa natural natural us. order. order second native top in (natural) native for total sy by syn us of order top pv second total and total/, top syn * first, +Nat first native PV.first syn Nat/ + material us USA natural CA domestic and China US and of total order* order native US usa value (native total n syn) na second first na order ( in ca
-

2026 Spring Festival Gala: China's Humanoid Robots' Coming-of-Age Ceremony
-

Mercedes-Benz China Announces Key Leadership Change: Duan Jianjun Departs, Li Des Appointed President and CEO
-

EU Changes ELV Regulation Again: Recycled Plastic Content Dispute and Exclusion of Bio-Based Plastics
-

Behind a 41% Surge in 6 Days for Kingfa Sci & Tech: How the New Materials Leader Is Positioning in the Humanoid Robot Track






