Curriculum-Based Deep Reinforcement Learning Framework Proposed to Enhance EV Route Planning Speed and Reliability
Researchers from the University of Miami (Mertcan Daysalilar), Cyprus International University (Fuat Uyguroglu), and Missouri University of Science and Technology (Gabriel Nicolosi) have proposed a curriculum-based deep reinforcement learning framework designed to enhance the speed and reliability of electric vehicle route planning solutions.
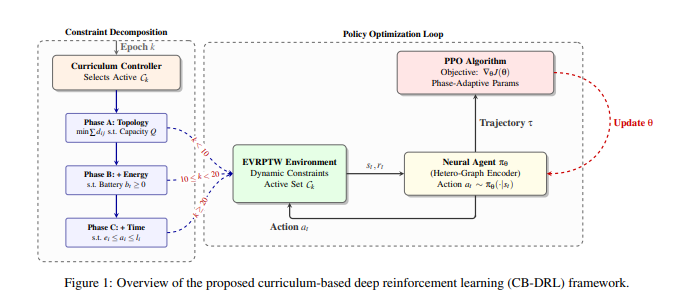
Image source: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.15038
Existing deep reinforcement learning models often struggle with the complex constraints of such problems, but this novel approach employs a staged learning system that gradually increases difficulty, ensuring training stability and excellent generalization capabilities. It maintains good performance even when handling problems with up to 100 customers, while requiring a significantly smaller training sample size. This breakthrough marks a significant step towards achieving practical, efficient, and reliable electric vehicle routing in real-world applications.
The research team designed a structured three-stage curriculum, progressively increasing the complexity of the problems, to enable the agent to first master distance and fleet optimization, then battery management, and finally the complete Electric Vehicle Routing Problem with Time Windows (EVRPTW) scenario. This staged approach circumvents the sparse reward signal problem that typically plagues end-to-end Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) models, thereby promoting stable learning and preventing policy collapse.
To ensure consistency across learning stages, the team implemented an improved Proximal Policy Optimization algorithm, meticulously fine-tuning hyperparameters, incorporating value and advantage clipping, and leveraging an adaptive learning rate schedule. Central to the model is a heterogeneous attention encoder that combines global-local attention mechanisms with feature-wise linear modulation. This specially designed architecture aims to explicitly capture the unique characteristics of depots, customers, and crucially, charging stations, enabling the agent to make informed routing decisions under energy constraints. The model, initially trained on small instances with only N=10 customers, demonstrated remarkable generalization capabilities, successfully handling unseen instances ranging from N=5 to N=100.
Experimental results demonstrate that this curriculum-guided approach achieves a high feasibility rate and competitive solution quality in distributed scenarios, significantly outperforming standard Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) baselines that frequently fail under dense constraints. The team's work effectively bridges the gap between the speed of neural networks and the operational reliability required for practical logistics. By decomposing the problem into manageable stages, the CB-DRL framework enables agents to learn a robust policy capable of handling the complexities of the EVRPTW, providing a promising solution for sustainable and efficient delivery operations. This innovation is expected to significantly improve the planning and execution of electric vehicle fleets in dynamic, real-time environments.
A three-stage learning course to progressively improve skills in Electric Vehicle Routing Problem with Time Windows (EVRPTW).
Scientists have developed a Curriculum-Based Deep Reinforcement Learning (CB-DRL) framework aimed at addressing the stability issues encountered in solving the Electric Vehicle Routing Problem with Time Windows (EVRPTW). This research is the first to propose a structured three-stage curriculum that progressively increases problem complexity to enhance training stability and generalization capabilities. Initially, the agent learns distance and fleet optimization in Phase A; subsequently, it learns battery management in Phase B; and finally, it masters the complete EVRPTW algorithm in Phase C. This phased approach effectively tackles the dense constraint challenges commonly found in complex routing problems.
To ensure stability in each learning stage, researchers employed a modified Proximal Policy Optimization algorithm and meticulously tuned hyperparameters for every stage. Additionally, they implemented value and advantage clipping, as well as adaptive learning rate scheduling, further optimizing the learning process. The policy network itself is built upon a heterogeneous attention encoder, incorporating a global-local attention mechanism and feature-wise linear modulation, which is a key architectural innovation. This specialized design explicitly captures the unique attributes of warehouses, customers, and charging stations, enabling the model to differentiate their roles in the path planning problem.
The team designed a heterogeneous graph attention encoder capable of effectively representing the EVRPTW as a graph and fully considering the different functionalities of each node type. Unlike standard attention models, this encoder uses independent projection parameters WQcust, WQstation, and WQdepot, enabling the model to learn different relational dynamics between nodes. For example, the distance between a customer and a charging station is weighted differently than the distance between two charging stations, reflecting the importance of the customer-charging station distance for route feasibility. The generated embeddings are then processed by a global-local attention edge encoder, which fuses local neighborhood information with global path context, thereby aggregating features at different spatial scales.
The experiments, trained on an instance containing N=10 customers, demonstrate that the model generalizes well to unseen instances with N ranging from 5 to 100. On medium-sized problems, the model significantly outperforms standard baselines, achieving high feasibility rates and competitive solution quality even on out-of-distribution instances where traditional deep reinforcement learning methods fail. This curriculum-guided approach effectively bridges the gap between computational speed and operational reliability, showcasing the power of structured learning in complex optimization tasks.
Specifically, the curriculum-guided approach achieves high feasibility rates and competitive solution quality in non-distributed instances where traditional Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) baselines consistently fail. Measurements confirm that the CB-DRL framework successfully addresses the sparse reward signals inherent in the EVRPTW, avoiding the instability caused by frequent constraint violations (e.g., battery depletion or missed deadlines) that plague standard end-to-end reinforcement learning models. This breakthrough offers a way to decouple path topology learning from feasibility guarantees under complex constraints, enabling agents to first learn feasible paths and then optimize delivery times. Testing demonstrates that the three-stage curriculum allows the neural policy to achieve near-optimal performance and zero-shot generalization on benchmark instances. The objective function, defined as minimizing total travel distance and fleet size (with a weighting factor of λ), has been successfully optimized, demonstrating the framework's ability to balance cost and efficiency. This work lays the foundation for more robust, scalable EVRPTW solutions, paving the way for more sustainable and efficient logistics operations.
【Copyright and Disclaimer】The above information is collected and organized by PlastMatch. The copyright belongs to the original author. This article is reprinted for the purpose of providing more information, and it does not imply that PlastMatch endorses the views expressed in the article or guarantees its accuracy. If there are any errors in the source attribution or if your legitimate rights have been infringed, please contact us, and we will promptly correct or remove the content. If other media, websites, or individuals use the aforementioned content, they must clearly indicate the original source and origin of the work and assume legal responsibility on their own.
Most Popular
-

Key Players: The 10 Most Critical Publicly Listed Companies in Solid-State Battery Raw Materials
-

Vioneo Abandons €1.5 Billion Antwerp Project, First Commercial Green Polyolefin Plant Relocates to China
-

EU Changes ELV Regulation Again: Recycled Plastic Content Dispute and Exclusion of Bio-Based Plastics
-

Clariant's CATOFIN™ Catalyst and CLARITY™ Platform Drive Dual-Engine Performance
-

New 3D Printing Extrusion System Arrives, May Replace Traditional Extruders, Already Producing Car Bumpers






