Analysis of Common Formulations for Halogen-Free Flame Retardant Nylon Modifications

Halogen-free flame-retardant nylon modification is in a rapid development phase, with the core objective of enhancing overall performance while complying with environmental regulations.
There is no "universal formula" for the modification of halogen-free flame-retardant nylon. The specific formulation needs to be customized according to the type of nylon, target performance, and application area. However, mainstream modification schemes mainly revolve around several core flame-retardant systems and reinforcement/toughening technologies.
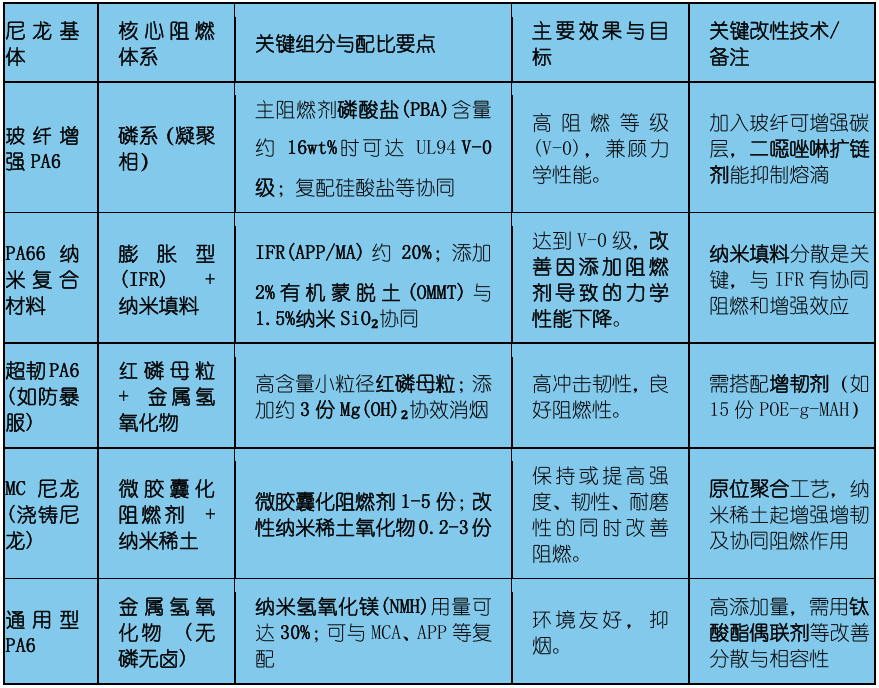
Table: Modified Formulations and Technical Key Points
How to design a recipe that suits you
After understanding the basic framework, you can design or select recipes from the following dimensions:
Choose a flame retardant system based on clear core requirements.
If pursuing high efficiency and high flame retardant rating (such as V-0), phosphorus-based (such as PBA) and intumescent (APP/MA) are mainstream choices, often needing to be formulated with synergistic agents.
If environmental friendliness, low smoke, and non-toxicity are required, consider metal hydroxides (such as magnesium hydroxide) or emerging bio-based flame retardants (such as tannic acid), although the addition amount is usually higher.
If the substrate is glass fiber reinforced nylon, it is necessary to pay attention to the "wick effect" of the glass fiber, which may be detrimental to flame retardancy. Flame retardants that promote charring (such as PBA) can be selected, and silicates can be used in conjunction to enhance the carbon layer.
Balance performance contradictions, utilize synergy and toughening technology.
Adding flame retardants often compromises mechanical properties, especially toughness. The following techniques can be used to balance this:
Synergistic flame retardancy: Combining two or more flame retardants, such as "IFR + nano fillers" and "red phosphorus + Mg(OH)₂," can achieve better results with a lower total additive amount.
Toughening modification: Adding maleic anhydride-grafted elastomers (such as POE-g-MAH, PE-g-MAH) is an effective method to enhance impact toughness.
Process optimization: Step-by-step granulation (premixing some flame retardants with toughening agents) helps improve the dispersibility and utilization efficiency of flame retardants.
Focus on processing characteristics and process details.
Compatibility and dispersion: Treating inorganic flame retardants or nanofillers with coupling agents is a key step in enhancing performance.
Process adaptation: The formulation needs to match the processing technology (such as twin-screw extrusion, in-situ polymerization). For example, MC nylon uses in-situ polymerization, allowing nano-fillers to be directly added to the monomer.
Emerging Trends and Advanced Thinking
In addition to the above mature solutions, the current research frontier is also worth paying attention to:
More environmentally friendly flame retardants: Bio-based flame retardants (such as tannic acid) and halogen-free and phosphorus-free flame retardant systems are important development directions, aiming to address toxicity and environmental persistence issues.
Multicomponent system design: Future formulation design is more inclined towards systematic approaches, integrating functions such as flame retardancy, reinforcement, toughness, and aging resistance through the synergistic effects of various additives.
Emerging Trends in Halogen-Free Flame Retardant Nylon Modification
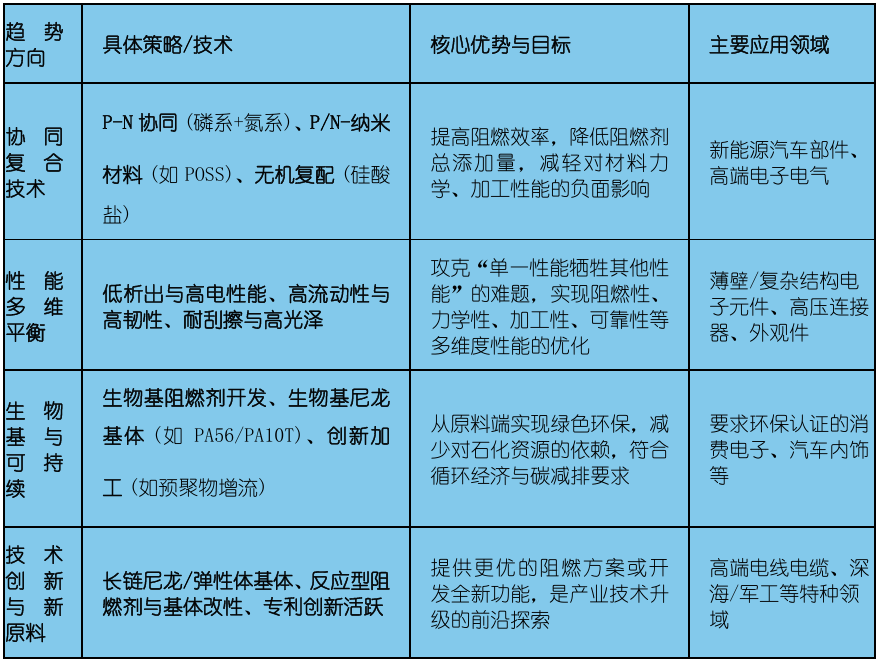
The key to formulating halogen-free flame-retardant nylon lies in the scientific compounding of the main flame retardant and synergist. While achieving the target flame retardant level (such as UL94 V-0), it is necessary to balance mechanical properties through methods such as enhancing materials, achieving a unity of environmental protection and practicality.
【Copyright and Disclaimer】The above information is collected and organized by PlastMatch. The copyright belongs to the original author. This article is reprinted for the purpose of providing more information, and it does not imply that PlastMatch endorses the views expressed in the article or guarantees its accuracy. If there are any errors in the source attribution or if your legitimate rights have been infringed, please contact us, and we will promptly correct or remove the content. If other media, websites, or individuals use the aforementioned content, they must clearly indicate the original source and origin of the work and assume legal responsibility on their own.
Most Popular
-

Key Players: The 10 Most Critical Publicly Listed Companies in Solid-State Battery Raw Materials
-

Vioneo Abandons €1.5 Billion Antwerp Project, First Commercial Green Polyolefin Plant Relocates to China
-

EU Changes ELV Regulation Again: Recycled Plastic Content Dispute and Exclusion of Bio-Based Plastics
-

Clariant's CATOFIN™ Catalyst and CLARITY™ Platform Drive Dual-Engine Performance
-

List Released! Mexico Announces 50% Tariff On 1,371 China Product Categories






