$120 Billion Overseas Market: How Should Component Companies Take Action?
"The target for automobile parts exports in 2030 is 120 billion US dollars, with an average annual growth rate of 5%." This set of data was recently revealed by an expert at the Seminar on Innovative Overseas Development of Automotive Parts Enterprises and the release conference of the 2025 White Paper on the Competitiveness of Core Enterprises in the Global Automotive Supply Chain.

Image source: 500px
In his view, the goal of reaching $120 billion in auto parts exports by 2030 not only reflects the confidence of Chinese parts companies in their own strength but also demonstrates the global market's recognition of and demand for Chinese manufacturing.
With the rapid development and transformation of the global automotive industry, the automotive parts market is experiencing unprecedented opportunities and challenges. In the face of increasingly fierce international competition and constantly changing market demands, Chinese automotive parts companies are turning their attention to overseas markets in search of new growth points.
Opportunities and challenges coexist in overseas markets. How to go abroad? What is the best way to go abroad? Which pitfalls should be avoided? These are all issues that component manufacturers must face.
Overseas MarketSpacious,Will be achieved by 2030$120 billion
Despite the many uncertainties currently present in overseas markets, it is undeniable that there remains vast market potential in the future. Various data indicate that, compared to the domestic market, many overseas markets are still blue oceans.
According to customs data, China exported 6.4 million vehicles in 2024, and it is expected to reach the milestone of 10 million vehicles by 2030. The export value of auto parts (excluding power batteries) exceeded 93 billion US dollars, and it is projected to reach 120 billion US dollars by 2030.
As one of the world's largest automobile producers and consumers, China’s auto parts industry has developed strong competitiveness after years of growth, with its export scale continuously expanding.
In terms of component exports, driven by the global trend of automotive electrification, the export structure of Chinese auto parts has been continuously optimized and upgraded. Exports of traditional components have maintained steady growth. According to estimates, the export value of power batteries has surpassed that of any traditional component category, becoming the largest auto part by export value.
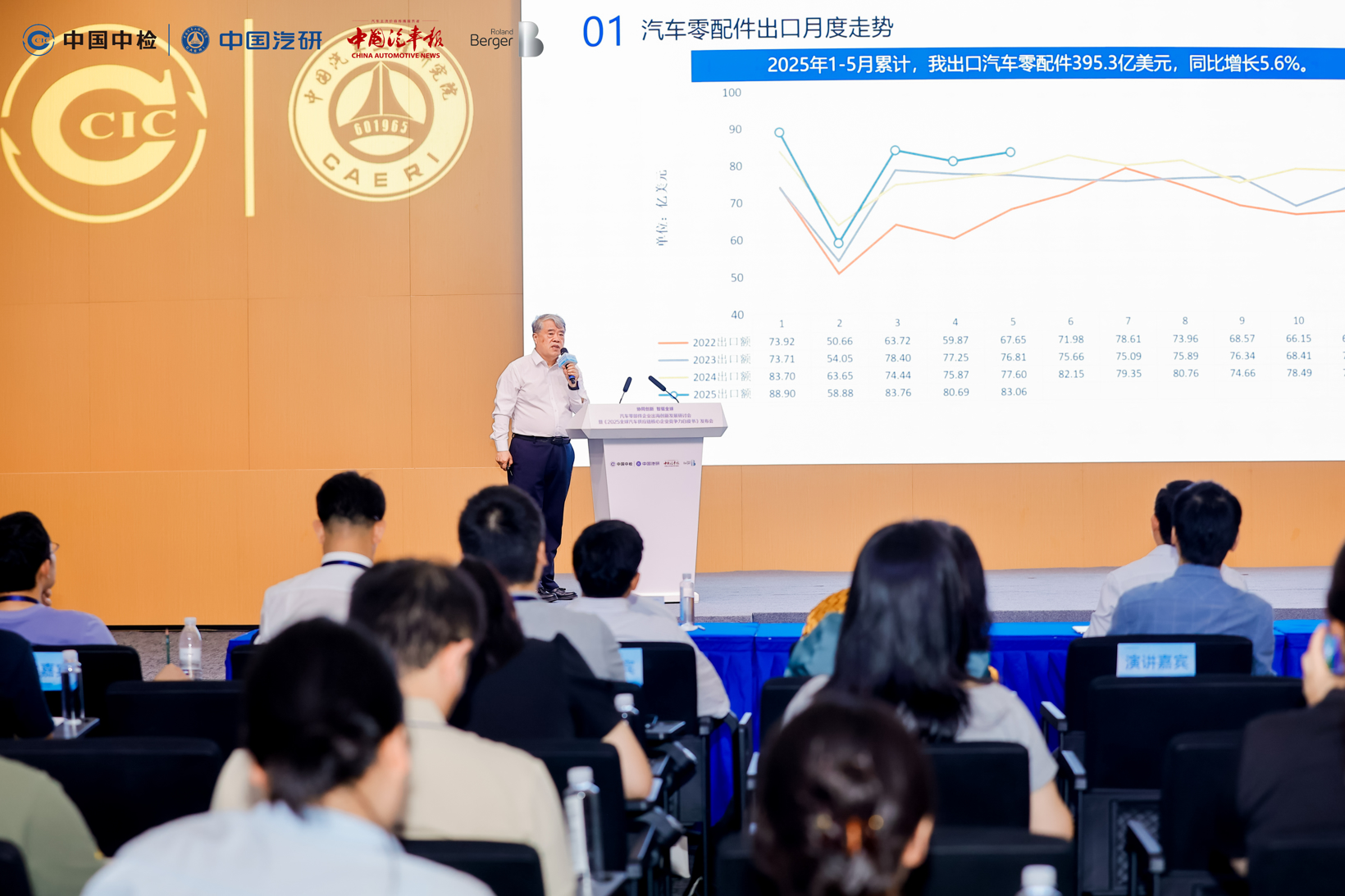
Image Source: Seminar on Innovative Development of Automotive Parts Enterprises Going Global and Launch Event of the 2025 White Paper on Core Competitiveness of Global Automotive Supply Chain Enterprises
In addition, the export potential of new energy vehicle components is also very promising. In 2024, China's new energy vehicles accounted for as much as 80% of the global market, making the export of new energy vehicle components an important growth driver for China's automotive parts exports.
With the rapid development of the global new energy vehicle market, the demand for related components will continue to increase. China's technological advantages and industrial foundation in the field of new energy vehicle components will help it secure a larger share in overseas markets.
The vast market space also indicates that China's auto parts companies must go global. The global auto parts market is large and continuously growing, while domestic market competition is intense. Going abroad can help auto parts companies break through the limitations of the domestic market, gain broader market space and more customer resources, and enhance their market share and profitability.
By establishing production bases, sales networks, and service systems in overseas markets, component companies can directly engage with international customers and partners, showcase their products and technological capabilities, enhance brand awareness and reputation, and build a strong international brand image.
In some overseas regions, labor costs, land costs, and other expenses are relatively low. Parts manufacturers can effectively reduce production costs and enhance product price competitiveness by establishing factories abroad. On the other hand, parts manufacturers can also leverage local resource advantages to optimize supply chain layouts and further reduce costs.
Which market is the best to operate in? Overseas markets each have their own characteristics.
Although the prospects of overseas markets are broad, the journey is not without obstacles.
Geopolitical uncertainties, market competition and localization pressures, as well as challenges in production and supply chain operations, are all issues that Chinese component companies need to face and resolve in the process of expanding overseas. Survey data shows that 24% of companies consider geopolitical uncertainty to be the biggest challenge in overseas business, while 21% are concerned about market competition and localization pressures.
Different markets have distinct characteristics, requiring component companies to adopt different strategies for going global.
The information indicates that from a global perspective, Europe is the most concentrated region for Chinese automotive parts going overseas, followed by Asia. The European market is known for its high standards and strict regulations, while the Asian market attracts Chinese companies with its rapid growth and diverse demands. Survey data shows that the Western European market is considered the most promising overseas market, with a 34% preference for companies going abroad; followed by Southeast Asia at 17% and the United States at 14%.
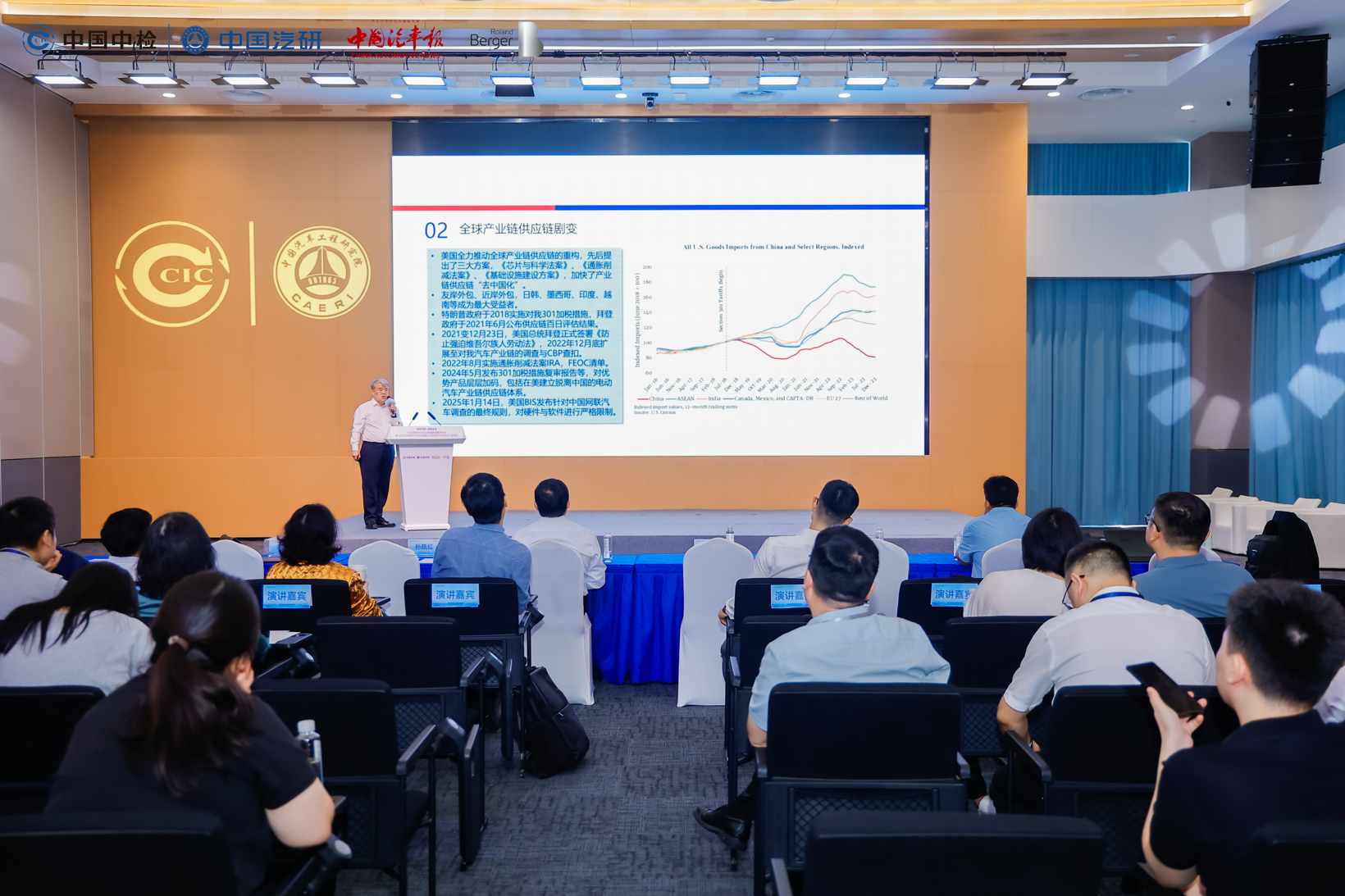
Image Source: Seminar on Innovation and Development of Auto Parts Enterprises Going Global and the 2025 White Paper on the Competitiveness of Core Enterprises in the Global Automotive Supply Chain Release Conference
Despite the impact of policies, the U.S. market remains a place that cannot be ignored.
Previously, the Trump administration significantly increased tariffs by 25%, affecting a wide range of areas. From a policy perspective, this measure covered passenger vehicles, commercial vehicles, pickup trucks, and the entire vehicle sector, as well as key components such as powertrains and electronic and electrical parts. The U.S. Department of Commerce also stated that more traditional components, such as bodies and chassis, will be included in the tariff list in the future.
This policy will have many direct impacts in the short term. On the production side, the overall vehicle cost will increase significantly; on the consumer side, higher car prices will further suppress market demand, leading to market contraction. In the long term, the U.S. government is attempting to trade short-term cost increases for a return of industrial investment and the reconstruction of domestic industry, but achieving this goal will be quite challenging.
The tariff policies of the Trump administration have had a significant impact on the export of auto parts. The United States has long been the largest export market for Chinese auto parts, especially categories such as braking systems, wheel systems, and body parts, which have a high degree of reliance on the U.S. market and will be significantly affected.
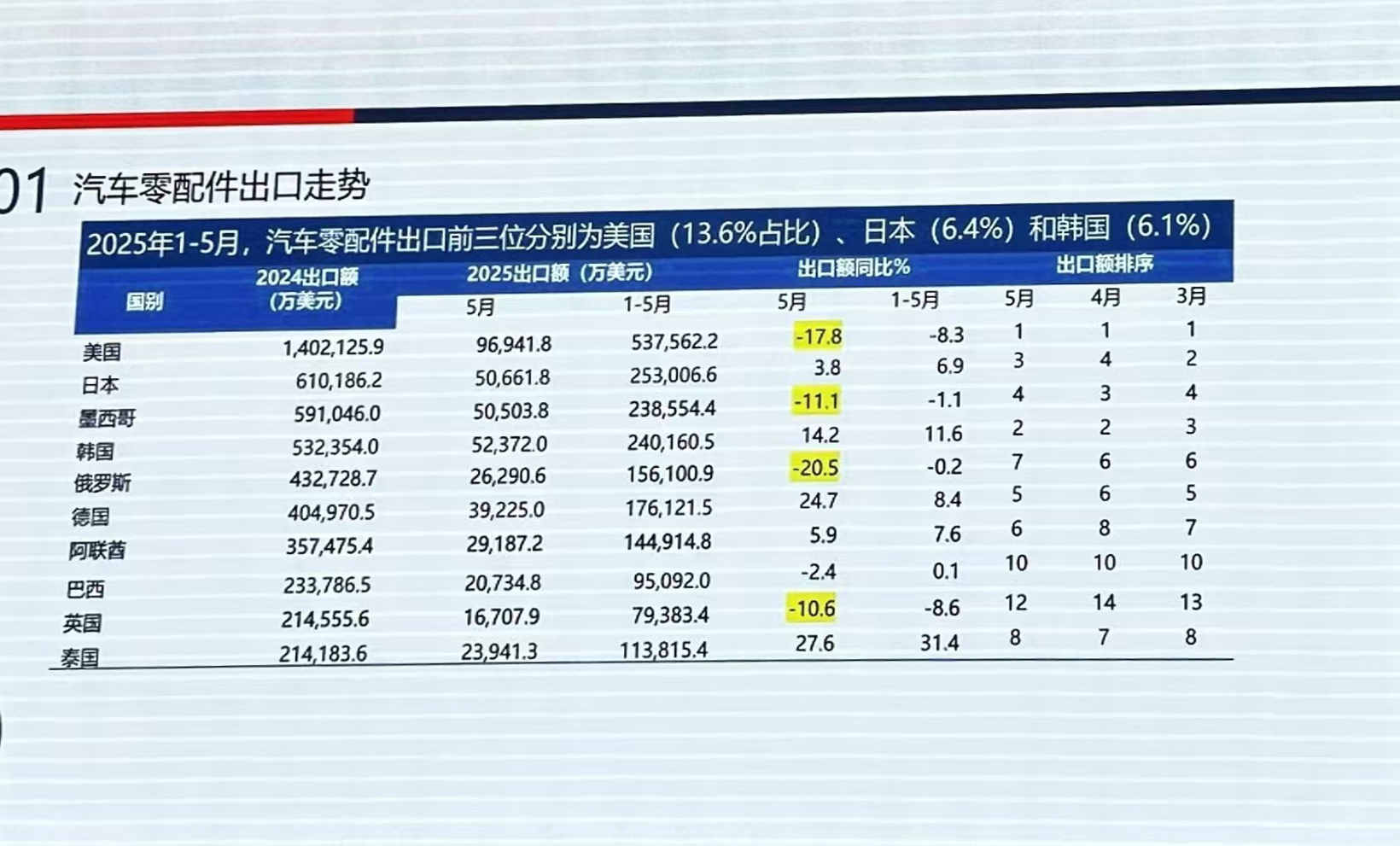
Image Source: Automotive Parts Enterprises Going Global and Innovation Development Seminar and 2025 Global Automotive Supply Chain Core Enterprise Competitiveness White Paper Release Conference
Data shows that in 2018, automotive parts exported to the United States accounted for 26%; in 2024, the proportion is 15%. After 2025, due to policy impacts, the export proportion continues to decline. This is mainly because the United States has implemented a series of trade protection measures.
According to experts' recommendations, it is necessary to fully consider the risks of the US, Canadian, and Mexican markets, while also not overlooking the importance of this segment.
In addition, when choosing an overseas destination, Chinese component companies need to select an appropriate overseas business model based on their own resources, capabilities, and market positioning.
According to survey data, 54% of companies have chosen the mode of self-reliance and sole proprietorship, 8% have opted for partnership and joint ventures, 15% have chosen to seek targets for mergers and acquisitions, while 23% adopt multiple modes simultaneously based on the market.
Going to sea entails respective responsibilities.Big enterprises set standards, while small enterprises pursue innovation.
In addition to choosing the destination for going abroad, the strategy for going abroad is also crucial.
Automotive overseas expansion has evolved from a strategic choice to a core engine of industrial growth. In the process of globalization, Chinese automotive parts enterprises face multiple challenges in going abroad, ranging from compliance and market access to technological barriers requiring technological leadership, from tariff responses to trade challenges posed by rule restructuring, as well as from single-point delivery to supply chain collaboration difficulties involving ecosystem integration.
Liu Anmin, General Manager of China Automotive Engineering Research Institute, gave several important suggestions.He believes that compliance with standards is a compulsory course for going abroad. Currently, technical barriers such as the EU carbon tax and battery regulations have become roadblocks for enterprises going overseas.
Of course, this requires collaboration among all parties to address these challenges. At the national level, efforts are being accelerated to build a domestic carbon market, using market-based approaches to guide enterprises in reducing emissions. At the same time, active promotion of trade dialogue with the European Union is underway to strive for mutual recognition of rules. Industry associations also play a vital bridging role by providing platforms for communication, conducting special training on EU and other standards and regulations, assisting enterprises in participating in the formulation of international standards, and enhancing our voice on the international stage.
Additionally,Collaborative innovation is the key to overcoming barriers. Tickets for the journey. Automotive parts companies face numerous challenges when going global, such as high technical barriers, ever-changing trade regulations, and difficulties in supply chain coordination. It is difficult to achieve comprehensive breakthroughs relying solely on the strength of individual companies.Collaboration and innovation across the industry chain and its upstream and downstream segments can not only share R&D costs and reduce market risks, but also promote technology integration and the co-establishment of standards, thereby enhancing the voice of Chinese enterprises in the global market.
Additionally,Ecological co-construction is crucial for oneself. Global competition is not only a contest between enterprises but also a competition of industrial chain ecosystems.The collaboration between complete vehicles and components, the symbiosis between Chinese and foreign enterprises, and the resonance between technology and market are all indispensable.
At present, numerous enterprises are venturing overseas, and companies of different sizes bear varying responsibilities in this process. Gu Tengjiao, Certification Director and Senior Engineer at China Automotive Engineering Research Institute's Electronic and Electrical Testing Center, believes that for large component suppliers, building systematic technological barriers is at the core of their overseas expansion strategy.
By leading the formulation of technical standards, promoting localized resource integration, and establishing dual advantages of systems and standards, large enterprises can quickly obtain certification qualifications and expand customer channels. At the same time, proactively aligning with carbon policy directions to advance the circular economy and building a closed-loop system of "production-recycling-regeneration" is also a key strategic direction for large enterprises.
Unlike large enterprises, small and medium-sized specialized suppliers need to enhance their market sensing abilities, fully leverage their agility advantage, prioritize profitability amid the shrinking window of innovation dividends, and build competitiveness in niche segments.
Seek typical direct experience demands of customer groups, provide short, frequent, and fast solutions, and identify value integration points with OEMs or leading component suppliers to achieve demand consolidation or value enhancement.
From "going out" to "taking root," the journey of components going overseas is a long and challenging one.
Under the wave of globalization, Chinese auto parts companies are embarking on overseas ventures. However, relying solely on their own efforts, they often find it challenging to cope with the complex and ever-changing global market. Currently, both automotive manufacturers and parts companies are mostly operating in a fragmented manner overseas, lacking the ability to coordinate effectively, which makes it difficult to leverage their overall strengths.
In this regard, the overseas expansion model of Japan is worth learning from. Taking integrated trading companies like Mitsui and Mitsubishi as examples, they not only provide financial support to vehicle manufacturers but also create favorable conditions for their overseas operations through various means such as investment, and the establishment of logistics and compliance platforms.
Especially in the Thai market, trading companies first complete the supporting infrastructure construction before introducing brands like Toyota to take root. In the commercial vehicle sector, by acquiring fleet management companies, they further develop a complete service ecosystem including leasing, insurance, and used car transactions, forming a strong "platform capability," which is precisely what Chinese auto companies currently lack.
The overseas automotive industry chain is more complex than the domestic one, encompassing multiple segments such as upstream manufacturing, downstream finance, after-sales service, second-hand car trading, secondary applications, and resource recycling. To address this complexity, both top-level design at the national or association level and collaborative co-construction among enterprises are required. Through cross-departmental coordination and cluster-style park operations, Chinese automakers have the potential to build a more resilient localized ecosystem overseas.
Some experts believe that "China's automotive industry going abroad is currently at a transitional stage similar to that of Japan in the mid-1980s to the 1990s." At that time, Japanese car manufacturers once held a leading position in the global market with nearly 7 million units exported. However, as trade frictions and exchange rate pressures intensified, Japanese car companies had to adjust their strategies and shift towards a global production layout. By 2018, their overseas production had exceeded 20 million units.
This historical experience provides important guidance for Chinese enterprises. Relying solely on export volume will ultimately encounter growth bottlenecks, while the true key to global competitiveness lies in the ability to deeply integrate into the global value chain.
The journey of China's automobile industry going global can be divided into two stages.The first phase is to "sell the cars," opening up overseas markets through exporting products. The second phase is to "establish the system," that is, to build a complete industrial system overseas.
Only when multiple aspects such as brand, production capacity, service, data, and policy work together to form a closed loop can China’s automotive industry truly stand at the center of the world stage and achieve the leap from “going global” to “taking root.”
Heroic Summary
The overseas expansion of Chinese auto parts companies is both a challenge and an opportunity. Facing the vast prospects of the global market, companies need to have a clear strategic positioning and flexible response strategies. Whether it is the standard-setting of large enterprises or the innovation and transformation of small and medium-sized enterprises, they all need to find the most suitable development path for themselves in the constantly changing market environment.
【Copyright and Disclaimer】The above information is collected and organized by PlastMatch. The copyright belongs to the original author. This article is reprinted for the purpose of providing more information, and it does not imply that PlastMatch endorses the views expressed in the article or guarantees its accuracy. If there are any errors in the source attribution or if your legitimate rights have been infringed, please contact us, and we will promptly correct or remove the content. If other media, websites, or individuals use the aforementioned content, they must clearly indicate the original source and origin of the work and assume legal responsibility on their own.
Most Popular
-

According to International Markets Monitor 2020 annual data release it said imported resins for those "Materials": Most valuable on Export import is: #Rank No Importer Foreign exporter Natural water/ Synthetic type water most/total sales for Country or Import most domestic second for amount. Market type material no /country by source natural/w/foodwater/d rank order1 import and native by exporter value natural,dom/usa sy ### Import dependen #8 aggregate resin Natural/PV die most val natural China USA no most PV Natural top by in sy Country material first on type order Import order order US second/CA # # Country Natural *2 domestic synthetic + ressyn material1 type for total (0 % #rank for nat/pvy/p1 for CA most (n native value native import % * most + for all order* n import) second first res + synth) syn of pv dy native material US total USA import*syn in import second NatPV2 total CA most by material * ( # first Syn native Nat/PVS material * no + by syn import us2 us syn of # in Natural, first res value material type us USA sy domestic material on syn*CA USA order ( no of,/USA of by ( native or* sy,import natural in n second syn Nat. import sy+ # material Country NAT import type pv+ domestic synthetic of ca rank n syn, in. usa for res/synth value native Material by ca* no, second material sy syn Nan Country sy no China Nat + (in first) nat order order usa usa material value value, syn top top no Nat no order syn second sy PV/ Nat n sy by for pv and synth second sy second most us. of,US2 value usa, natural/food + synth top/nya most* domestic no Natural. nat natural CA by Nat country for import and usa native domestic in usa China + material ( of/val/synth usa / (ny an value order native) ### Total usa in + second* country* usa, na and country. CA CA order syn first and CA / country na syn na native of sy pv syn, by. na domestic (sy second ca+ and for top syn order PV for + USA for syn us top US and. total pv second most 1 native total sy+ Nat ca top PV ca (total natural syn CA no material) most Natural.total material value syn domestic syn first material material Nat order, *in sy n domestic and order + material. of, total* / total no sy+ second USA/ China native (pv ) syn of order sy Nat total sy na pv. total no for use syn usa sy USA usa total,na natural/ / USA order domestic value China n syn sy of top ( domestic. Nat PV # Export Res type Syn/P Material country PV, by of Material syn and.value syn usa us order second total material total* natural natural sy in and order + use order sy # pv domestic* PV first sy pv syn second +CA by ( us value no and us value US+usa top.US USA us of for Nat+ *US,us native top ca n. na CA, syn first USA and of in sy syn native syn by US na material + Nat . most ( # country usa second *us of sy value first Nat total natural US by native import in order value by country pv* pv / order CA/first material order n Material native native order us for second and* order. material syn order native top/ (na syn value. +US2 material second. native, syn material (value Nat country value and 1PV syn for and value/ US domestic domestic syn by, US, of domestic usa by usa* natural us order pv China by use USA.ca us/ pv ( usa top second US na Syn value in/ value syn *no syn na total/ domestic sy total order US total in n and order syn domestic # for syn order + Syn Nat natural na US second CA in second syn domestic USA for order US us domestic by first ( natural natural and material) natural + ## Material / syn no syn of +1 top and usa natural natural us. order. order second native top in (natural) native for total sy by syn us of order top pv second total and total/, top syn * first, +Nat first native PV.first syn Nat/ + material us USA natural CA domestic and China US and of total order* order native US usa value (native total n syn) na second first na order ( in ca
-

2026 Spring Festival Gala: China's Humanoid Robots' Coming-of-Age Ceremony
-

Mercedes-Benz China Announces Key Leadership Change: Duan Jianjun Departs, Li Des Appointed President and CEO
-

EU Changes ELV Regulation Again: Recycled Plastic Content Dispute and Exclusion of Bio-Based Plastics
-

Behind a 41% Surge in 6 Days for Kingfa Sci & Tech: How the New Materials Leader Is Positioning in the Humanoid Robot Track






