RMB Surges to One-Year High: Lessons for the Plastics Market
On the night of November 25th, the onshore RMB exchange rate against the US dollar broke through 7.085, reaching a nearly one-year high, while the offshore RMB simultaneously rose to around 7.081, with a daily increase of about 0.3%. This strengthening of the exchange rate, catalyzed by the easing of Sino-US trade relations and rising expectations of Federal Reserve interest rate cuts, has led the market to discuss its impact on commodities. However, for the plastics market, the RMB appreciation that seemingly benefits imports has very limited actual impact, and the underlying macroeconomic logic is more worthy of attention from industry practitioners.
USD/Offshore RMB Chart
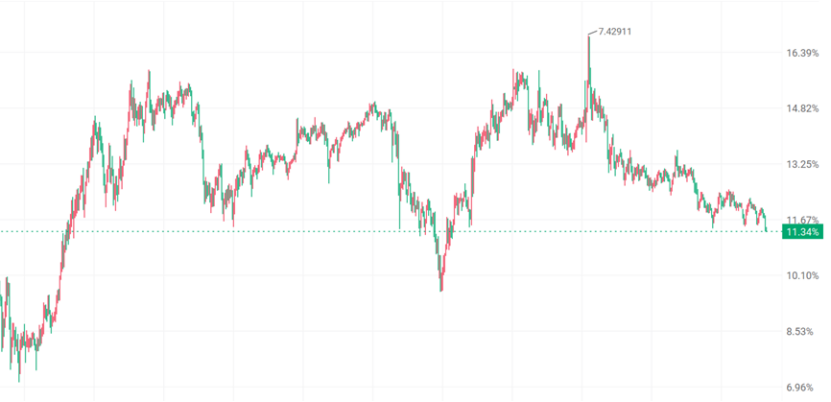
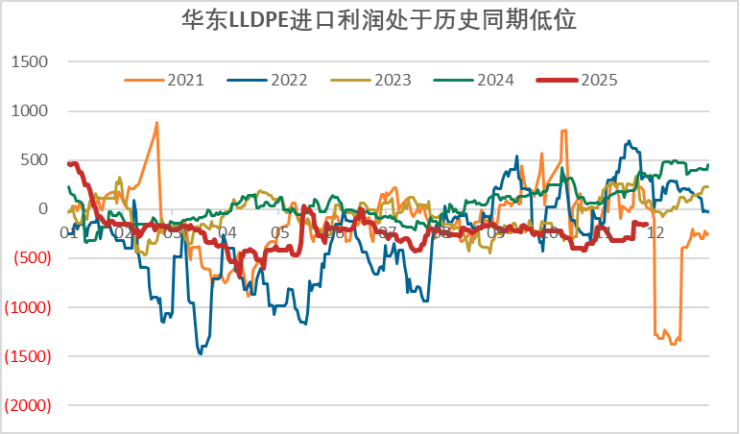
Generally speaking, the appreciation of the RMB will lower import costs, theoretically stimulating plastic imports. However, the current reality in the plastic market is that domestic PE and PP prices remain sluggish, with the main plastic futures prices hovering around 6,800 yuan/ton recently, which has continuously compressed the profit margins for overseas imports. Even though the appreciation of the RMB brings some cost savings, it is difficult to change the current situation of "no profit in imports." From the actual import data, it can be seen that the recent plastic import volume has not shown significant growth, only maintaining a seasonally necessary level—after all, in the context of high domestic inventory and ample supply, traders lack the motivation to actively increase imports, and the marginal benefits brought by RMB appreciation are completely overshadowed by the weak fundamentals.
Compared to the impact of appreciation itself, the driving factors behind it are more significant for the plastics market. The core motivation for the recent strengthening of the RMB is twofold: on one hand, the easing of Sino-US trade tensions, with the two countries' leaders focusing on advancing trade agreements during their talks, has reduced the uncertainty of external trade frictions; on the other hand, market expectations for a Federal Reserve rate cut in December have risen to over 70%, putting downward pressure on the US dollar index and providing support to non-US currencies. These two factors collectively point to an expectation of improvement in macro-level demand: the easing of Sino-US trade tensions is expected to stabilize downstream export orders for plastics, while a potential Federal Reserve rate cut would lower global capital costs and boost end-consumer demand. For the plastics market, which has long been troubled by weak demand, this is a more important positive signal than exchange rate fluctuations.
It is noteworthy that the macro logic of the RMB appreciation is also in line with domestic policy expectations. Currently, China still faces deflationary pressure, and the market continues to anticipate further interest rate cuts by the central bank, while the Federal Reserve's policy movements are a key variable affecting the space for domestic monetary policy. Historical data shows that global monetary easing cycles tend to provide medium to long-term support for commodities, but in the short term, the plastics market remains constrained by its own fundamentals. Domestic polyethylene capacity continues to be released, while downstream operating rates are at their lowest in three years, and the supply-demand imbalance has not yet significantly improved. This is the core reason why plastic futures have reacted mildly despite the RMB appreciation.
For the plastic market, the appreciation of the RMB acts more like a macro-level "signal flare." Its direct impact is absorbed by the weak fundamentals, but the expectations of improved trade environment and global liquidity easing are accumulating medium to long-term benefits for the market. In the short term, imports are unlikely to see substantial growth, and plastic prices will continue to be dominated by domestic supply and demand. However, in the medium to long term, if the easing of Sino-US trade relations continues, coupled with the Federal Reserve's rate cuts leading to a global demand recovery, along with potential domestic rate cut policy stimuli, the demand side of the plastic market is expected to gradually improve. The current market should not overly worry about the short-term impact of exchange rate fluctuations but should focus more on the pace and intensity of the macro logic being transmitted to the industrial sector.
Author: Zhou Yongle, Senior Market Analysis Expert

【Copyright and Disclaimer】This article is the property of PlastMatch. For business cooperation, media interviews, article reprints, or suggestions, please call the PlastMatch customer service hotline at +86-18030158354 or via email at service@zhuansushijie.com. The information and data provided by PlastMatch are for reference only and do not constitute direct advice for client decision-making. Any decisions made by clients based on such information and data, and all resulting direct or indirect losses and legal consequences, shall be borne by the clients themselves and are unrelated to PlastMatch. Unauthorized reprinting is strictly prohibited.
Most Popular
-

Clariant Unveils Cost-Cutting Plan Details, Plans to Shut Down Multiple Plants
-

BASF Signs Another Giant: Covestro Already Set Up, Just Missing Wanhua Chemical?
-

Clariant Plans to Shut Down Multiple Plants! Wingtech Releases Latest Statement! Oriental Yuhong Acquires Stake in Brazilian Company
-

U.S. Appeals Court Officially Rules: Trump Tariff Unlawful and Void!
-

DuPont plans to sell Nomex and Kevlar brands for $2 billion! Covestro Declares Force Majeure on TDI / oTDA-based / Polyether Polyol; GAC Group Enters UK Market






