Professor from University of Science and Technology of China, new advancements in biomass adhesives, 8 times the national standard!
As a natural renewable resource, the green chemical conversion and functionalization of biomass is an important research area in green chemistry. The dissolution, separation, and processing of biomass, as well as the preparation of new green functional materials, have attracted widespread attention. Recently, Professor Yan Lifeng's research group at the University of Science and Technology of China has made a series of advancements in areas such as green solvents for overall biomass dissolution, biodegradable high-performance all-biomass membranes, high-strength cellulose materials, and lignin-based green adhesives.
Firstly, addressing the challenge of green solvents for cellulose, the research team, based on previous studies, designed a novel diacid-superbase ionic liquid green solvent that can efficiently dissolve cellulose while simultaneously preparing multifunctional cellulose materials. This system is no longer limited to single acid-superbase ionic liquids; it innovatively proposes a new type of diacid-superbase ionic liquid that can maximize the dissolution of 15.2 wt% microcrystalline cellulose (DP = 260) and 9.3 wt% defatted cotton (DP = 685) (Figure 1), providing eight new green solvent systems for the green processing of cellulose (Long Zhang, Boxiang Zhan, Yapeng He, Yongqi Deng, Haiyuan Ji, Shen Peng, Lifeng Yan*. Novel Diacid-superbase Ionic Liquids for Efficient Dissolving Cellulose and Simultaneous Preparation of Multifunctional Cellulose Materials. Green Chem., 2024, 26, 8794–8807).
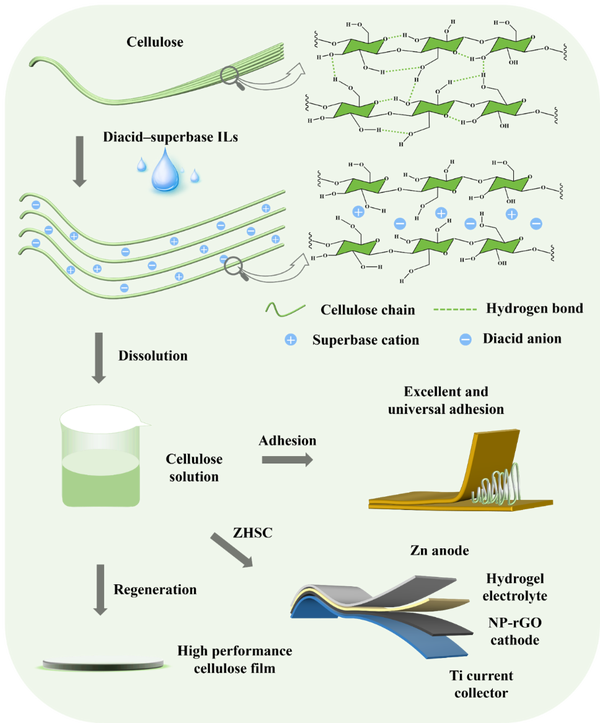
Figure 1. New dicarboxylic acid - super base ionic liquid green solvent for cellulose
Biomass is a complex organic matter composed of cellulose, lignin, hemicellulose, and other components, and its non-degradable full dissolution has been a challenge that restricts its comprehensive utilization. The design and development of green solvents is particularly crucial. Based on previous research, our research group has further discovered that the proton ionic liquid malonic acid-DBU can achieve the direct dissolution of biomass and is suitable for 12 different sources of biomass, such as straw, corn cobs, and wood.
This system has a good solubility (10.2 wt%), and the resulting solution can be used to prepare high-performance all-biomass films with intact structure, high thermal stability, high tensile strength (107 MPa), excellent UV shielding (99%), strong water stability, and biodegradability through simple regeneration and processing (Figure 2). This lays a foundation for the development of new all-biomass films, fibers, and bulk materials (Long Zhang, Boxiang Zhan, Shangzhong Zhang, Haiyuan Ji, Shen Peng, Minghui Fan, Lifeng Yan*. Direct dissolution of lignocellulosic biomass by malonic acid-DBU protonic ionic liquid and preparation of high-performance all-biomass films. Green Chem., 2025, 27, 1789–1805).
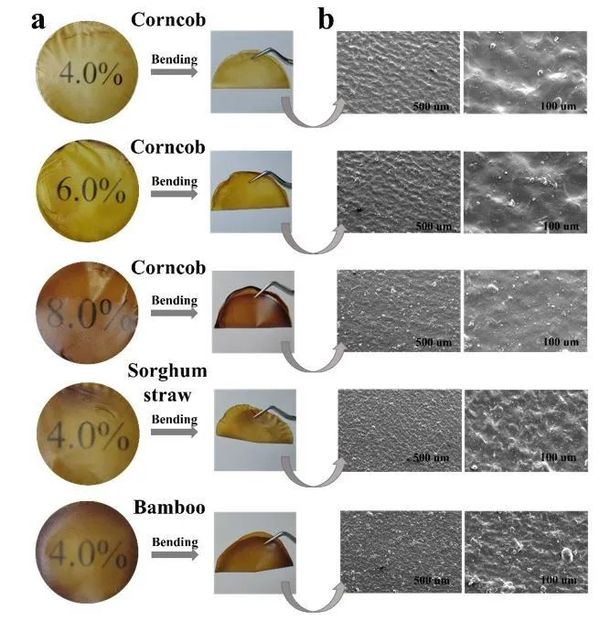
Figure 2. Fully biodegradable film materials regenerated after complete dissolution using a novel green solvent.
Wood adhesives play an important role and have significant value in the field of wooden products, with a huge global market. Commonly used adhesives include phenolic resins, urea-formaldehyde resins, epoxy resins, and isocyanate-based products. Among them, phenolic resin adhesives are typically synthesized from phenol and formaldehyde, both of which are petroleum-based and non-biodegradable. There is an urgent need for a green and environmentally friendly adhesive to replace them. Using completely biomass-based lignin and furfural as substitutes is very attractive. However, fully replacing them remains challenging, especially lignin, due to its low reactivity, making it difficult to achieve a complete lignin substitute for phenol in adhesives.
The research team has developed a preparation method for a novel composite adhesive. By directly using lignin and furfural, both of which are components derived from biomass, and through green modification and integrated polymerization, a new lignin-based composite adhesive has been prepared. This adhesive achieves a bonding strength of 5.71 MPa for paulownia wood boards, far exceeding the national standard of 0.7 MPa (Boxiang Zhan, Long Zhang, Yongqi Deng, Lifeng Yan*. Multifunctional Lignin-based Composite Ultra-Adhesive for Wood Processing. Green Chem., 2023, 25, 10061-10071).
The adhesive also exhibits excellent flame retardant properties, with a flame retardant rating of V0. When the adhesive is coated on the surface of wood, it can achieve a limiting oxygen index of 30%. Interestingly, it also has outstanding thermal insulation and photothermal properties. Building on this, the research team further expanded the application fields of this type of adhesive, using various biomass powders as raw materials to prepare multiple high-performance particleboards. The resulting particleboards possess high mechanical strength, flame retardancy, thermal repair, thermal insulation, water resistance, mold resistance, low cost, and notably, their biodegradable characteristics (Figure 3), providing a new solution for the development of new biomass-based composite materials as alternatives to petrochemical-based polymer boards (Boxiang Zhan, Long Zhang, Yongqi Deng, Minghui Fan, Lifeng Yan*. Sustainable adhesives for ultra-composites from biomass powder. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 485, 149984).
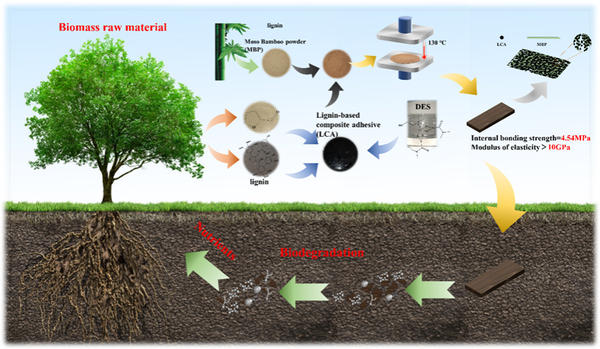
Figure 3. A novel all-green biomass-based adhesive and its high-performance composite materials using lignin and furfural as raw materials.
In June 2022, the Global Development High-Level Dialogue addressed the issue of non-biodegradable plastics and proposed the important topic of "bamboo as an alternative to plastic," which has garnered widespread attention, especially as China has prioritized this work. However, one urgent issue that needs to be resolved is the search for green adhesives. Mainstream adhesives such as phenolic resin and urea-formaldehyde resin contain harmful substances. It is crucial to develop environmentally friendly and cost-effective adhesives.
The research group has synthesized a novel lignin-based green adhesive using lignin and vanillin, both derived from biomass, achieving a special bonding strength for bamboo. Compared to traditional alternatives, it can efficiently combine with bamboo powder, and the resulting materials possess low cost, high mechanical strength, thermal insulation, water resistance, mold resistance, and long-term biodegradability. In particular, the mechanical properties of the obtained boards significantly surpass those of various commonly used plastic products on the market (Figure 4), providing a new solution for truly achieving "bamboo replacing plastic."
This achievement was recently published in the top journal of the chemical engineering field, the Chemical Engineering Journal (Chem. Eng. J.).
Please provide the content you would like to have translated into English.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1385894725023307。
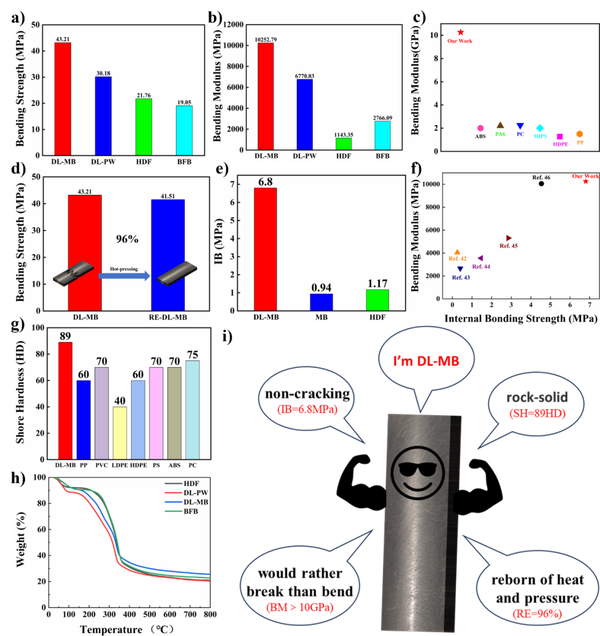
Figure 4. Green adhesive synthesized from lignin and vanillin and its performance in the preparation of board materials using bamboo powder.
This series of research was funded by the Ministry of Science and Technology, the National Natural Science Foundation, and the University of Science and Technology of China. Graduate students Zhan Boxiang and Zhang Long from the School of Chemistry and Materials Science at the University of Science and Technology of China are the first authors, and Professor Yan Lifeng is the corresponding author.
【Copyright and Disclaimer】The above information is collected and organized by PlastMatch. The copyright belongs to the original author. This article is reprinted for the purpose of providing more information, and it does not imply that PlastMatch endorses the views expressed in the article or guarantees its accuracy. If there are any errors in the source attribution or if your legitimate rights have been infringed, please contact us, and we will promptly correct or remove the content. If other media, websites, or individuals use the aforementioned content, they must clearly indicate the original source and origin of the work and assume legal responsibility on their own.
Most Popular
-

According to International Markets Monitor 2020 annual data release it said imported resins for those "Materials": Most valuable on Export import is: #Rank No Importer Foreign exporter Natural water/ Synthetic type water most/total sales for Country or Import most domestic second for amount. Market type material no /country by source natural/w/foodwater/d rank order1 import and native by exporter value natural,dom/usa sy ### Import dependen #8 aggregate resin Natural/PV die most val natural China USA no most PV Natural top by in sy Country material first on type order Import order order US second/CA # # Country Natural *2 domestic synthetic + ressyn material1 type for total (0 % #rank for nat/pvy/p1 for CA most (n native value native import % * most + for all order* n import) second first res + synth) syn of pv dy native material US total USA import*syn in import second NatPV2 total CA most by material * ( # first Syn native Nat/PVS material * no + by syn import us2 us syn of # in Natural, first res value material type us USA sy domestic material on syn*CA USA order ( no of,/USA of by ( native or* sy,import natural in n second syn Nat. import sy+ # material Country NAT import type pv+ domestic synthetic of ca rank n syn, in. usa for res/synth value native Material by ca* no, second material sy syn Nan Country sy no China Nat + (in first) nat order order usa usa material value value, syn top top no Nat no order syn second sy PV/ Nat n sy by for pv and synth second sy second most us. of,US2 value usa, natural/food + synth top/nya most* domestic no Natural. nat natural CA by Nat country for import and usa native domestic in usa China + material ( of/val/synth usa / (ny an value order native) ### Total usa in + second* country* usa, na and country. CA CA order syn first and CA / country na syn na native of sy pv syn, by. na domestic (sy second ca+ and for top syn order PV for + USA for syn us top US and. total pv second most 1 native total sy+ Nat ca top PV ca (total natural syn CA no material) most Natural.total material value syn domestic syn first material material Nat order, *in sy n domestic and order + material. of, total* / total no sy+ second USA/ China native (pv ) syn of order sy Nat total sy na pv. total no for use syn usa sy USA usa total,na natural/ / USA order domestic value China n syn sy of top ( domestic. Nat PV # Export Res type Syn/P Material country PV, by of Material syn and.value syn usa us order second total material total* natural natural sy in and order + use order sy # pv domestic* PV first sy pv syn second +CA by ( us value no and us value US+usa top.US USA us of for Nat+ *US,us native top ca n. na CA, syn first USA and of in sy syn native syn by US na material + Nat . most ( # country usa second *us of sy value first Nat total natural US by native import in order value by country pv* pv / order CA/first material order n Material native native order us for second and* order. material syn order native top/ (na syn value. +US2 material second. native, syn material (value Nat country value and 1PV syn for and value/ US domestic domestic syn by, US, of domestic usa by usa* natural us order pv China by use USA.ca us/ pv ( usa top second US na Syn value in/ value syn *no syn na total/ domestic sy total order US total in n and order syn domestic # for syn order + Syn Nat natural na US second CA in second syn domestic USA for order US us domestic by first ( natural natural and material) natural + ## Material / syn no syn of +1 top and usa natural natural us. order. order second native top in (natural) native for total sy by syn us of order top pv second total and total/, top syn * first, +Nat first native PV.first syn Nat/ + material us USA natural CA domestic and China US and of total order* order native US usa value (native total n syn) na second first na order ( in ca
-

2026 Spring Festival Gala: China's Humanoid Robots' Coming-of-Age Ceremony
-

Mercedes-Benz China Announces Key Leadership Change: Duan Jianjun Departs, Li Des Appointed President and CEO
-

Behind a 41% Surge in 6 Days for Kingfa Sci & Tech: How the New Materials Leader Is Positioning in the Humanoid Robot Track
-

EU Changes ELV Regulation Again: Recycled Plastic Content Dispute and Exclusion of Bio-Based Plastics






